Digital holographic detection device for subsurface defect of optical element
A subsurface defect, digital holographic technology, applied in optical testing flaws/defects, phase influence characteristic measurement, etc., can solve problems such as low detection efficiency, limited practicability, and inability to achieve quantitative analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
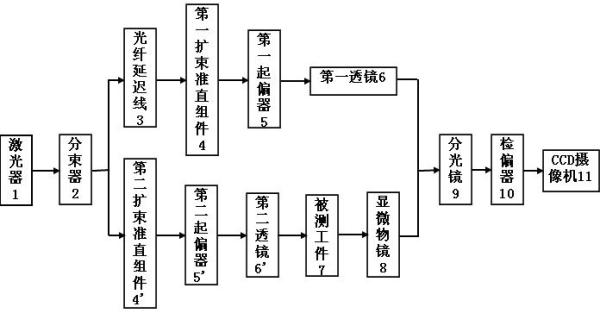
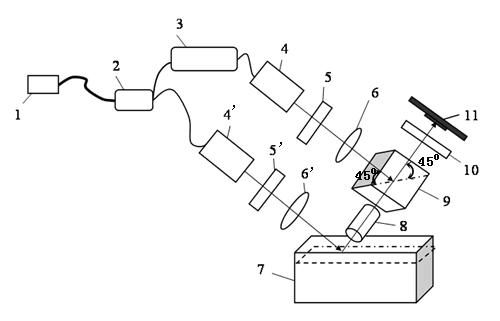
[0024] Embodiment one: figure 1 The optical element subsurface defect detection device shown is a structural block diagram of this implementation, consisting of figure 1 It can be seen that the device consists of a laser 1, a beam splitter 2, a fiber delay line 3, the first and second two beam expander collimation components 4, 4', the first and second two polarizers 5, 5 ', the first and second lenses 6, 6', a microscope objective lens 8, a beam splitter 9, an analyzer 10 and a CCD camera 11.
[0025] For implementation steps see image 3 , the beam emitted by the laser 1 is divided into two beams by the beam splitter 2, one beam is the measurement beam and the other is the reference beam, the reference beam passes through the fiber delay line 3, and then the two beams are collimated through the first and second beam expanders of their respective optical paths Components 4, 4', first and second polarizers 5, 5' and first and second lenses 6, 6', and then the measuring beam...
Embodiment 2
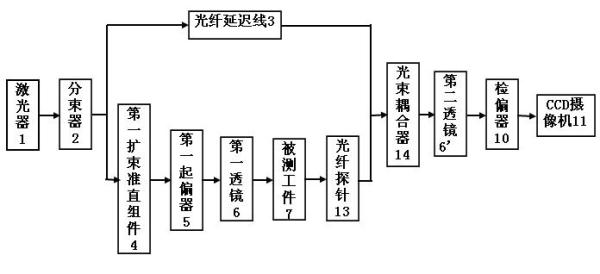
[0026] Embodiment two: figure 2 The optical element subsurface defect detection device shown is a structural block diagram of this implementation, consisting of figure 2 It can be seen that this set consists of a laser 1, a beam splitter 2, a fiber delay line 3, a first beam expander collimator assembly 4, a first polarizer 5, a first and a second lens 6, 6', a A fiber probe 13, a beam coupler 14, a polarizer 10 and a CCD camera 11 are composed.
[0027] For implementation steps see Figure 4 : The beam emitted by the laser 1 is divided into two beams by the beam splitter 2, one beam is used as the measurement beam and the other is used as the reference beam, the reference beam passes through the fiber delay line 3, the measurement beam passes through the first beam expander and collimator assembly 4, and the first polarizer 5 and the first lens 6 are then irradiated on the workpiece 7 to be measured, reflected by the workpiece 7, and the reflected light is detected by the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com