Method for extracting water-insoluble dietary fiber of osmunda cinnamomea
A technology of soluble dietary fiber and sage water, applied in food preparation, food science, application, etc., can solve the problems of water-insoluble cellulose and low purity, and achieve the effect of promoting deep processing research.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Preparation of the water-insoluble dietary fiber of Osmanthus
[0032] The method for extracting the water-insoluble dietary fiber of Osmanthus chinensis comprises the following steps: (see Table 1 for specific parameters):
[0033] 1) Degreasing: use a pulverizer to crush the dried vetch, then add ethyl acetate and soak it at room temperature for 3 hours, then use distilled water to remove the residual organic solvent, filter and dry it with suction, then crush it again, pass through 40 mesh Sieve, and put the obtained degreased sample into a dry dish for later use.
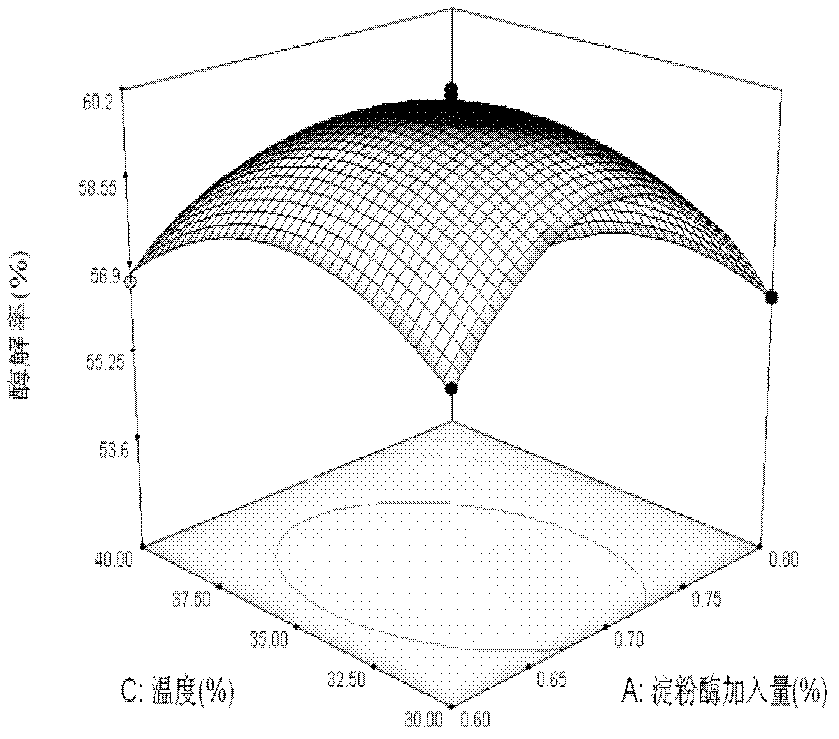
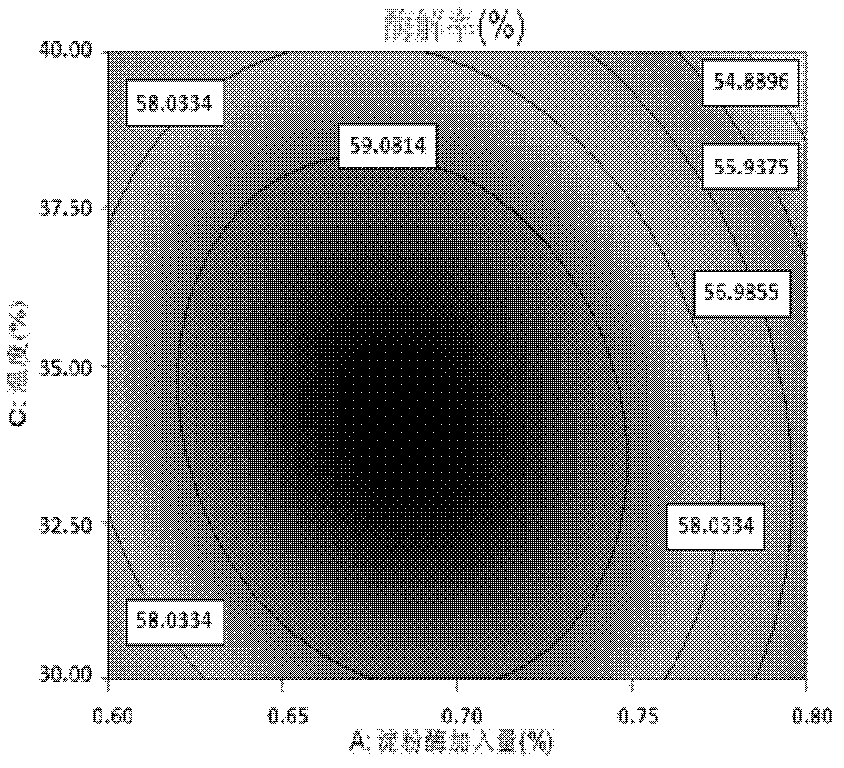
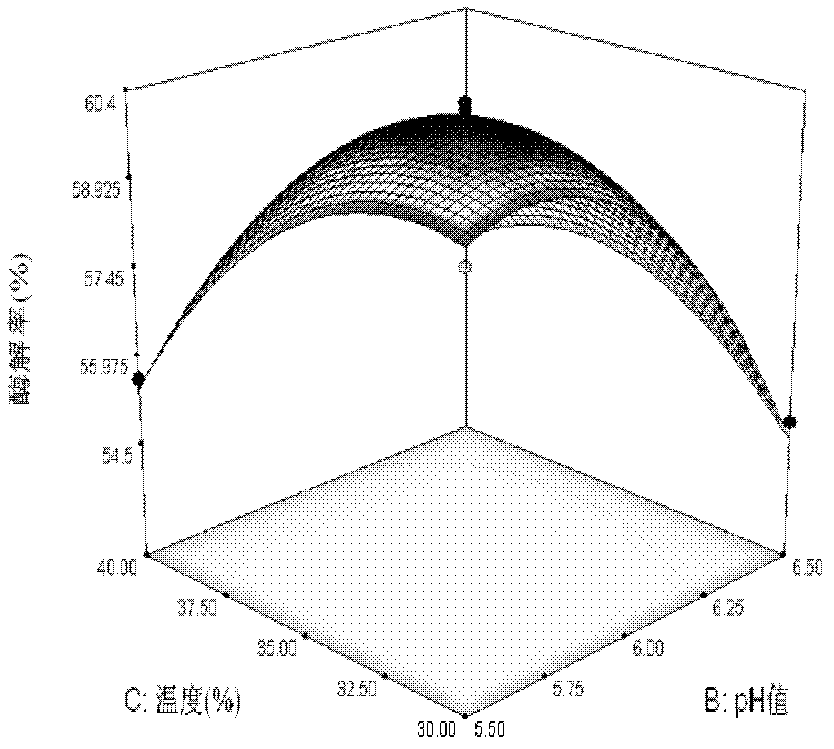
[0034] 2) α-amylase hydrolysis; put 10 g of degreased vetch dry powder in a 500ml beaker, add distilled water according to the ratio of material to liquid 1:20 and stir evenly, soak for 30min; add 2.5g / L citric acid solution ( or 1.0g / L sodium carbonate solution), adjust the pH value to a certain value, add a certain amount of α-amylase, put it into a constant temperature water bath for enzymol...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2 The research of alkaline hydrolysis extraction process
[0067] 1. Response surface method optimization research of alkaline hydrolysis extraction process
[0068] The purpose of using alkaline hydrolysis is to remove the protein and fat in Osmanthus chinensis, and to decompose the protein in Osmanthus vetense into small molecular peptides and free amino acids through short-term and low-concentration lye treatment, and the fat is decomposed into glycerol and Salts of fatty acids, which facilitate their removal by diafiltration. In addition, another purpose is to inactivate the previously added α-amylase.
[0069] On the basis of determining the optimal process conditions of α-amylase enzymolysis by response surface method, the single factor experiment of alkali hydrolysis was carried out, and then the single factor experiment results of alkali hydrolysis were integrated, according to the principle of central combination experiment design of Box-Benhnken, t...
Embodiment 3
[0086]1) Degreasing: use a pulverizer to crush the dried vetch, then add ethyl acetate and soak it at room temperature for 3 hours, then use distilled water to remove the residual organic solvent, filter and dry it with suction, then crush it again, pass through 40 mesh Sieve, and put the obtained degreased sample into a dry dish for later use.
[0087] Step 2) α-amylase enzymatic hydrolysis: Soak the degreased dried vetch in water with a mass 10-25 times the degreased vetch dry mass for 20-60 min, then add α-amylase for enzymatic hydrolysis, and filter Obtain filter residue A after the enzymolysis reaction, the added amount of α-amylase is 0.7%, the enzymolysis pH value is 5.8, the enzymolysis temperature is 35°C, and the enzymolysis time is 1.0h; the enzymolysis rate measured after this step is 60.68%.
[0088] Step 3) Alkali hydrolysis: add 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide solution according to the ratio of material to liquid of 1:10, put it into a constant temperature water bath...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Degree of swelling | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Degree of swelling | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com