Evaporation and dehydration method for N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide solvent in cellulosic fiber production through solvent method
A technology of cellulose fiber and methylmorpholine, which is applied in the fields of fiber chemical characteristics, final product manufacturing, textile/flexible product manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of no energy-saving measures, large energy consumption, and large energy consumption, so as to reduce energy consumption Consumption, less decomposition products, and the effect of increasing the evaporation temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
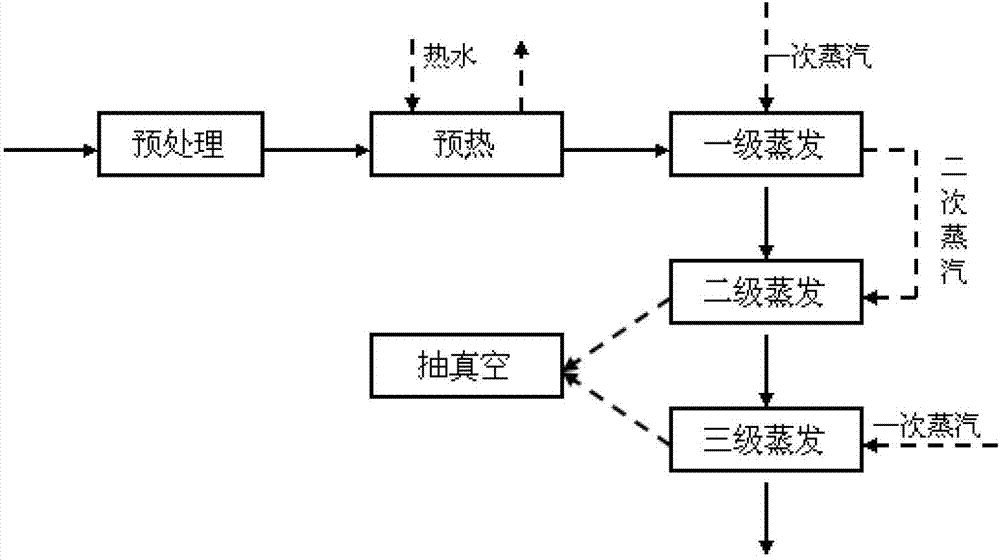
[0034] Get the Lyocell fiber spinning coagulation bath solution that contains NMMO mass percent as 10%, after purification, add 20% phosphoric acid to adjust the pH value to 7, add 100ppm propyl gallate, enter the preheater after fully mixing, make The solvent and the by-product hot water are fully exchanged and preheated to 70°C. Then enter the three-stage two-effect evaporation system, the process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the evaporator is a natural circulation evaporator. The first stage is heated by primary steam, the primary steam temperature is 120°C, the primary heating chamber temperature is 115°C, the primary material temperature is 107°C, the primary operating pressure is 120kpa, the primary secondary steam temperature is 103°C, and the primary discharge concentration 26%. The second stage is heated by the secondary steam generated by the first stage, the temperature of the secondary heating chamber is 101°C, the temperature of the secondary material is 65°...
Embodiment 2
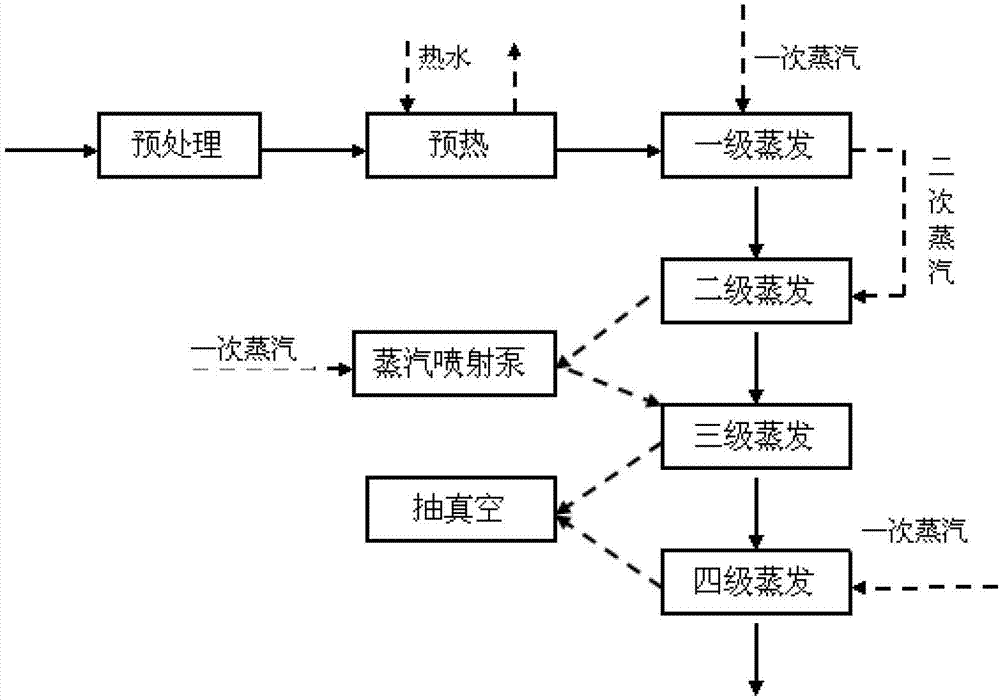
[0038] Take the Lyocell fiber spinning coagulation bath solution containing 15% NMMO mass percentage, add 20% phosphoric acid after purification to adjust the pH value to 8, add 200ppm hydrogen peroxide, and enter the preheater after fully mixing to make the solvent and side The hot water produced is fully heat exchanged and preheated to 66°C. Then enter the four-stage three-effect evaporation system, the process is as follows figure 2As shown, the evaporator is a forced circulation evaporator. The first stage is heated by primary steam, the primary steam temperature is 117°C, the primary heating chamber temperature is 115°C, the primary material temperature is 108°C, the primary operating pressure is 130kpa, the primary secondary steam temperature is 105°C, and the primary discharge concentration twenty three%. The second stage is heated by the secondary steam generated by the first stage, the temperature of the secondary heating chamber is 101°C, the temperature of the se...
Embodiment 3
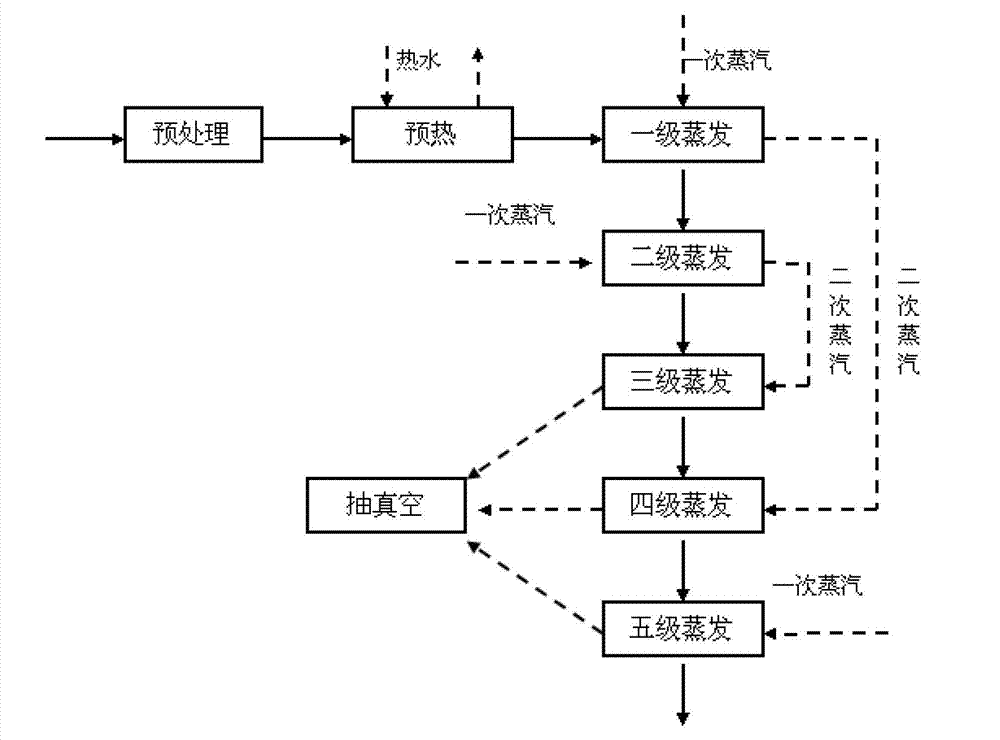
[0041] Get the Lyocell fiber spinning coagulation bath solution that contains NMMO mass percent as 20%, after purification, add 20% phosphoric acid to adjust the pH value to 6.5, add 200ppm oxalic acid, enter the preheater after fully mixing, make the solvent and side The hot water produced is fully heat exchanged and preheated to 70°C. Then enter the five-stage two-effect evaporation system, the process is as follows image 3 As shown, the first and second evaporators use rising film evaporators, and the third, fourth and fifth use falling film evaporators. The first stage is heated by primary steam, the primary steam temperature is 118°C, the primary heating chamber temperature is 115°C, the primary material temperature is 108°C, the primary operating pressure is 130kpa, the primary secondary steam temperature is 105°C, and the primary discharge concentration twenty three%. The second stage is heated by primary steam, the temperature of the secondary heating chamber is 115...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com