Method for detecting enzyme intermediates in real time by use of electrochemical biosensor
An intermediate and enzyme detection technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, scientific instruments, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of immature sensor applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Before the modification, the surface of the glassy carbon electrode was polished and polished with 0.05 mm of alumina paste covered on the emery cloth, and then the glassy carbon electrode was ultrasonically cleaned with acetone, 50% NaOH solution, 50% nitric acid, and double distilled water, respectively. Dry at room temperature.
[0026] Disperse 1 mg of activated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in 10 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide and vibrate ultrasonically to obtain a black suspension. 10 mL of the suspension was dropped on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, and the solvent was evaporated under an infrared lamp to prepare an HRP-modified electrode.
[0027] Dissolve 2.5mg 300U / mL HRP and 4mg BSA in 0.2mL of KH 2 PO 4 -Na 2 HPO4 A mixed solution was formed in phosphate buffer (0.05mol / L, pH 7.0). Then 20 μL of the mixture was dropped onto the surface of the carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode. The electrodes were then placed in a closed containe...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Cyclic voltammetry experiments were performed with an electrochemical workstation and a conventional three-electrode system. Among them, modified glassy carbon electrode was used as working electrode; platinum wire was used as counter electrode; saturated calomel electrode (SCE) was used as reference electrode; PBS (0.05mol / L, pH 7.0) was used as supporting electrolyte. The electrolyte was degassed with nitrogen for 30 min before the test, and the electrochemical reactor was protected with nitrogen during the experiment.
[0030] The potential scanning range (relative to SCE) of the cyclic voltammetry experiment is -0.4~0.2V, and the scanning rate is 100mV / s. Experiments were performed at room temperature.
Embodiment 3
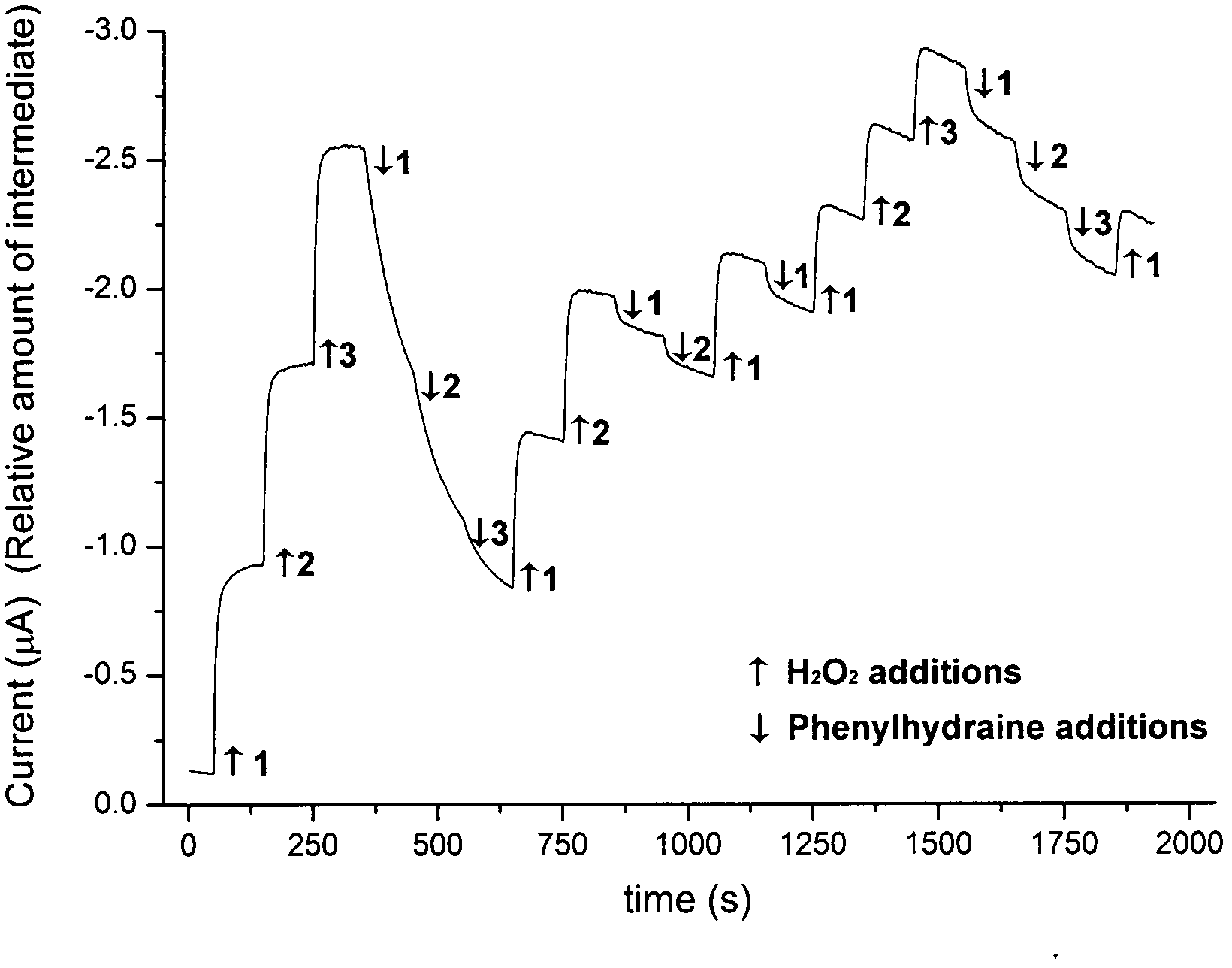
[0032] Experiments investigating the effect of substrates were performed in a reaction cell filled with 20 mL of supporting electrolyte. Under stirring, 1 mmol / L hydroquinone was added, and the baseline of the initial current was recorded at -0.25 V. Then, add 0.1 mL of 0.1 mol / L H at intervals of about 50 s 2 o 2 solution, a current-time curve showing a step-up trend was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com