Method for preparing nucleic acid probe-coated porous solid support strip
A porous solid and nucleotide technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism measurement/testing, etc., can solve the difficulty of controlling the level of cross-linking of thymine bases, long-term cycle, high cost and other issues to achieve the effect of mass production and automated processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
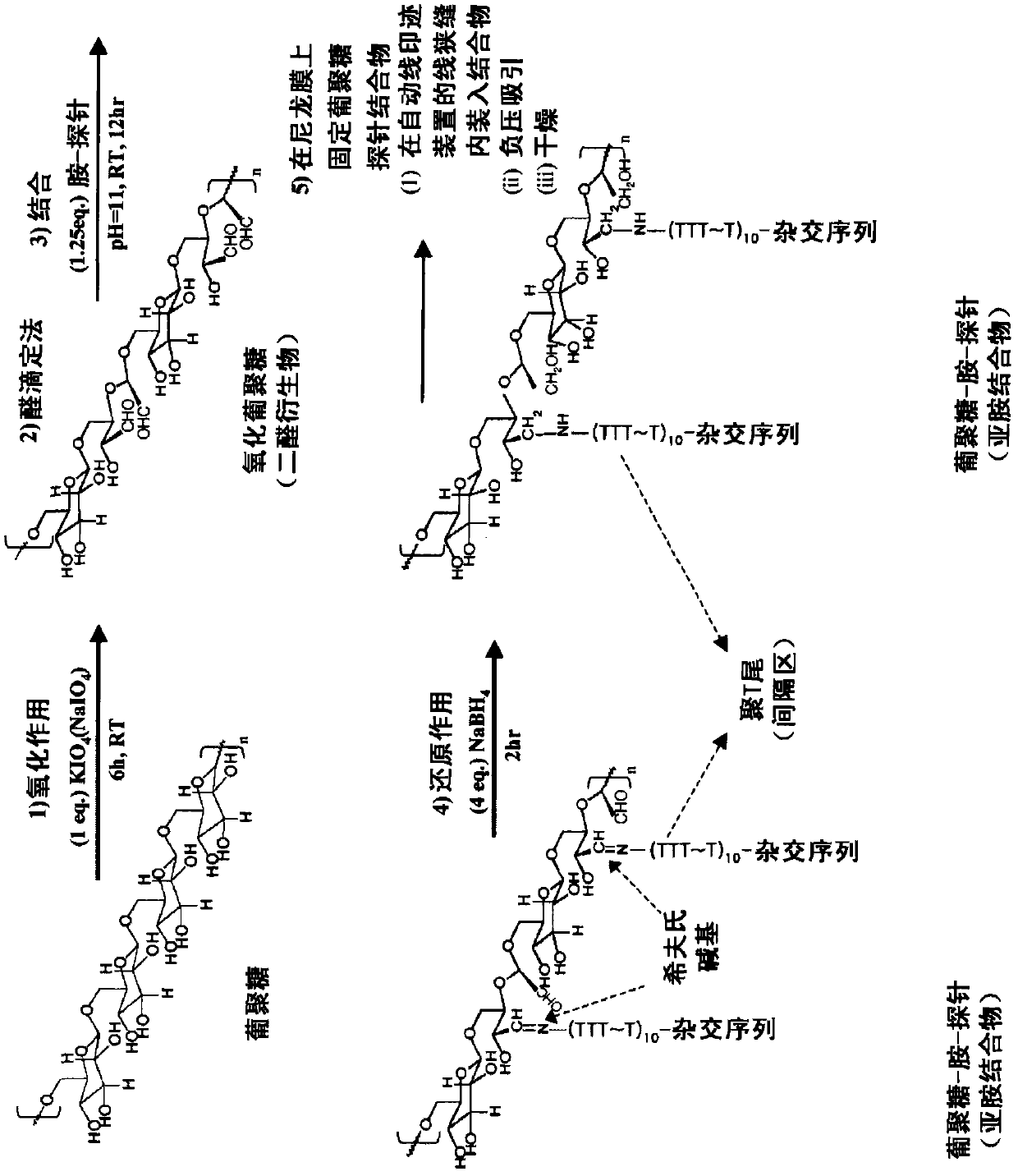
[0109] Embodiment 1: Preparation polyaldehyde dextran (PAD)
[0110] (1) Preparation of required reagents and instruments
[0111] Using dextran (Sigma, D-4133, Mr ~ 43kDa), KIO 4(Aldrich, 32242-3, F.W230.00), cellulose dialysis membrane cut-off 12000: Spectra / Por, MWCO 12-14000), hydroxylamine hydrochloride (NH 2 OH-HCl=69.49), methyl orange powder, 10N hydrochloric acid, acidity meter, 0.1N sodium hydroxide (NaOH), freeze dryer and vacuum centrifugal evaporation concentrator, etc.
[0112] (2) Preparation of oxidized dextran
[0113] 0.5 g of dextran (Sigma, D-4133, Mr~43 kDa / equivalent to 62.5 mmol of glucose) was completely dissolved in autoclaved D.W to adjust the total volume to 10 ml. Add 0.72g of KIO to it 4 (equivalent to the same equivalent of 62.5 mmol) (reference: Azzam T et al., J.Med.Chem., 45, 1817-1824, 2002; Azzam T et al., Macromolecules, 35, 9947-9953, 2002; Azzam T et al. People, J. Controlled Release, 96, 309-323, 2004; Hosseinkhani H. et al,. G...
Embodiment 2
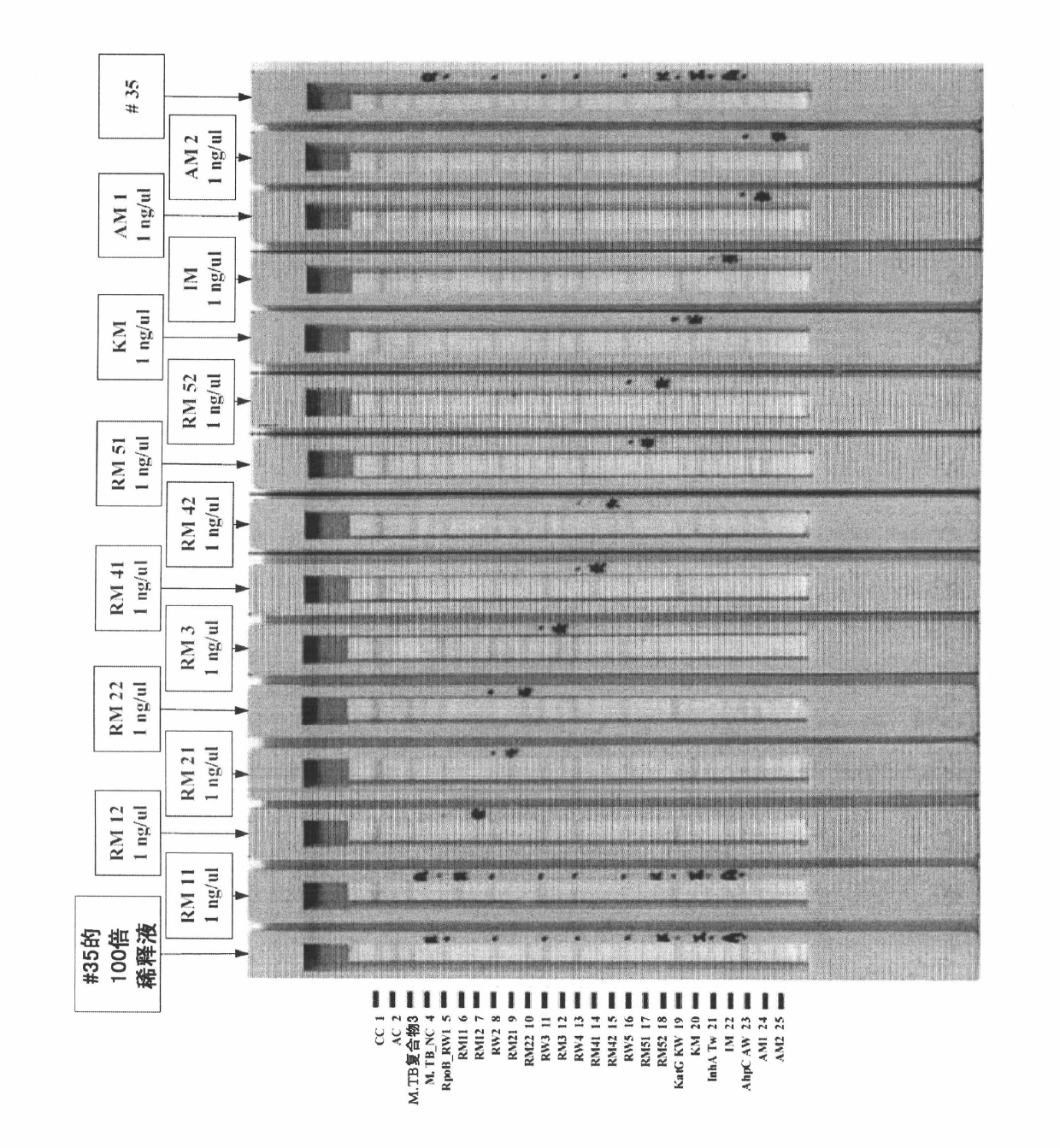
[0135] Embodiment 2: the preparation of nucleotide probe
[0136] The probes used in this experiment were designed to detect: (i) Mycobacterium tuberculosis and identify resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid drugs, (ii) detect mycobacteria, i.e. distinguish non-tuberculous mycobacteria ( NTM) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) species.
[0137] First, for aspect (i), when the probe goes to detect M. tuberculosis and recognizes M. tuberculosis resistance to rifampicin and isoniazid, it will target the transcript specific for the M. tuberculosis complex Probes for the interspacer (ITS) locus were used for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
[0138] When using probes to identify susceptibility and resistance to rifampicin (antituberculosis drug), use an anti-tuberculosis drug that is wild-type or mutated in the gene encoding rpoB (ie, RNA polymeric beta-subunit) Oligonucleotides of type base sequence.
[0139] In addition, when probes were used to detect sus...
Embodiment 3
[0153] Embodiment 3: Preparation of nucleotide probe-polyaldehyde dextran conjugate
[0154] (1) Preparation of required reagents
[0155] Prepare 0.5 M sodium borate buffer (pH 11.0) and use it as buffer for binding reaction, prepare 0.1 mM NaBH 4 solution to serve as a mild reducing agent for the conversion of Schiff's bases through the reaction between the aldehyde group of polyaldehyde dextran as a support and the amino group at the 5'-terminus of the nucleotide probe via Stable covalent linkages are formed.
[0156] (2) Preparation of the main mixed solution for the binding reaction
[0157] The main mixed solution consisted of polyaldehyde dextran (1 pmol / μL), 0.5M sodium borate buffer (pH 11.0) and sterilized distilled water. These components were mixed in the proportions listed in Table 5 below.
[0158] [table 5]
[0159]
[0160] (3) Binding reaction
[0161] 40 sheets of films having a size of 16.7 cm x 5.5 cm and a thickness of each line of 0.8 mm ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com