Method for preparing blue-green algae pigment
A technology of cyanobacteria pigments and cyanobacteria, applied in chemical instruments and methods, azo dyes, organic dyes, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome methods, environmental pollution, increase production costs, etc., and achieve the effect of high color price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
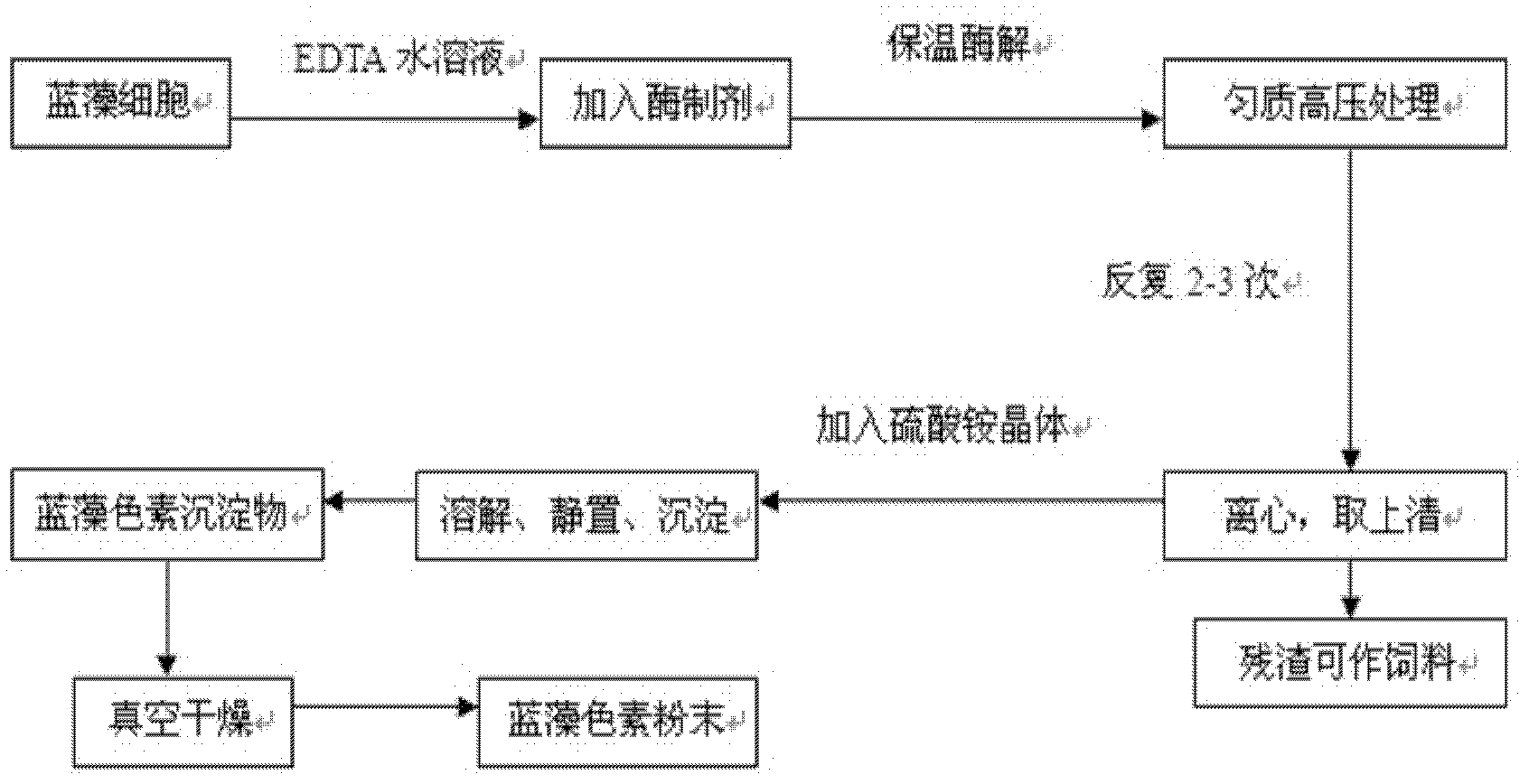
[0031] The cyanobacteria used in the preparation method of the cyanobacteria pigment of the present invention has a wide range of sources, and various cyanobacteria such as spirulina, cyanobacteria, and Nostococcus can be used. The rest of the protein in the cyanobacteria pulp after the pigment is extracted will not be destroyed, and can also be used as feed protein. It does not affect the protein content, makes the best use of everything, and increases the value of by-products.
[0032] The route of the traditional extraction process of cyanobacteria pigment is too long, most of the process needs to be carried out at low temperature, and the extraction period is long, so the cost is high, the efficiency is low, and the production and application value is not high. The preparation method of the cyanobacteria pigment of the present invention uses cyanobacteria as the main raw material, combined with the deep processing of the cyanobacteria by using biotechnology methods, and the...
experiment example 1
[0035] Experimental example 1, high pressure homogeneous method
[0036] (1) Weigh 9 portions (100g each) of spirulina in 1000ml of distilled water containing 0.02M EDTA, stir and soak at 25°C for 4 hours;
[0037] (2) Homogenize the spirulina liquid under different pressures (20, 30, 40kPa) and different cycle times (1, 2, 3 times), control the homogenization speed to be 200L / h, and keep the temperature at 25°C;
[0038] (3) Centrifuge the homogeneous solution at 12,000 r / min for 20 minutes (min), remove sediment, and obtain a supernatant.
[0039] (4) Add 10 g of ammonium sulfate crystals to the supernatant, dissolve it, let stand, and precipitate crude phycocyanin.
[0040] (5) Centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for 15 minutes to obtain a precipitate.
[0041] (6) Results and analysis
[0042] The number of cycles of high-pressure homogenization has a greater impact on the extraction rate of the target product (phycocyanin) than the homogenization pressure. It can be concluded...
experiment example 2
[0045] Experimental example 2, enzymatic dissolution method
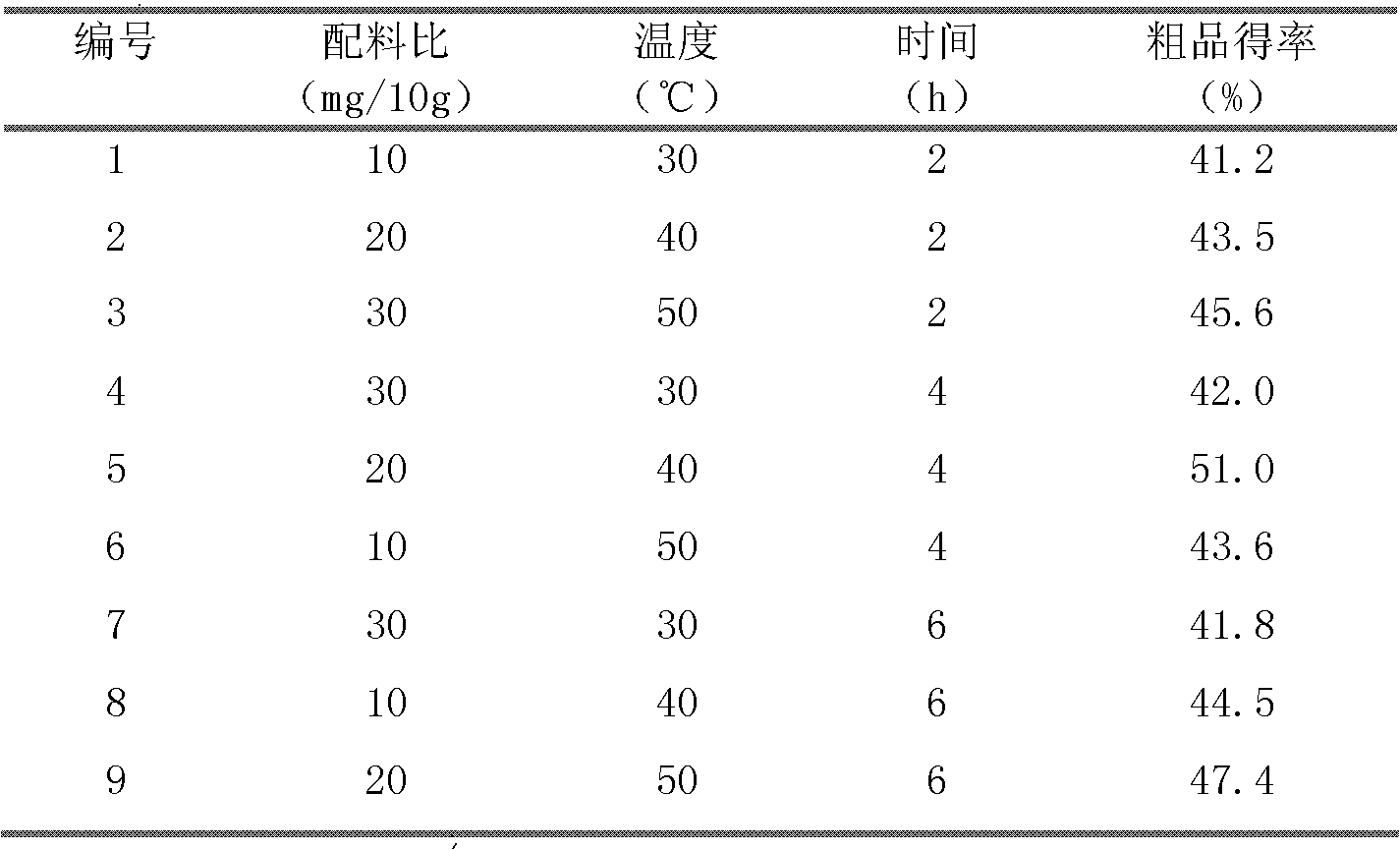
[0046] (1) Weigh 9 portions (100g each) of spirulina, dissolve them in 1000ml of distilled water containing 0.02M EDTA, stir and soak at 25°C for 4 hours;
[0047] (2) Add different total amounts (100, 200, 300 mg) of lysozyme and pectinase (lysozyme: pectinase = 1: 2) to 9 samples respectively and mix them at different temperatures (30, 40, 50 °C) at constant temperature for different time (2, 4, 6h) treatment:
[0048] (3) Centrifuge the spirulina liquid after enzymolysis for 15min under the condition of 10000r / min, and remove the sediment;
[0049] (4) Add 10g of ammonium sulfate crystals respectively in the supernatant, dissolve it, let it stand, and precipitate crude phycocyanin;
[0050] (5) Centrifuge at 10000r / min for 15min to obtain a precipitate.
[0051] From the range analysis in Table 2 below, it can be seen that the enzyme treatment temperature has the greatest impact on the target product (phycocya...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com