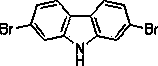
Method for preparing 2,7-dibromocarbazole
A technology of dibromocarbazole and dibromobiphenyl, which is applied in the field of organic chemical synthesis, can solve the problems of difficult operation, long reaction time, and high synthesis temperature, achieve shortened reaction time, easy operation and control, and increase product yield Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0017] Add 40 g (0.128 mol) of 4,4′-dibromobiphenyl, 0.2 g (1.32 mmol) of ferrous sulfate and 80 mL of 1,2-dichloroethane into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and slowly raise the temperature to 1 , 2-dichloroethane began to reflux, and 50 mL (0.25 mol) of 5 mol / L dilute nitric acid was slowly added dropwise to the reaction flask, and the temperature of the system was maintained at 80 °C for 2 h. No raw materials were detected by HPLC. Cool the reaction solution to room temperature, separate the layers, collect the organic phase in the lower layer, extract the aqueous phase once with 10 mL 1,2-dichloroethane, combine the organic phases, and recover 1,2-dichloroethane by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain crude product. Add methanol to the crude product, stir and heat until the solids are completely dissolved. After natural cooling, crystals are precipitated, filtered under reduced pressure, and dried in vacuo to obtain 42.4 g of 2-nitro-4,4'-dibromobiphenyl light yello...
example 2
[0020] Add 40 g (0.128 mol) of 4,4′-dibromobiphenyl, 0.24 g (1.8 mmol) of aluminum trichloride and 80 mL of 1,2-dichloroethane into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and slowly heat up to 1,2-Dichloroethane began to reflux, and 44 mL (0.22 mol) of 5 mol / L dilute nitric acid was slowly added dropwise to the reaction flask, and the temperature of the system was maintained at 82 °C for 2.5 h. No raw materials were detected by HPLC. Cool the reaction solution to room temperature, separate the layers, collect the organic phase in the lower layer, extract the aqueous phase once with 10 mL 1,2-dichloroethane, combine the organic phases, and recover 1,2-dichloroethane by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain crude product. Add methanol to the crude product, stir and heat until the solids are completely dissolved, and crystals precipitate after natural cooling, vacuum filtration under reduced pressure, and vacuum drying to obtain 41.9 g of 2-nitro-4,4'-dibromobiphenyl light yellow p...
example 3
[0023] Add 40 g (0.128 mol) of 4,4′-dibromobiphenyl, 0.32 g (1.97 mmol) of ferric chloride and 80 mL of 1,2-dichloroethane into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and slowly heat up to 1,2-Dichloroethane began to reflux, and 40 mL (0.2 mol) of 5 mol / L dilute nitric acid was slowly added dropwise to the reaction flask, and the temperature of the system was maintained at 84 °C for 3 h. No raw materials were detected by HPLC. Cool the reaction solution to room temperature, separate the layers, collect the organic phase in the lower layer, extract the aqueous phase once with 10 mL 1,2-dichloroethane, combine the organic phases, and recover 1,2-dichloroethane by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain crude product. Add methanol to the crude product, stir and heat until the solids are completely dissolved, and crystals precipitate after natural cooling, vacuum filtration under reduced pressure, and vacuum drying to obtain 42.7 g of 2-nitro-4,4'-dibromobiphenyl light yellow powder, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com