Method for detecting content of each group of free polysaccharide in meningococcus polysaccharide conjugate vaccine finished product
A meningococcal-conjugated vaccine technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of influence, large difference in the properties of polysaccharide conjugates, and affect the immune protection effect, etc., and achieve high accuracy and precision, strong durability, and strong specificity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
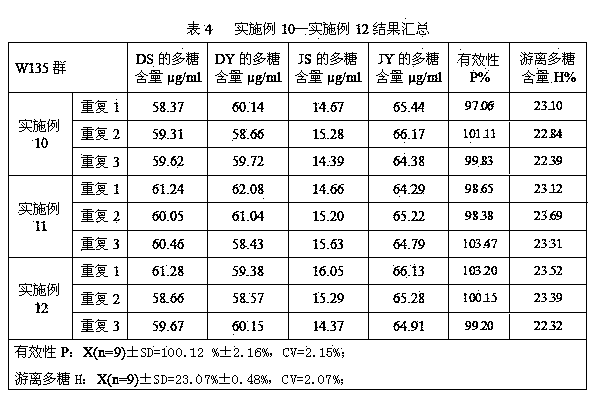
[0045] Example 1 Determination of Group A Free Polysaccharide Content in A, C, Y, W135 Group Meningococcal Polysaccharide Conjugated Vaccine Finished Products
[0046] The determination of the free polysaccharide content of group A in the finished product of group A, C, Y, and W135 meningococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccines was repeated 3 times, respectively repeating 1, repeating 2, and repeating 3, and each repetition was carried out according to the following steps:
[0047] (1) Preparation of test products for inspection
[0048] ①Pretreatment: Take 12 bottles of finished meningococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccines of groups A, C, Y, and W135 to be tested (the labeled amount is 0.5ml per bottle), reconstitute with 6ml of water for injection (that is, use water for injection according to the labeled amount) redissolve), take 5.0ml of the reconstituted solution in an ultrafiltration cup, centrifuge ultrafiltration at 5000×g 4°C for 40min, collect the concentrate, ad...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Determination of Group A Free Polysaccharide Content in A, C, Y, W135 Group Meningococcal Polysaccharide Conjugated Vaccine Finished Products
[0071] Except that the operations of the following steps are different, other operations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0072] (1) Preparation of inspection and test products
[0073] ②Protease K treatment: Take 70 μl of the ultrafiltration concentrated solution, add 4 μl of proteinase K, 42 μl of proteinase K buffer and make up water for injection to 420 μl, mix well and incubate at 37°C for 6 hours to obtain the original solution of the test product JY; add The amount of proteinase K is 4 times of the protein content in the enzymolysis reaction system.
[0074] ③ Cold phenol treatment: take another 0.6ml of ultrafiltration concentrate, add 1.8ml of sodium acetate saturated cold phenol solution, the volume ratio of ultrafiltration concentrate to sodium acetate saturated cold p...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Determination of Group A Free Polysaccharide Content in A, C, Y, W135 Group Meningococcal Polysaccharide Conjugated Vaccine Finished Products
[0082] Except that the operations of the following steps are different, other operations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0083] (1) Preparation of inspection and test products
[0084] ②Protease K treatment: Take 70 μl of the ultrafiltration concentrate, add 8 μl of proteinase K, 42 μl of proteinase K buffer and make up to 420 μl of water for injection, mix well and incubate at 37°C for 8 hours to obtain the original solution of the test product JY; add The amount of proteinase K is 8 times of the protein content in the enzymolysis reaction system;
[0085] ③Cold phenol treatment: Take another 0.6ml of ultrafiltration concentrate, add 1.2ml of sodium acetate saturated cold phenol solution, shake and mix for 30min, place in an ice bath for 20min, centrifuge at 10000rpm, 8°C for 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com