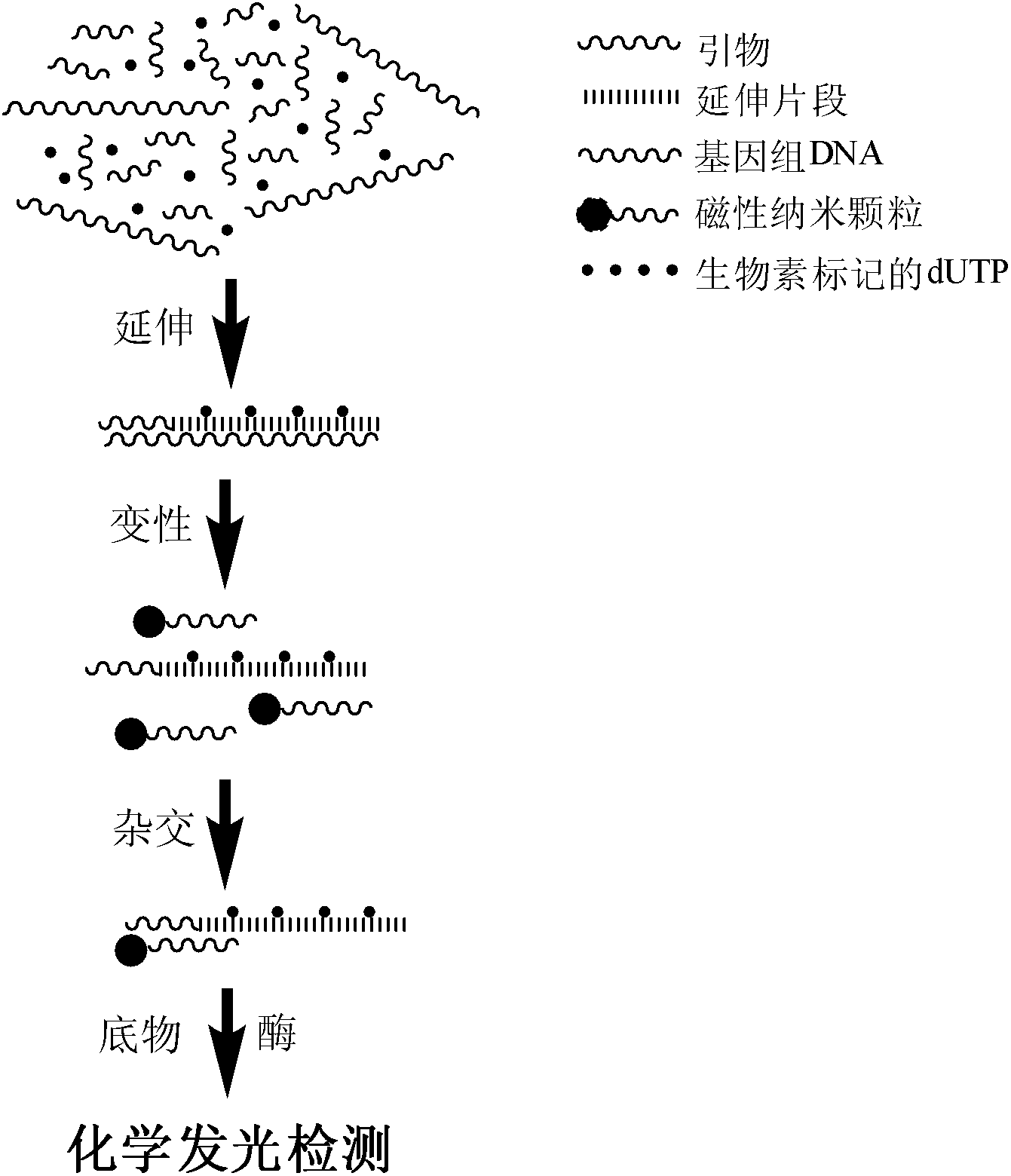
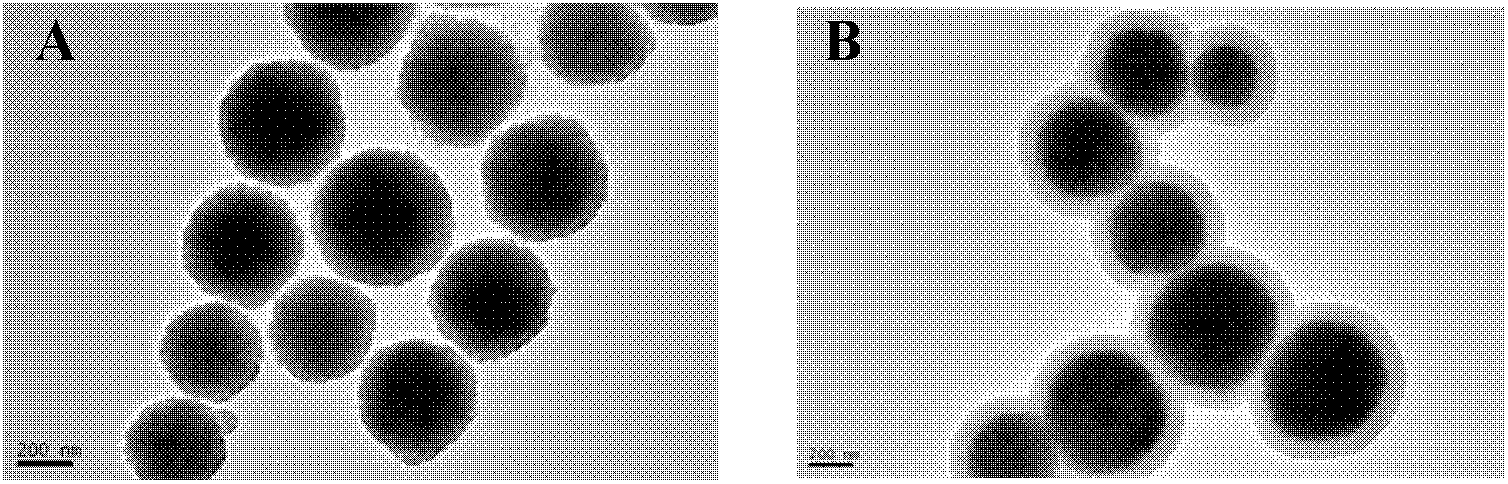Chemiluminescence detection method for copy number polymorphism based on magnetic separation and primer extension
A technology for chemiluminescence detection and copy number polymorphism, which is applied in the field of molecular genetics and can solve problems such as high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Acquisition of nucleic acid sequence copy number information using artificially synthesized GAPDH gene fragments as templates
[0043] The experimental process of obtaining the copy number information of the nucleic acid sequence using the artificially synthesized GAPDH gene fragment as a template is as follows:
[0044] 1) Preparation of magnetic particles. Preparation of Fe with a diameter of about 300 nm by solvothermal method 3 o 4 magnetic particles. Weigh 1.35 g of FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O, 3.6 g of sodium acetate (NaAc) and 1.0 g of polyethylene glycol (polyethylene glycol, PEG), dissolved in 40 mL of ethylene glycol, magnetically stirred to dissolve, forming a yellow-brown colloid. Transfer the colloid to a tetrafluoroethylene reactor, seal it, and place it in an oven at 200°C for 8 hours; after the reaction is completed, wash it with ethanol and deionized water, and dry it to obtain Fe 3 o 4 Magnetic particle samples such as figure 2 A show.
[0045] ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Acquisition of nucleic acid sequence copy number information using genomic DNA as a template
[0054] 1) Preparation of magnetic particles. Magnetic particles were prepared as described in Example 1 for use.
[0055] 2) Primer and probe design. The primers and probes for GAPDH, GSTT1 and GSTM1 described in Example 1 were used.
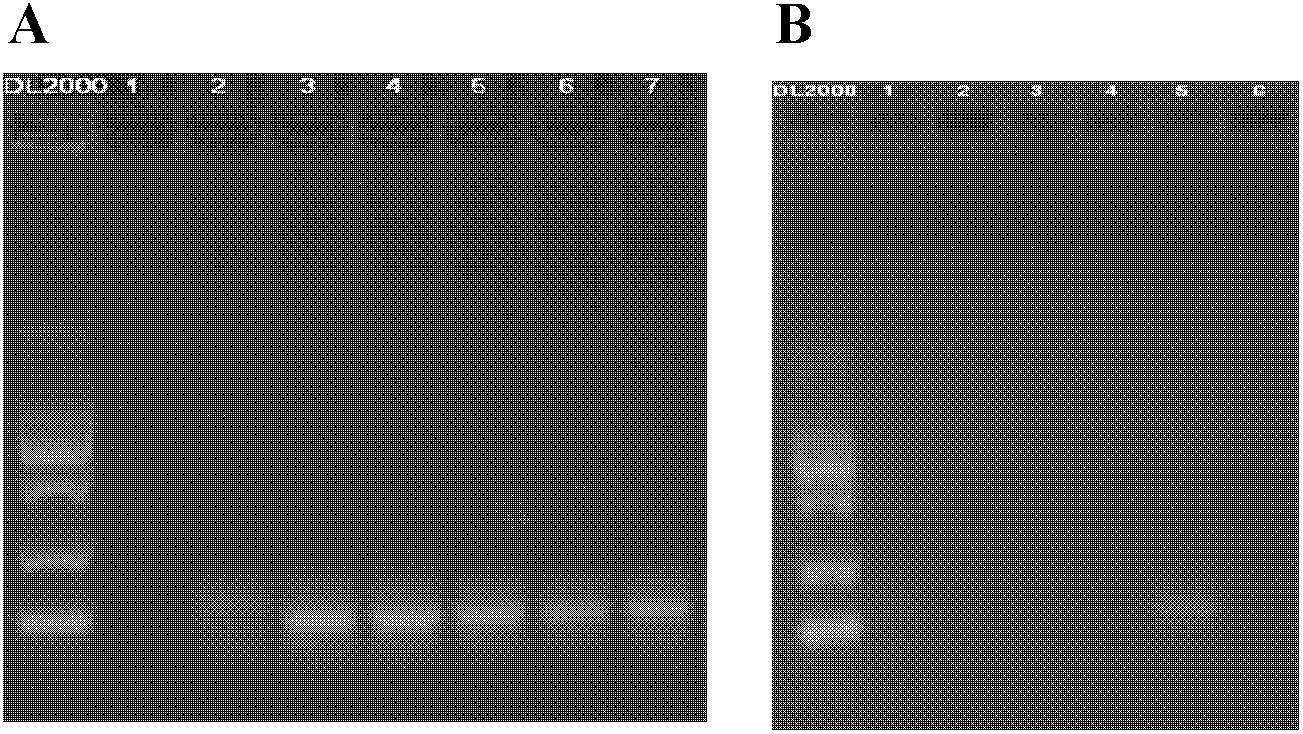
[0056] 3) The product capture method obtains the copy number information of the target nucleic acid fragment in the human genome DNA template. Add 5 μL of genomic DNA template, denature at 98°C, add hybridization buffer and primers, and hybridize, so that the primers are fully combined with the genomic DNA template. The copy number information of the target nucleic acid fragment in the genomic DNA template was obtained by following the reaction system and specific experimental steps described in Example 1. The result is as Figure 4 shown. Lane 2 is the human genome DNA template control, and lane 3 is the primer control. Lane 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Chemiluminescent detection of extension products of GAPDH, GSTT1 and GSTM1
[0060] Examples 1 and 2 demonstrate that the target nucleic acid fragment can be obtained through primer extension reaction using artificially synthesized DNA as a template or genomic DNA as a template, and the following detection work can be performed.
[0061] 1) Preparation of magnetic particles. Magnetic particles were prepared as described in Example 1 for use.
[0062] 2) Primer and probe design. The primers and probes for GAPDH, GSTT1 and GSTM1 described in Example 1 were used.
[0063] 3) Extension formation of biotin-labeled nucleic acid fragments. The specific experimental process is as follows: add 10×Buffer 2 μL, Mg 2+ (25 mM) 2 μL, dNTP (2.5 mM) 1.5 μL (including Biotin-dUTP / dTTP: 4 / 21), primer 2.5 μL, artificially synthesized DNA template 2.5 μL, DNA polymerase 0.5 μL, add deionized water to make up the volume to 20 μL and place the reaction mixture in a PCR machin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com