Degradable composite material containing chitin or chitosan
A technology of composite materials and chitin, which is applied in the field of degradable composite materials, can solve the problems that the self-degradation ability of chitin and chitosan has not been established, and achieve storage stability, long-term storage stability, The effect of burden reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] The chitin molded article can be produced by a known production method, or can be obtained as a commercial product.
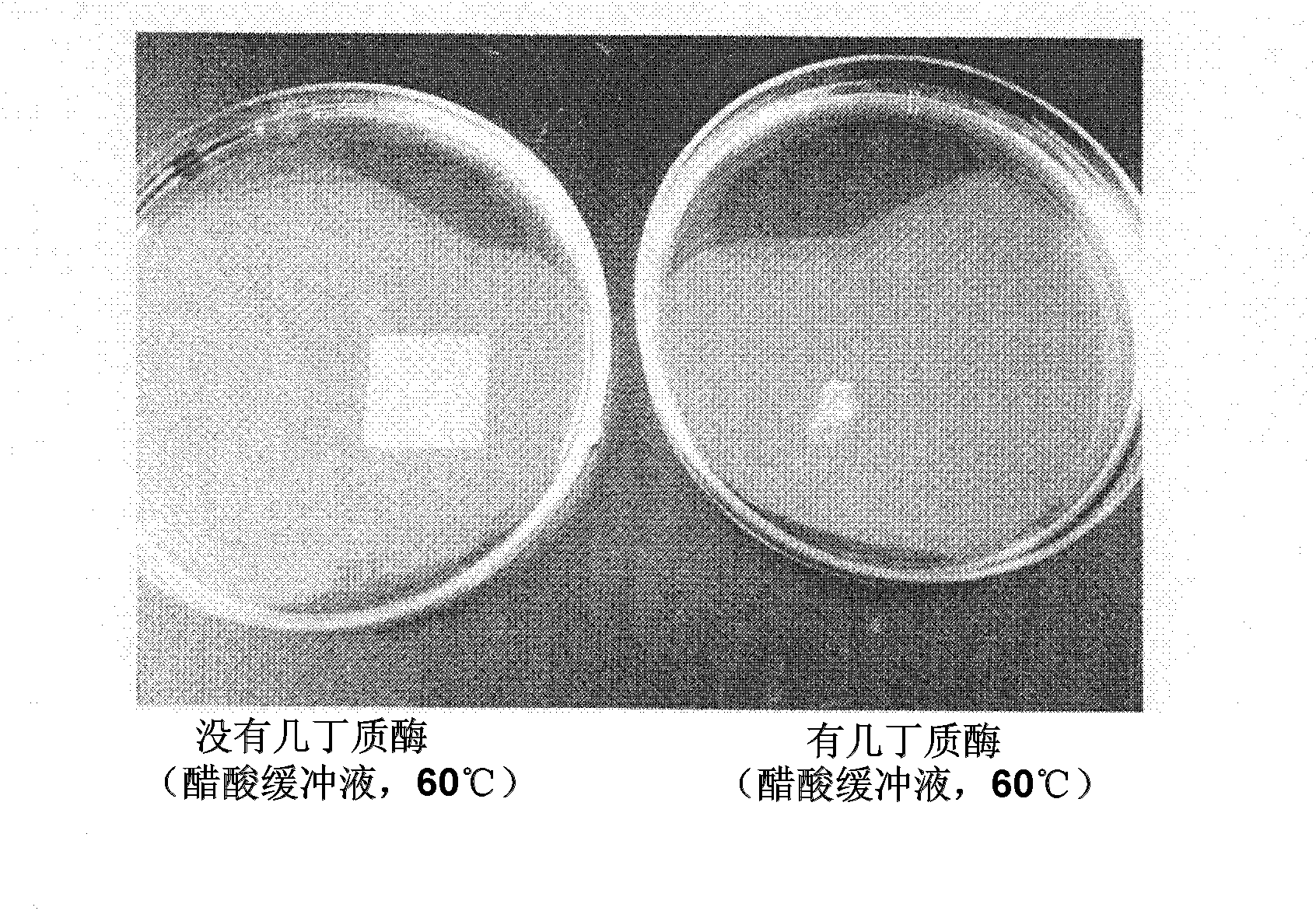
[0034] The degrading enzyme used in the degradable composite material of the present invention is not particularly limited herein, as long as it can hydrolyze the polysaccharide and is pharmaceutically acceptable. Specific examples of such degrading enzymes include chitinase, chitosanase, and the like. For example, if the polysaccharide is chitin, chitinase is used, and if the polysaccharide is chitosan, chitosanase is used. The degrading enzyme used for the degradable composite material of the present invention may be one enzyme used alone, or two or more enzymes used in combination.
[0035] The effective temperature of the degrading enzyme used in the present invention is not particularly limited herein, as long as it exhibits activity at the temperature and environment at which the degradable composite material will be used, preferably the degrading...
Embodiment 1
[0052] 1. Preparation of Chitinase
[0053] Use LB medium (containing 10 g / L polypeptone, 5 g / L yeast extract, and 10 g / L sodium chloride) to shake culture at 37 °C on Escherichia coli carrying the plasmid, which has been introduced into the plasmid encoding DNA of the chitinase of Pyrococcus furiosus (amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2004-344160), and in the logarithmic growth phase (optical density at 600 nm of 0.2 to 0.4 ) was added isopropyl β-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) so that the final concentration was 0.2 mM. Culturing was continued unchanged overnight, and then E. coli cells were collected by centrifugation (6,000 xg, 7 min).
[0054] E. coli cells recovered from 1 liter of culture were suspended in 20 mL of buffer A (25 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 1 mM EDTA, 25 mM NaCl) and lysed by sonication. After lysis, extracts were obtained by high-speed centrifugation (13,000 xg, 15 min). The extract was heated at 85...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com