Method for treating lean ferrous manganese ore by directly reducing electric furnace melting components through rotary hearth furnace
A rotary hearth furnace and manganese iron ore technology, which is applied in the treatment field of lean manganese iron ore, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, large amount of flue gas, viscous slag, etc., and achieves simple process, low energy consumption and high recovery rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
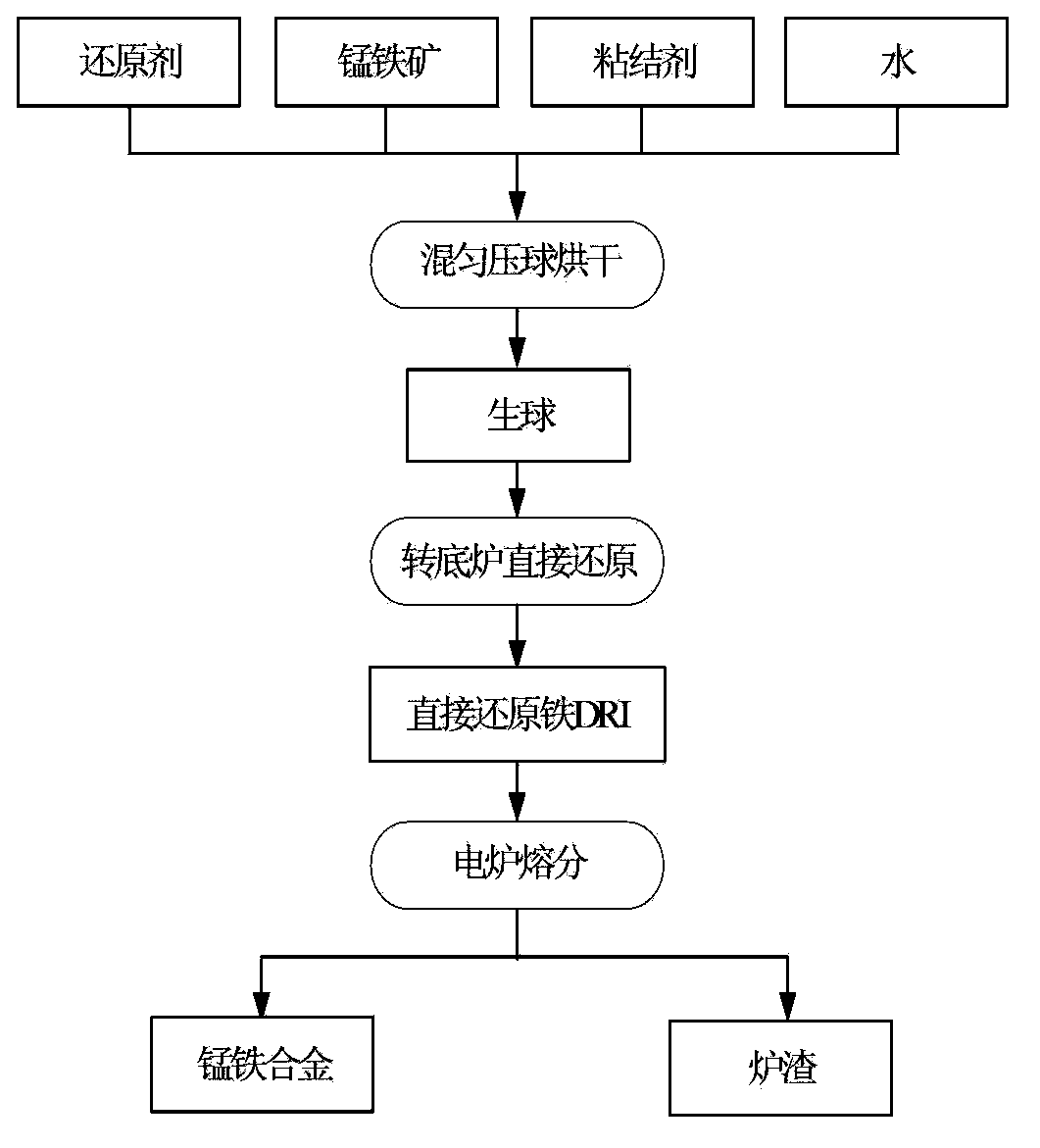
[0048] Manganite composition: TFe 11.1%, Mn 24.2%. The manganese ore and anthracite are crushed to less than 4mm, the fixed carbon in the reducing agent is 78.15%, the ash content is 8.21%, the volatile matter is 12.23%, and the total sulfur is 0.15%. The material ratio is: ferromanganese ore: pulverized coal: binder = 100:13:4. Control the moisture content of the mixture between 6% and 8% to prevent dust or roll sticking caused by material mixing and over-drying or over-wetting of the mixture in the roller pressing ball. After the pressed pellets are dried (moisture content <2%), they enter the bottom of the rotary hearth furnace through a distribution machine, with a double-layer distribution and a thickness of about 24mm. The reduction temperature in the furnace is 1100-1300°C, of which the temperature in the preheating zone is 1100-1200°C, the temperature in the middle temperature zone is 1200-1300°C, the temperature in the high temperature zone is controlled at about 1...
specific Embodiment 2
[0049] Manganite composition: TFe 12.47%, Mn 26.25%. The ferromanganese ore and anthracite are crushed to less than 4mm. The fixed carbon in the anthracite is 78.15%, the ash content is 8.21%, the volatile matter is 12.23%, and the total sulfur is 0.15%. The material ratio is: ferromanganese ore: pulverized coal: binder = 100:18:4. Control the moisture content of the mixture between 6% and 8% to prevent dust or roll sticking caused by material mixing and over-drying or over-wetting of the mixture in the roller pressing ball. After the pressed pellets are dried (moisture content <2%), they enter the bottom of the rotary hearth furnace through a distribution machine, with a double-layer distribution and a thickness of about 24mm. The reduction temperature in the furnace is 1100-1320°C, of which the temperature in the preheating zone is 1100-1200°C, the temperature in the middle temperature zone is 1200-1300°C, the temperature in the high temperature zone is controlled at abou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com