Lightweight, flame retardant and rubber foaming sole material and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for flame-retardant rubber and shoe sole materials, which is applied in the field of lightweight flame-retardant rubber foam shoe sole materials and its manufacturing, and can solve problems such as poor storage stability, unfavorable storage, and environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
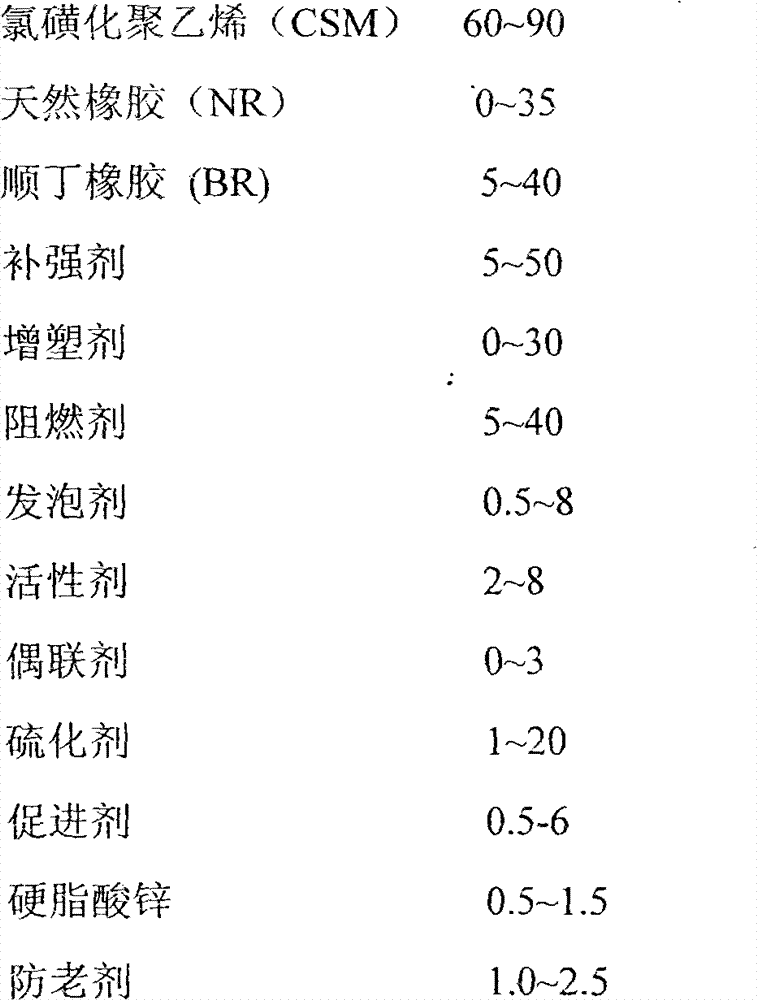
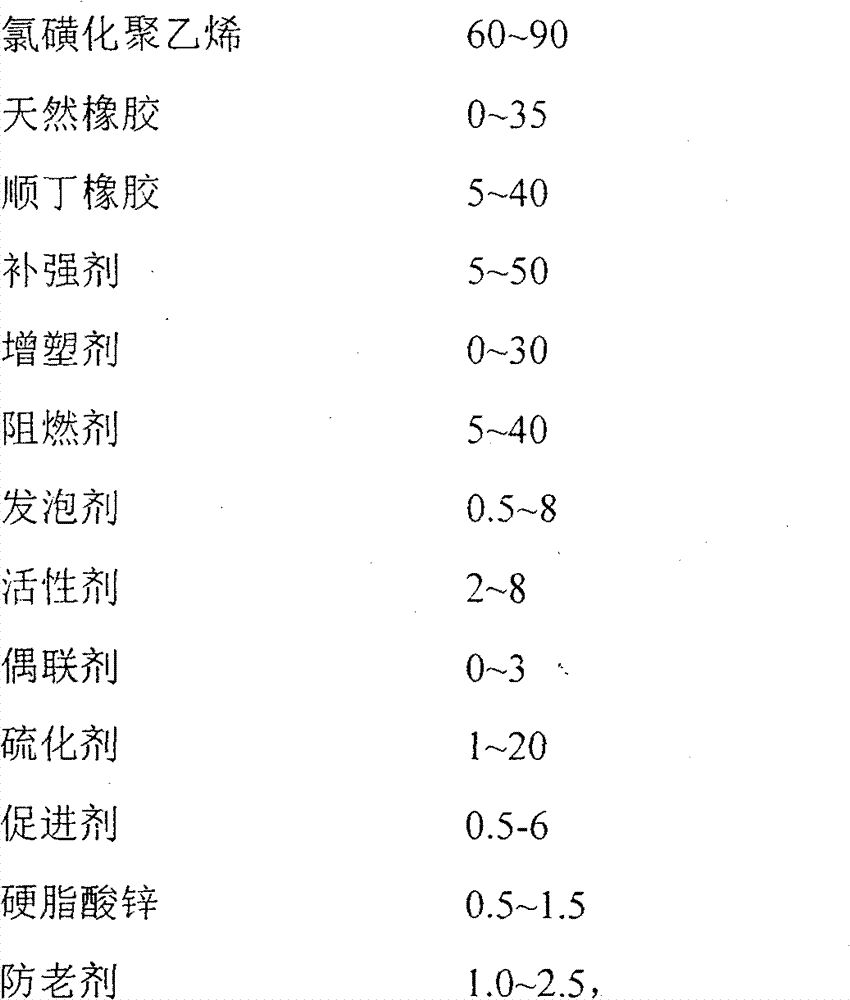
[0029] The composition (mass ratio) is: 85 parts of CSM, 15 parts of BR, 30 parts of white carbon black, 3.0 parts of PEG, 5.0 parts of TOTM, 5.0 parts of magnesium oxide, 3.0 parts of DPTT, 0.5 parts of TAIC, 2.0 parts of pentaerythritol, stearic acid 1.0 parts of zinc, 1.0 parts of anti-aging agent NBC, 0.5 parts of microcrystalline wax.
[0030] Weigh according to the above ratio, mix according to the above process, and measure the engineering vulcanization time of the mixed rubber at 150°C by a rotorless rheometer. 90418s, and then molded at 150°C. Place the sample at room temperature 22.0°C for more than 24 hours to test its hardness (Shore A) 58, and the relative density is 1.25g / cm 3 ;According to the QB / T2884-2007 standard, the DIN wear is 79mm 3 ; According to the GB1040 standard, the tensile strength is 20.2MPa, and the elongation at break is 653%; according to the GB / T 3903.12-2005 standard, the right-angle tear strength is 37N / mm. According to the ASTM E 1354 / IS...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The composition (mass ratio) is: 85 parts of CSM, 15 parts of BR, 30 parts of white carbon black, 10 parts of polybrominated styrene, 3.0 parts of PEG, 5.0 parts of TOTM, 5.0 parts of magnesium oxide, 3.0 parts of DPTT, 0.5 parts of TAIC, 2.0 parts of pentaerythritol, 1.0 part of zinc stearate, 1.0 part of anti-aging agent NBC, and 0.5 part of microcrystalline wax.
[0033] Weigh according to the above ratio, mix according to the above process, and measure the engineering vulcanization time of the mixed rubber at 150°C by a rotorless rheometer. 90 It is 406s, and then molded at 150°C. Place the sample at room temperature 22.0°C for more than 24 hours to test its hardness (Shore A) 63, and the relative density is 1.29g / cm 3 ;According to the QB / T2884-2007 standard, the DIN wear is 86mm 3 ; According to the GB1040 standard, the tensile strength is 12.3MPa, and the elongation at break is 573%; according to the GB / T 3903.12-2005 standard, the right-angle tear strength is ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The composition (mass ratio) is: 85 parts of CSM, 15 parts of BR, 30 parts of white carbon black, 20 parts of polybrominated styrene, 3.0 parts of PEG, 5.0 parts of TOTM, 5.0 parts of magnesium oxide, 3.0 parts of DPTT, 0.5 parts of TAIC, 2.0 parts of pentaerythritol, 1.0 part of zinc stearate, 1.0 part of anti-aging agent NBC, and 0.5 part of microcrystalline wax.
[0036] Weigh according to the above ratio, mix according to the above process, and measure the engineering vulcanization time of the mixed rubber at 150°C by a rotorless rheometer. 90 for 400s, and then molded at 150°C. Place the sample at room temperature 22.0°C for more than 24 hours to test its hardness (Shore A) 64, and the relative density is 1.32g / cm 3 ;According to QB / T2884-2007 standard test DIN wear is 99mm 3 ; According to the GB1040 standard, the tensile strength is 11.4MPa, and the elongation at break is 583%; according to the GB / T 3903.12-2005 standard, the right-angle tear strength is 36N / mm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com