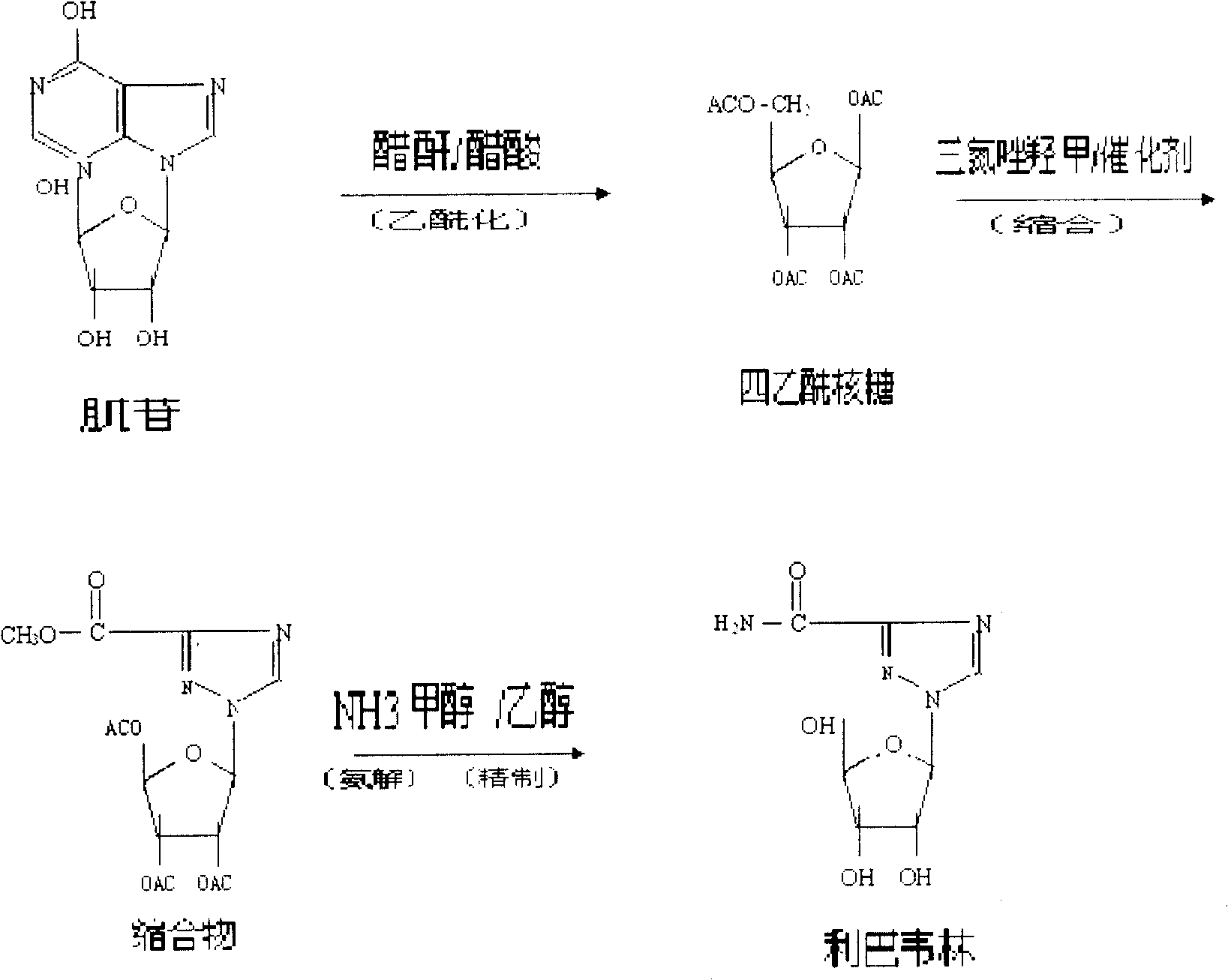
A kind of preparation method of ribavirin
A technology of ribavirin and catalyst is applied in the field of preparation of ribavirin, and can solve the problems of many operation steps, no application, low yield of by-products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] Acylation:
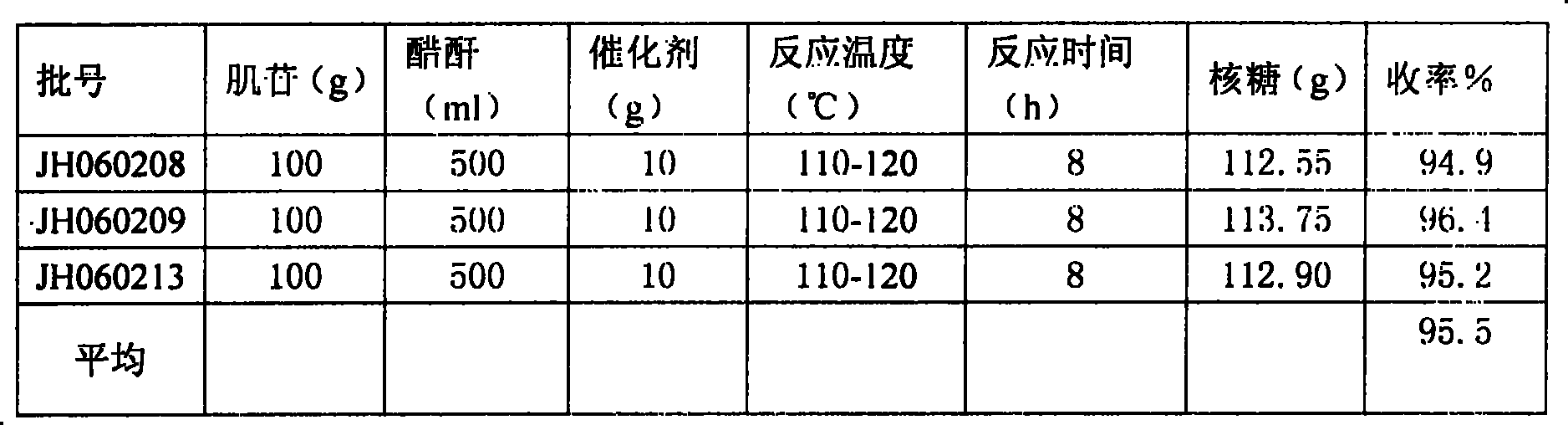
[0012] Take a 1000mL flask, add 50g of inosine, 200ml of acetic anhydride and heat to reflux under stirring. 3 with Na 2 HPO 4 Mix according to 2:1) 10g at 110°C for 2 hours, connect to a Vickers fractionation column, evaporate the mixture of acetic acid and acetic anhydride under slight negative pressure, and evaporate 100ml of acid for about 100min. Continue to incubate at 110°C for 6 hours, and track the end point with a TLC plate until triacetyl inosine basically disappears. Cool down to 30°C, filter, combine the filtrates, evaporate the mixed acetic anhydride in a rotary evaporator in a vacuum, cool the residue to 90-100°C, add distilled water, 150ml, crystallize under stirring, and precipitate tetraacetyl ribose. The rate is 94.8%. The validation experimental data in Table 1 also yielded this level of yield.
Embodiment 2
[0014] condensation
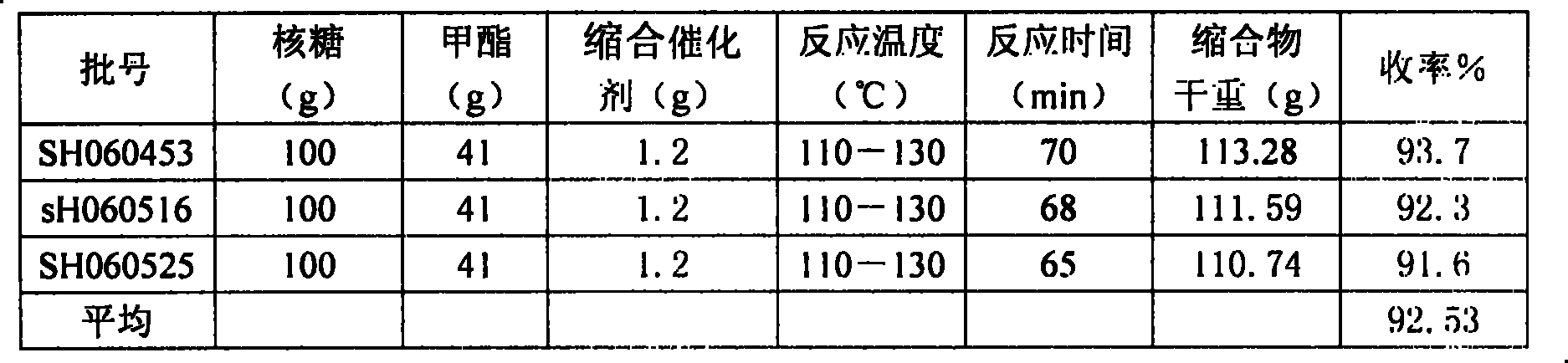
[0015] 500ml there-necked flask, heated to 110°C, put in 50g of tetraacetyl ribose, stirred, melted until the temperature rose to 120°C, then put in 20.5g of 1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxylate methyl ester, stirred evenly, Raise the temperature to 130°C, put in the catalyst, turn on the vacuum immediately, react at 110-130°C until no acetic anhydride is drawn out, stop heating and cool down to 80°C, add 80ml of methanol, stir and pour it out to crystallize, put it in the refrigerator freezer and pump it out Filter, wash with 10ml of methanol, and dry to obtain the crude product of the condensate. The yield of the crude condensate was 92.5%. The validation experimental data in Table 2 also yielded this level of yield.
Embodiment 3
[0017] Ammonolysis
[0018] Add 50g of condensate and 175ml of methanol into the three-necked bottle, stir evenly, cool down to below 5°C, receive the ammonia gas discharged from another three-necked bottle, and control the reaction temperature so that it cannot be too high. Dissolve the ammonia completely, stop passing the ammonia, leave it at room temperature for more than 12 hours, and drain the ammonia with hot water, and the discharged ammonia is received by another three-necked bottle containing the condensate-methanol mixture. Cool below 5°C, filter with suction, wash the filter cake with an appropriate amount of 95% ethanol, and dry to obtain the crude product of ribavirin, with an ammonolysis yield of 96.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com