An electrophoresis method for removing the interference of rubisco enzyme from watermelon leaves and separating the remaining low-abundance proteins
A protein and watermelon technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of cumbersome and complicated operations, need to be further investigated and verified, and not identical.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
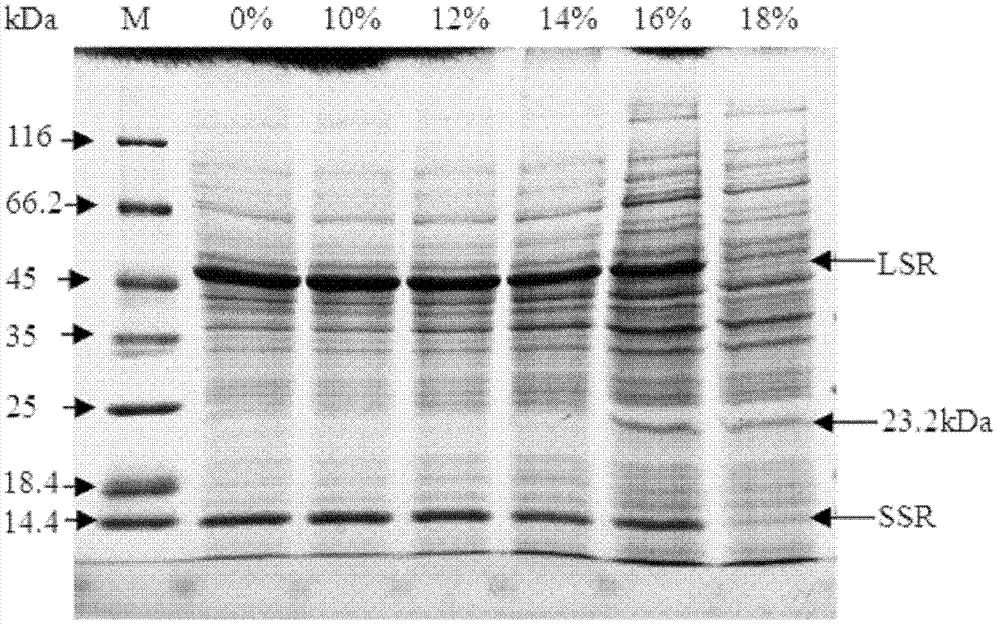
[0028] Example 1 Screening of the best PEG concentration of Rubisco in precipitation of watermelon leaves
[0029] A. Take 2g of mature leaves of watermelon (Citrullus Ianatus Mansfeld) seedlings, place them in liquid nitrogen and quickly grind them to a fine powder (particle size is about 0.01mm). Use a small spatula to quickly transfer the powder to a 10ml centrifuge tube, and add 7ml Cold homogenization buffer, then shake and mix on a vortexer, and incubate horizontally on ice for 10 minutes.
[0030] B. Centrifuge at 1500g for 3 minutes at 4°C, discard the precipitate and save the supernatant; then centrifuge at 1,500g at 4°C for 20 minutes, discard the precipitate and save the supernatant.
[0031] C. Add different concentrations of PEG-4000 to the supernatant, incubate horizontally on ice for 20 minutes, centrifuge at 1,500g at 4°C for 25 minutes, discard the precipitate, and save the supernatant.
[0032] D. Quantify the protein in the supernatant obtained in step C to 2ug / ul b...
Embodiment 2
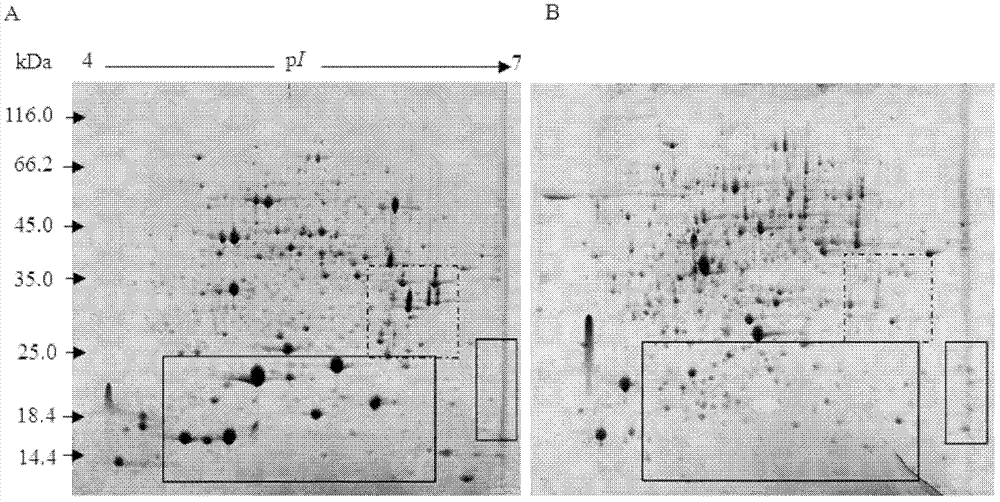
[0035] 1) Preparation of remaining protein samples after precipitation of Rubisco of watermelon leaves
[0036] A. Repeat step AB of Example 1 to obtain the whole protein supernatant. Add 60% PEG-4000 to the supernatant to make the final concentration of PEG-4000 in the solution reach 18%. Vibrate and mix well on a vortex. Incubate on ice for 20 minutes, centrifuge at 1,500g at 4°C for 25 minutes, discard the pellet, and save the supernatant.
[0037] B. Add 8 volumes of 10% trichloroacetic acid-acetone solution (w / v, containing 0.07% β-mercaptoethanol) to the supernatant, and place it at -20°C overnight. Centrifuge at 2,500g for 25 minutes at 4°C, discard the supernatant, and save the precipitate.
[0038] C. Add 8ml of acetone (containing 0.07% β-mercaptoethanol) to the precipitate to clean the precipitate, place it at -20°C for 1 hour, centrifuge under the same conditions as in step B, discard the supernatant, and save the precipitate.
[0039] D. Repeat step C 3-4 times until the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com