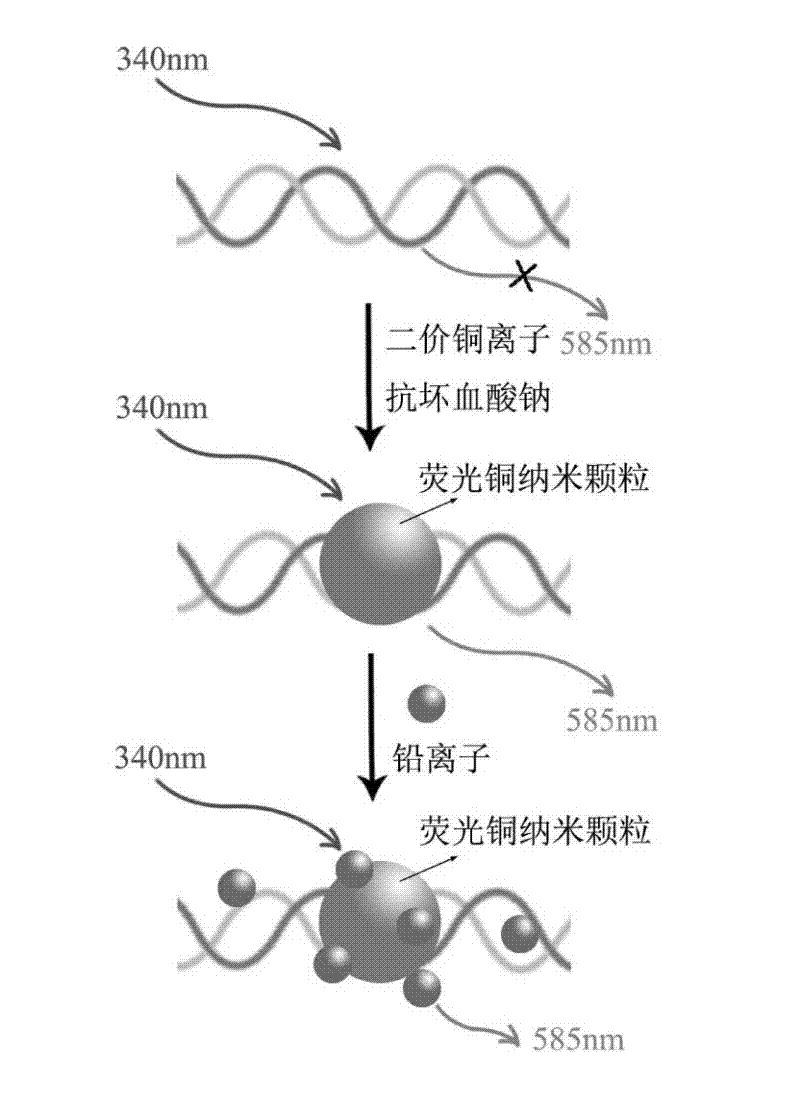
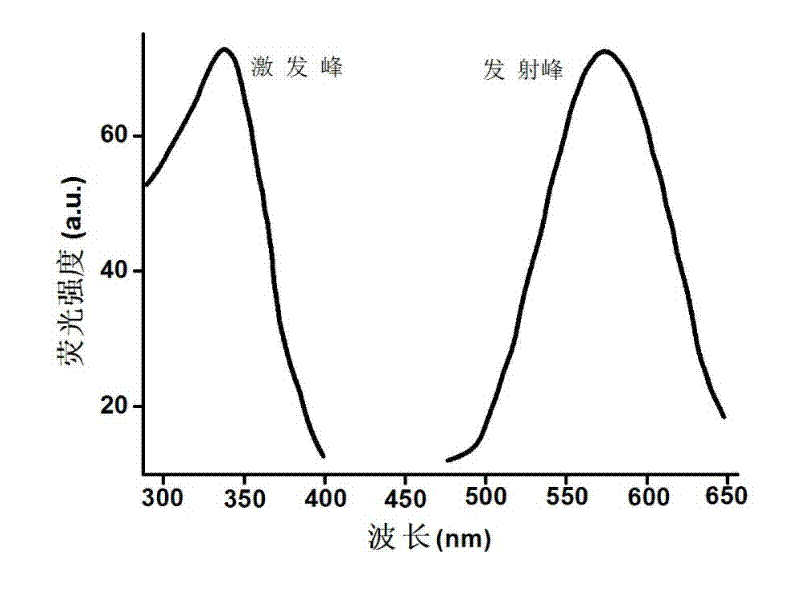
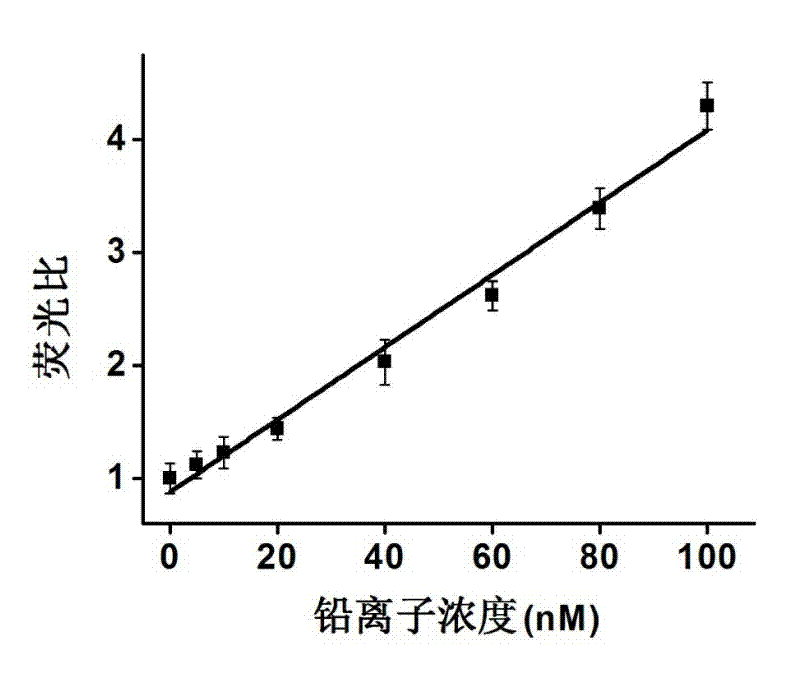
Quick label-free detection method for lead ions
A lead ion, label-free technology, applied in the direction of material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable rapid detection, troublesome operation, time-consuming and labor-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of low detection limit, simple operation and high detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The steps for label-free detection of lead ions using fluorescent copper nanoparticles formed based on random double-stranded DNA as a template are as follows:
[0035] 1) Dissolve random complementary double-stranded DNA with 3-(N-morpholine) propanesulfonate sodium salt (MOPS) buffer solution (10 mM, pH=7.5) containing 150 mM sodium acetate. The sequence of the randomly adopted DNA is : 5'-TACTCATACGCTCATACGTTCATCACGACTACACA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1) (synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.), 500 nM two random complementary DNAs were mixed evenly, reacted in a 90°C water bath for 10 minutes, and then slowly Cool down to room temperature to obtain 500 nM random complementary double-stranded DNA solution;
[0036] 2) Add 1 mM sodium ascorbate to 500 mL of 500 nM complementary double-stranded DNA, mix well, then add 100 mM copper acetate, mix well, and react at room temperature for about 20 minutes in the dark to obtain random double-stranded DNA Fluorescent c...
Embodiment 2
[0042] In order to investigate the specificity of fluorescent copper nanoparticles synthesized based on random double-stranded DNA as a template for label-free detection of lead ions, a selectivity experiment was carried out as follows:
[0043] 1) Dissolve random complementary double-stranded DNA with 3-(N-morpholine) propanesulfonate sodium salt (MOPS) buffer solution (10 mM, pH=7.5) containing 150 mM sodium acetate. The sequence of the randomly adopted DNA is : 5'-ATGAACGTATGAGCG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2) (synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.). Two random complementary DNAs of 500 nM were mixed evenly, reacted in a 90°C water bath for 10 minutes, and then slowly lowered to room temperature to obtain a 500 nM random complementary double-stranded DNA solution;
[0044] 2) Add 1 mM sodium ascorbate to 500 mL of 500 nM complementary double-stranded DNA, mix well, then add 100 mM copper sulfate, mix well, and react at room temperature for about 20 minutes in the da...
Embodiment 3
[0048] In order to investigate the use of fluorescent copper nanoparticles synthesized based on random double-stranded DNA as a template for label-free detection of lead ions in actual samples, the recovery rate experiment was carried out as follows:
[0049] 1) Dissolve random complementary double-stranded DNA with 3-(N-morpholine) propanesulfonate sodium salt (MOPS) buffer solution (10mM, pH=7.5) containing 150 mM sodium acetate. The sequence of the randomly used DNA is: 5'-AGTTGCAAGAAGATGACAGAGAAGT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3) (synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.). Two random complementary DNAs of 500 nM were mixed evenly, reacted in a 90°C water bath for 10 minutes, and then slowly lowered to room temperature to obtain 500 nM random complementary double-stranded DNA;
[0050] 2) Add 1 mM sodium ascorbate to 500 mL of 500 nM complementary double-stranded DNA, mix well, then add 100 mM copper nitrate, mix well, and react at room temperature for about 20 minutes in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com