Method for detecting sulfate reducing bacteria in water environment
A detection method and sulfate technology, applied in the measurement of color/spectral characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of limited detection sensitivity and stability, easy inactivation of biological reagents, complex testing process, etc., and achieve short detection cycle, low cost, and equipment. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
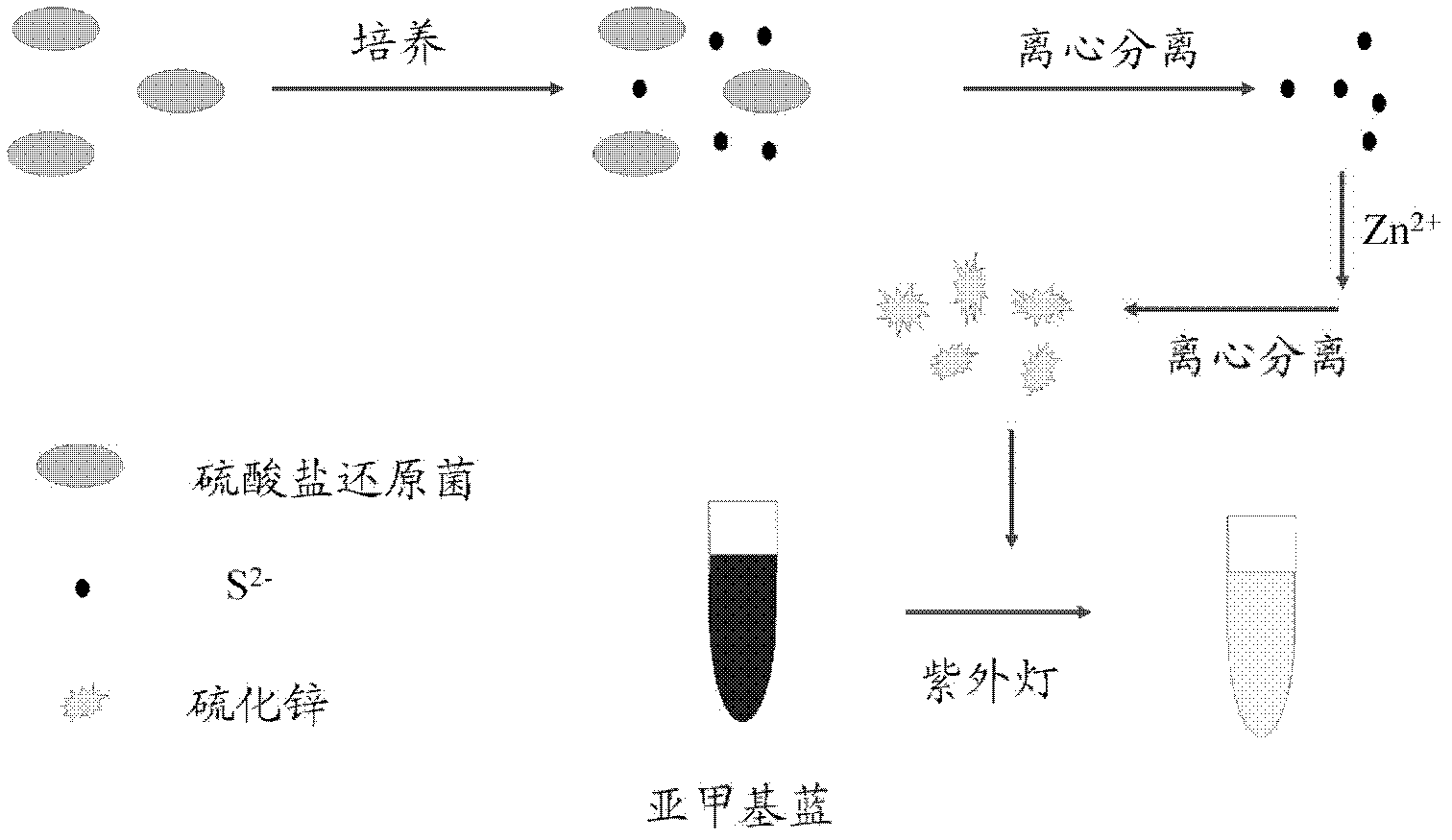
[0015] Take the aqueous solution to be tested containing sulfate-reducing bacteria and centrifuge (centrifugal speed is 8000-10000 rpm, centrifugation time 8-10 minutes), suck out the upper layer and pour it off, take the lower layer and deposit it in the culture medium of sulfate-reducing bacteria Medium continuous culture, the culture temperature is stable at 30-35 ℃. Take it out after 3-4 days of cultivation, take the bacterial solution and centrifuge (centrifugation speed is 12000-14000 rpm, centrifugation time 10-15 minutes), and take the supernatant. Add zinc nitrate solution to the supernatant, wherein the volume ratio of supernatant to zinc nitrate is 9:1, and the concentration of zinc nitrate is 2-3mM. After reacting for 20-30 minutes, centrifuge again (centrifugal speed is 12000-14000 rpm, centrifugation time 10-15 minutes), discard the supernatant and keep the precipitated substance. Wash the precipitated substance with ultrapure water, and centrifuge again (centri...
Embodiment 2
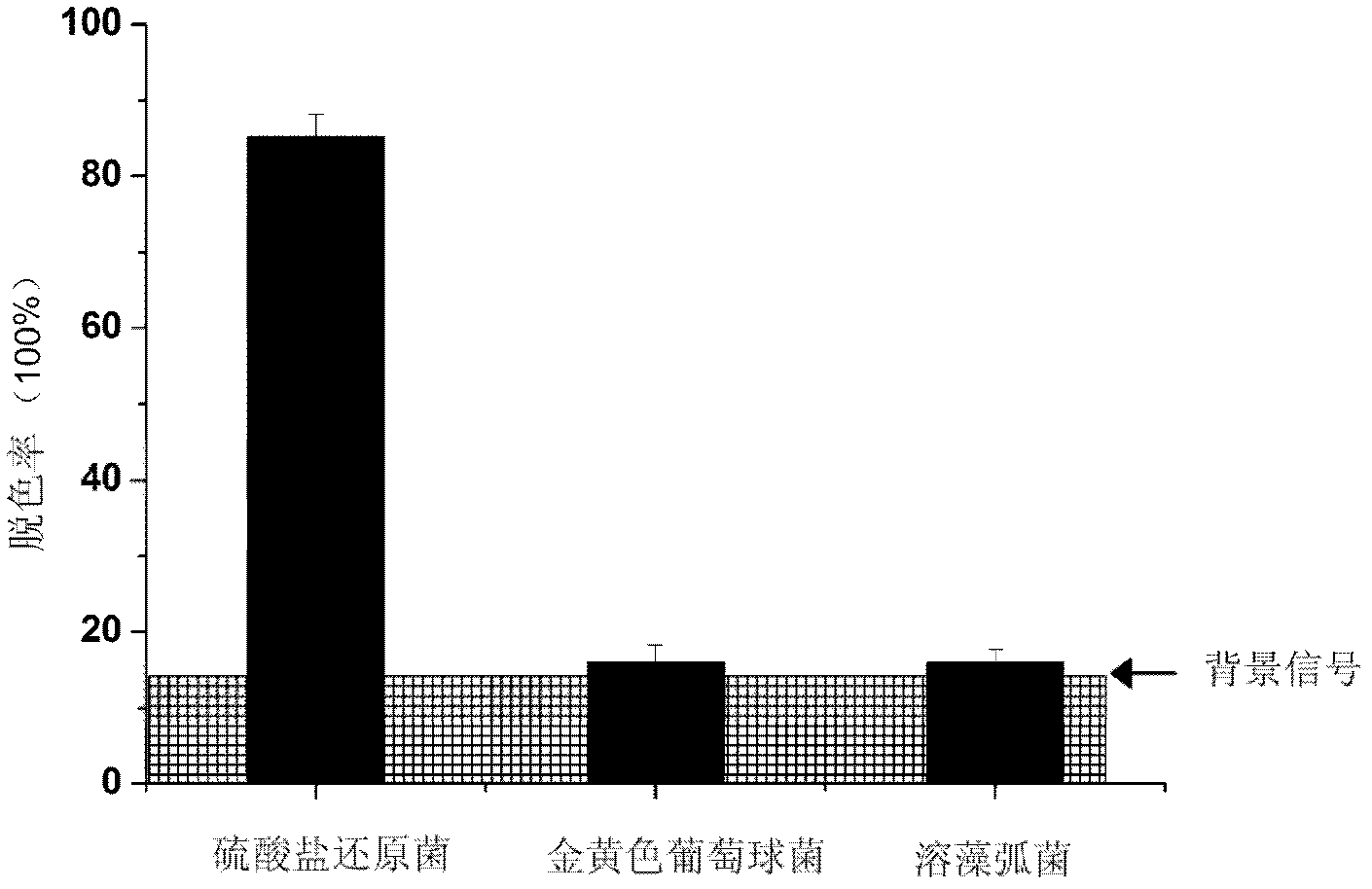
[0020] According to the method in Example 1, detect the signal response of three kinds of bacteria (sulfate-reducing bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio alginolyticus) of the same concentration under the same culture time and the same ultraviolet light time conditions (see image 3 ). By measuring the absorbance of the sample at 665nm before and after ultraviolet light irradiation, the decolorization rate of different species of bacteria at the same concentration was calculated. The results showed that after deducting the background, the signal of sulfate-reducing bacteria detected by this method far exceeded that of the other two bacteria, indicating that the detection method had good selectivity. Compared with the selective detection of biological components, this method does not need to consider the activity of biomolecules and the problem of non-specific recognition.
Embodiment 3
[0022] According to the method in embodiment 1, detect a series of different concentration sulfate-reducing bacteria (from 10 1 to 10 8 cfu / mL), and the control was done without UV light irradiation. By measuring the absorbance of the sample at 665nm before and after ultraviolet irradiation, calculate the decolorization rate of sulfate-reducing bacteria in different concentrations with or without ultraviolet irradiation (see Figure 4 ). The results show that in 10 3 to 10 8 The decolorization rate increased with the concentration of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the concentration range of cfu / mL, and showed a good linear correlation. There was no significant change in the decolorization rate under the experimental conditions without light.
[0023] The invention provides a method for selective detection based on metabolites of sulfate-reducing bacteria, and the method can effectively detect the quantity and change of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a water environment. Comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com