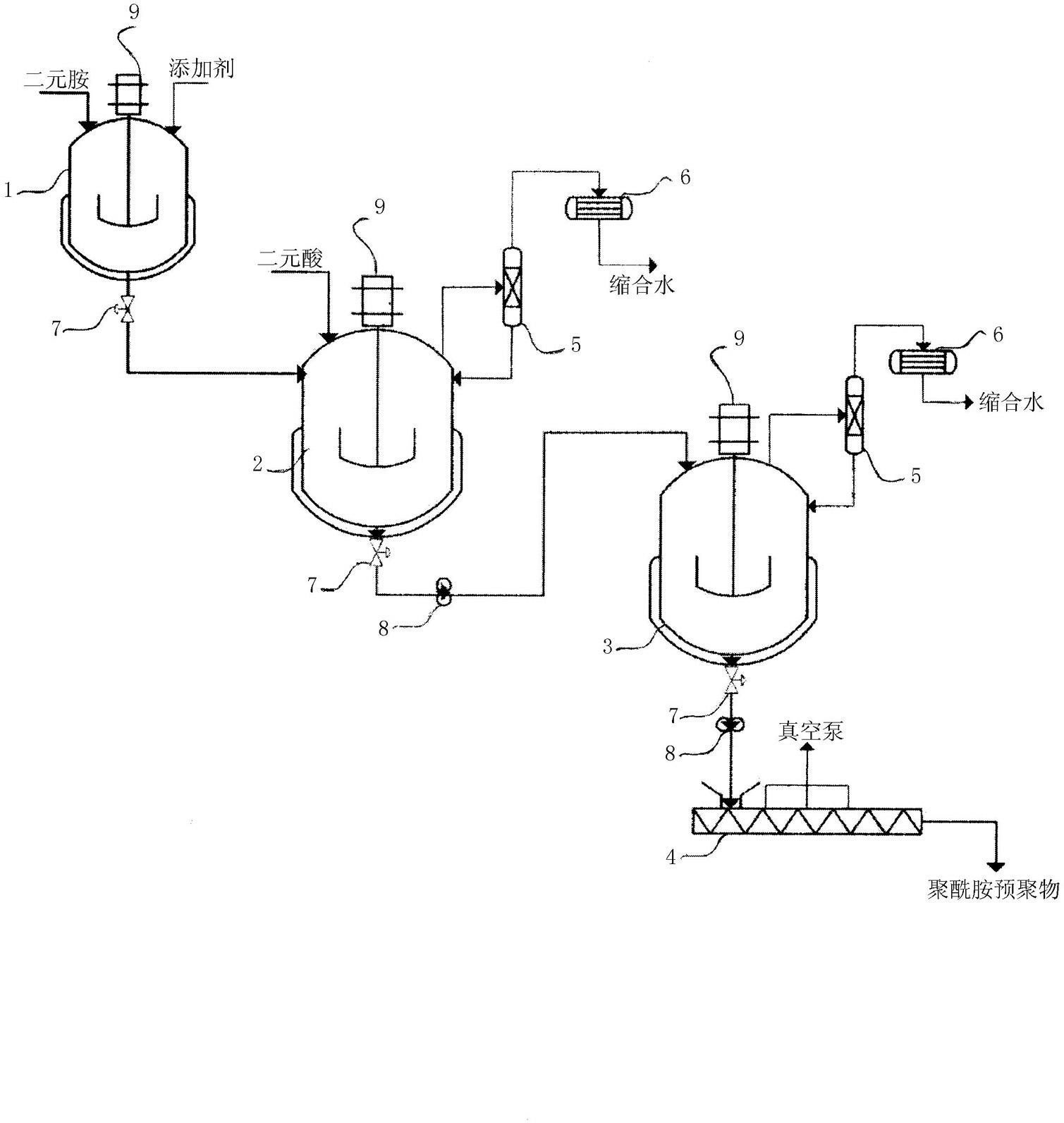
Method for producing polyamide
A polyamide and diamine technology, applied in the field of polyamide production, can solve the problems of easy contact with oxygen, easy absorption of metal impurities, oxidation and decomposition of monomeric carboxylic acid, shortening residence time, increasing molecular weight, and improving polymerization. degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In the following examples, the intrinsic viscosities [η] of polyamide prepolymers and endpolymers were determined by the following methods and standards.
[0033] The intrinsic viscosity [η] of polyamide was measured by the method specified in standard ISO307. which is:
[0034] Dissolve the polyamide sample to be tested in 96% concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain a solution with a concentration of 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 or 0.4g / dl, and measure the inherent viscosity η of each sample solution at 30°C rlh as follows:
[0035] n rln =[ln(t / t 0 )] / C (dl / g)
[0036] where t 0 represents the flow time (seconds) of the solvent, t represents the flow time (seconds) of the sample solution, and C represents the concentration of the sample in the sample solution.
[0037] Will η rln The data were extrapolated to the concentration range of 0 to obtain the intrinsic viscosity [η] of the sample.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com