Slurry and ceramic for high-strength anti-bacterial ceramic, and preparation methods thereof
A technology of antibacterial ceramics and slurry, applied in the field of antibacterial ceramics and its preparation, can solve the problems of stability problems that have not been effectively and finally solved, affecting the appearance of white or light-colored products, etc., and achieves convenient implementation, easy implementation and high gloss. The effect of catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Weigh 50g of zinc oxide whiskers and 1.5g of PEG20000 into a beaker, add distilled water to 500ml; emulsify and stir at 2000 rpm for 20 minutes; add LaCl 3 , CeCl 3 5g each; ultrasonic oscillation for 20 minutes; emulsification and stirring at 3000 rpm for 20 minutes; negative pressure suction filtration of the resulting dispersion, discard the filtrate, transfer the obtained solid to a constant temperature drying oven at 60°C for 72 hours; fully grind the dried solid A powdered product is obtained, that is, a rare earth modified tetrapod zinc oxide whisker antibacterial agent.
[0038] Obtain ceramic green bodies and prepared glaze slurry from a sanitary ceramics factory.
[0039] The prepared modified T-ZnOw was first heat-treated at 1200°C for 1 hour, and then 10% of the antimicrobial compound additive was added, and the additive formula was 20% ZrO 2 , 30% CaCO 3 , 20% NaCO 3 , 30% MgO.
[0040] The treated antibacterial agent and water are prepared in a ratio ...
Embodiment 2
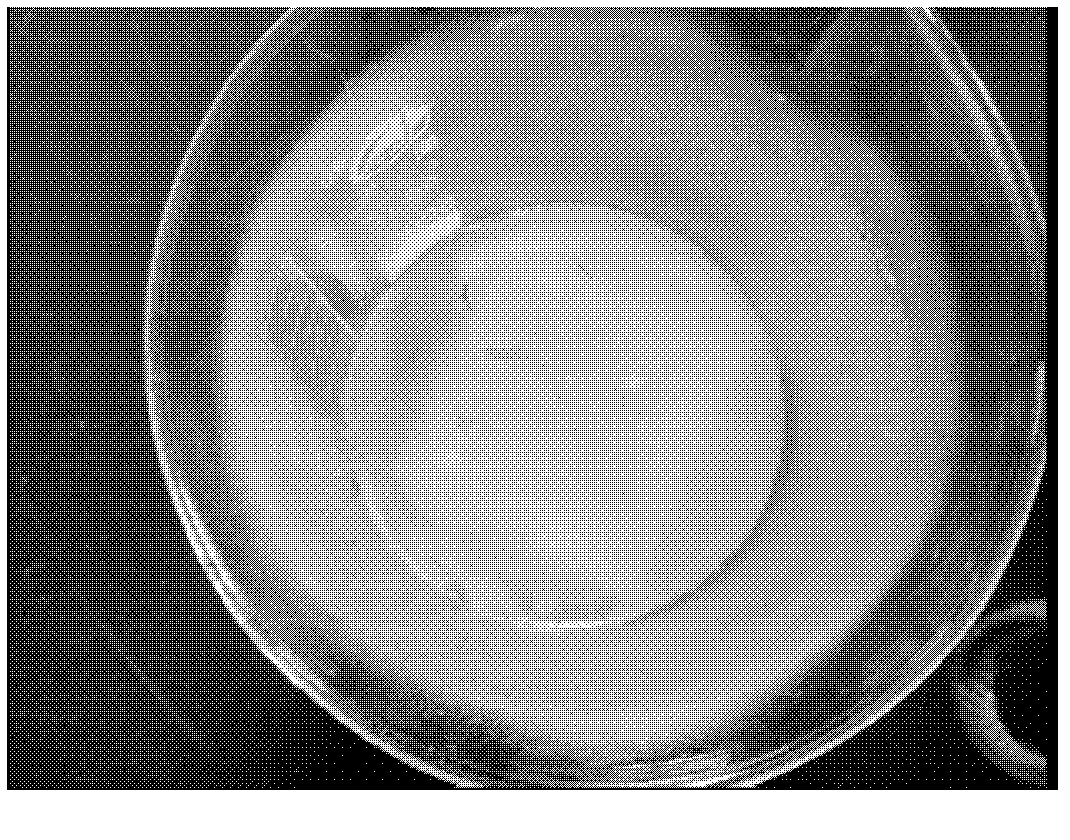
[0046] With embodiment 1, but the mixing ratio of antibacterial slurry and ceramic glaze is 1: 30 when preparing antibacterial mixed glaze, promptly the ratio of antibacterial agent is 10% of embodiment 1 (promptly antibacterial agent is 1% of ceramic glaze ). The photos of the prepared antibacterial ceramics after the antibacterial test of Staphylococcus aureus in the dark are as follows: Figure 4 . From Figure 4 It can be seen that the antibacterial performance of the antibacterial agent is also excellent when the content of the antibacterial agent in the glaze is reduced to 1%.
[0047] The color of antibacterial ceramics is similar to that of ceramics without adding antibacterial agents, and there is no obvious change after 60 days of testing.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The antibacterial agent was changed to four-needle zinc oxide whiskers that had not been modified by rare earth. The photos of the prepared ceramics after the antibacterial experiment of Staphylococcus aureus are as follows: Figure 5 .
[0050] From Figure 5 It can be seen that the antibacterial ceramics with 10% four-needle zinc oxide whiskers that have not been modified by rare earths in the glaze grow a little bacteria after being infected and cultured, but the amount is not as much as that of non-antibacterial ceramics. It has a little antibacterial effect, but the antibacterial effect is not good, and it is not as good as adding only 1% rare earth modified four-needle zinc oxide whisker. It can be seen that the rare earth modification in the antibacterial agent is very obvious for improving the antibacterial effect.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com