Method for recovering rare earth from low-concentration rare earth solution through prussian blue colloidal nanoparticles
A nanoparticle and Prussian blue technology, which is applied to the improvement of process efficiency, adsorption water/sewage treatment, osmosis/dialysis water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of large secondary pollution, high resin cost, and small loading capacity. Achieve the effect of large loading capacity of rare earth, high recovery rate of rare earth and wide application prospect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
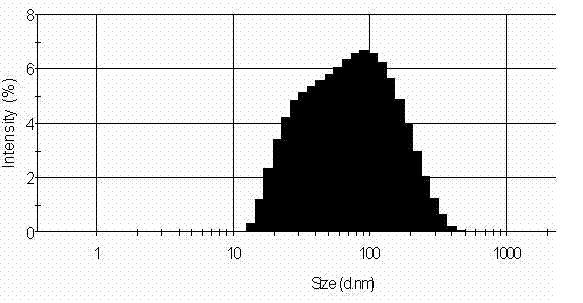
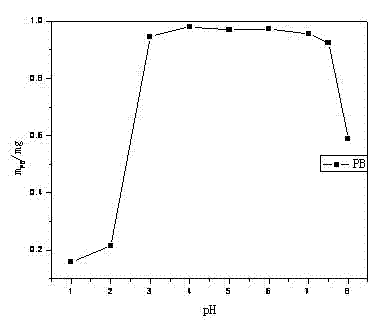
[0027] Embodiment 1: with FeCl 3 . 6H 2 O and K 4 Fe(CN) 6 as raw material, according to 1:1.2 (K 4 Fe(CN) 6 Slight excess to ensure the molar ratio of colloidal PB) Accurately weigh the corresponding raw materials, at room temperature, after being dissolved in distilled water, FeCl 3 The solution was slowly added dropwise to K 4 Fe(CN) 6 In the solution, after stirring for 15 minutes, add a small amount of acetone, let stand, centrifuge, and dry naturally to obtain solid PB. Its particle size distribution diagram is shown in figure 1 . Disperse the synthesized PB-CNP into 20mL aqueous solution with pH=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, and the concentration of PB-CNP is 0.1mg / mL. After standing for 3 hours, centrifuge at a speed of 6000 rpm in a high-speed centrifuge, take the supernatant to measure the absorbance, calculate the amount of unsettled PB-CNP according to the standard curve of PB-CNP, and then calculate the amount of PB that has settled. Its relat...
Embodiment approach 2
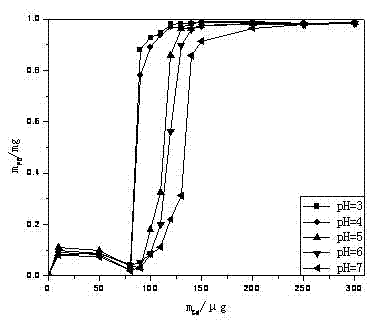
[0028] Embodiment 2: At room temperature, different amounts of Gd were added to aqueous solutions of pH=3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 containing 1 mg of PB-CNP 3+ (10~300μg), let stand for 3 hours and centrifuge at high speed, measure the amount of PB-CNP remaining in the supernatant by colorimetry, and investigate the coagulation characteristics of PB-CNP caused by the adsorption of rare earth ions. Taking the condition of pH=3 as an example, take 12 parts of colloidal aqueous solution containing 1mg PB in a beaker, add 10μg / mLGd respectively 3+ Solutions 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 20, 25, 30mL, after stirring, stand for adsorption for 3 hours, centrifuge at high speed, take the supernatant to measure the absorbance, and calculate the non-sedimentation according to the standard curve of PB The amount of PB-CNP, thus inferring the amount of PB that has settled. The pH=4~7 relationship curve is also made in the same way. Its adsorption curve is shown in image 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Determination of 1mg PB-CNP to 300μg Gd under constant temperature (T=30°C) constant volume (50mL) shaking conditions 3+ The change curve of adsorption capacity under different pH and equilibrium time conditions. The specific experimental method is: taking the condition of pH=2 as an example, put six dialysis bags containing 10mL 0.2mg / mL PB into conical flasks respectively, and add 60mL 10μg / mL Gd 3+ After mixing with 10mL of distilled water, adjust the solution to the set pH, shake at constant temperature for different times (10-60min), take the supernatant, and use the azoarsenic III colorimetric method to measure the residual gadolinium concentration in the solution (measure the absorbance, according to Gd 3+ Calculate the unadsorbed Gd from the standard curve 3+ amount), the Gd that has been adsorbed by PB was calculated by subtraction method 3+ amount. The adsorption amount of gadolinium was plotted against time to obtain the adsorption curves under ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com