Pretreatment method for improving enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiency of non-wood fiber raw material
A technology of non-wood fiber and saccharification efficiency, which is applied in the field of pretreatment to improve the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification of non-wood fiber raw materials, and can solve the problem of low utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
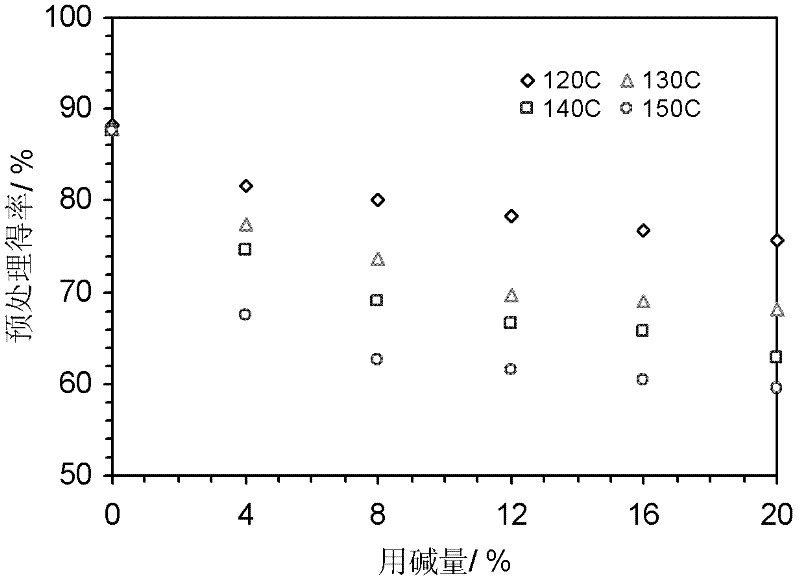
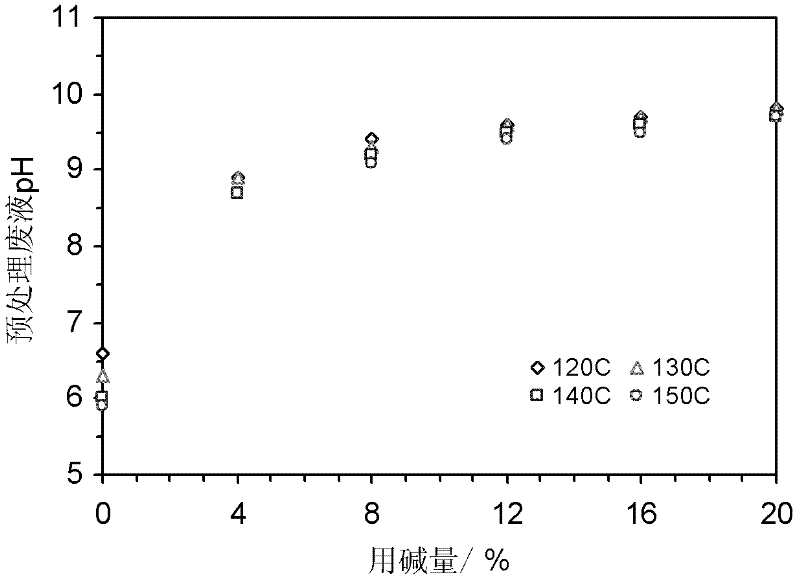
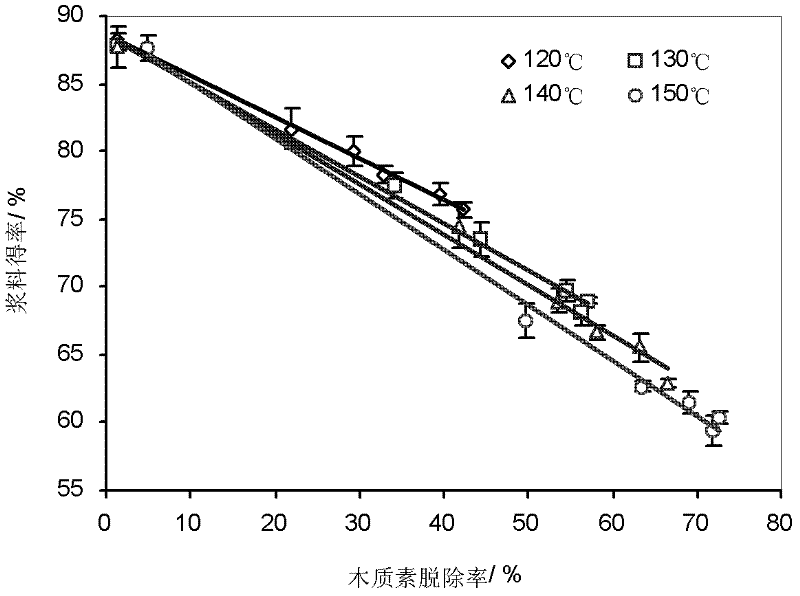
[0050] Embodiment 1: Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis method using rice straw as raw material.
[0051] raw material:
[0052] The straw used in the experiment was produced in northern Jiangsu and provided by a paper mill in Jiangsu. After the raw materials are air-dried, the roots are removed, the stems, leaves, and sheaths are kept, and they are cut into 3-5cm grass pieces, mixed evenly, and the water is balanced for later use.
[0053] Cellulase (CCN03110, enzyme activity 118 FPU / mL), xylanase (CFN00244, enzyme activity 153FXU / mL), β-cellobiase (DCN00207, enzyme activity 480 CBU / mL) were provided by Novozymes. Use acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.8) to make cellulase, xylanase and β-cellobiase into a mixed enzyme solution with an enzyme activity ratio of 1FPU: 1.2FXU: 1CBU, and the enzyme activity of the mixed enzyme solution The enzyme activity of the cellulase filter paper was 20 FPU / mL, and excess β-cellobiase was added to prevent the accumulation of cellob...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis method using wheat straw as raw material.
[0065] raw material:
[0066] The raw material of the experiment is wheat straw. After air-drying, the roots and ears are removed, and the stems, leaves, and sheaths are kept. They are cut into 3-5cm grass pieces, mixed evenly, and the water is balanced for later use.
[0067] The enzyme used in the experiment is a mixture of cellulase (NS50013, enzyme activity 84 FPU / mL), xylanase (NS50014, enzyme activity 109FXU / mL) and β-cellobiase (NC188, enzyme activity 350CBU / mL) , provided by Novozymes. Use acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.8) to mix cellulase, xylanase and β-cellobiase with an enzyme activity ratio of 1FPU: 1.2FXU: 1CBU to make a mixed enzyme solution, and the enzyme in the mixed enzyme solution The enzyme activity of cellulase filter paper is 20FPU / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3: Pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis method using wheatgrass leaves and sheaths as raw materials.
[0087] raw material:
[0088] The experimental raw materials are wheat grass leaves and sheaths, which are cut into 3-5 cm grass pieces, mixed evenly, and balanced in water for later use.
[0089] The enzyme used in the experiment is the same as in Example 2.
[0090] Sodium carbonate pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis process are identical with embodiment 2.
[0091] Wheatgrass leaves and leaf sheaths are the main components of waste residues in paper mills. At present, there is no better treatment and utilization measures except burning. The main chemical components of wheatgrass leaves and sheaths are shown in Table 2.
[0092] Table 2 Analysis of main chemical components of each part of wheat straw, %
[0093]
[0094]
[0095] Figure 13 It is the content of lignin (Klason lignin, acid-soluble lignin), ash and various polysaccharides (dex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com