Method for fixing chlorobenzene volatile organic pollutants by straw biomass charcoal
A volatile organic, biomass carbon technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
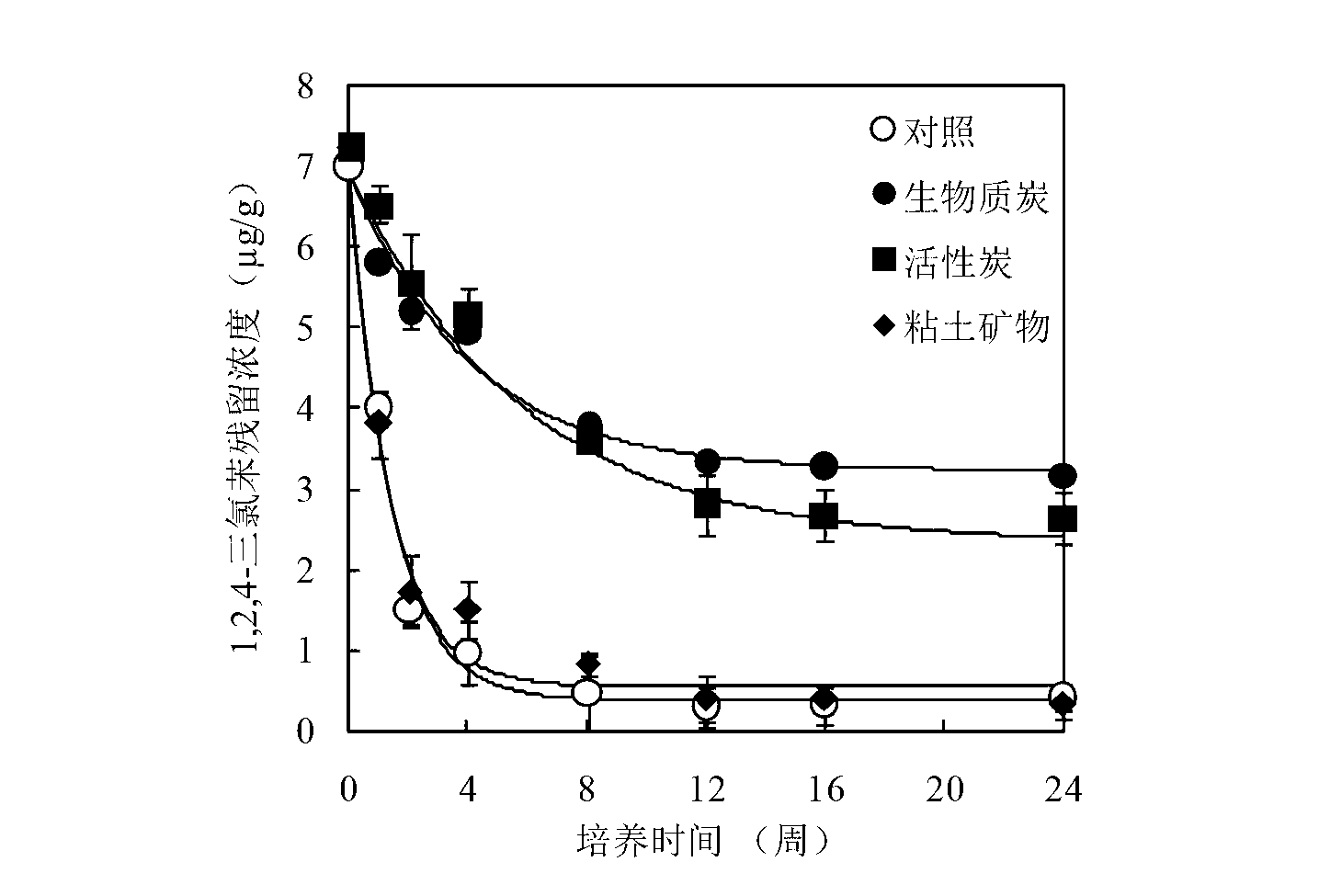
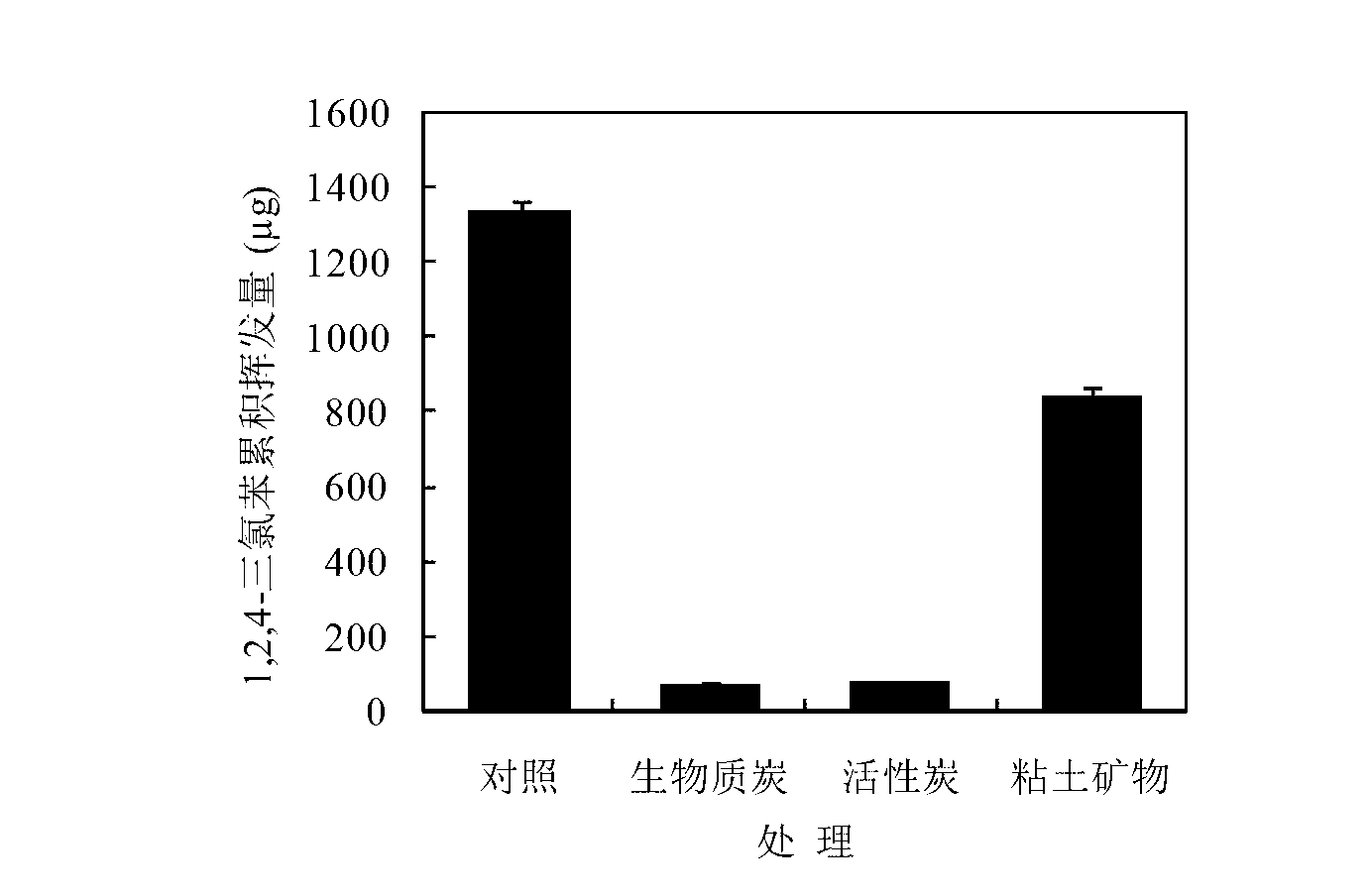
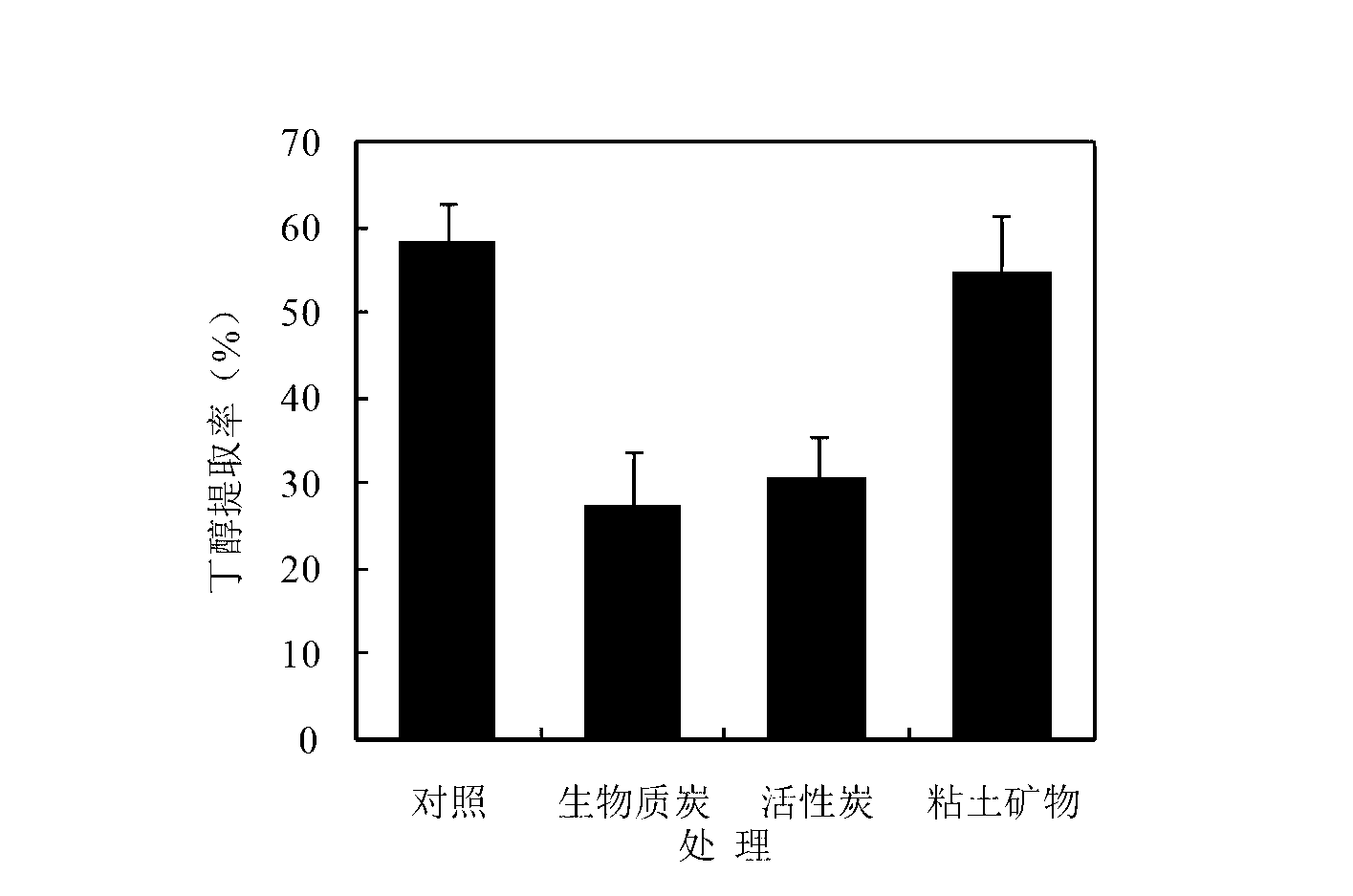
[0032] Biochar, activated carbon, and clay minerals were added to 300 g of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene in an amount of 1% of the dry weight of the soil. The concentration was 7 μg g ?1 In the contaminated soil, stir and mix well, then transfer to a 1-L jar, adjust the soil moisture content to 28%, and compact the soil to a density of 1.3 g cm ?3 , sealed with a rubber stopper with an air inlet and an air outlet, and incubated at 25°C in the dark. The treatment without adding any material was used as the control. At the 1st, 2nd, 4th, 8th, 12th, and 24th weeks of culture, airtight trapping devices were used to ventilate. After the aeration was over, the soil was collected, and the total amount of chlorobenzene was extracted and analyzed by n-hexane-accelerated solvent extraction, and extracted by butanol. Bioavailability of chlorobenzenes in soil.
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, there was no significant difference in the residual dynamics of trichlorobenzene in the addition ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Biochar was added to 300 g of PeCB at an addition rate of 0.1% of the dry weight of the soil at a concentration of 1 μg g ?1 In the contaminated soil, stir and mix well, then transfer to a 1-L jar, adjust the soil moisture content to 28%, and compact the soil to a density of 1.3 g cm ?3 , sealed with a rubber stopper with an air inlet and an air outlet, and incubated at 25°C in the dark. 0.5%wt, 1%wt and 2%wt of biochar were added in the same treatment as above, and the treatment without adding biochar was used as the control (0%wt). At the 1st, 2nd, 4th, 8th, 12th, and 24th weeks of culture, airtight trapping devices were used to ventilate. After the aeration was over, the soil was collected, and the total amount of chlorobenzene was extracted and analyzed by n-hexane-accelerated solvent extraction, and extracted by butanol. Bioavailability of chlorobenzenes in soil.
[0037] Such as Figure 4 It was shown that after the addition of biochar, the residual concentrati...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Biochar was added to 300 g of 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene at an addition rate of 0.1% of the dry weight of the soil at a concentration of 0.9 μg g ?1 In the contaminated soil, stir and mix well, then transfer to a 1-L jar, adjust the soil moisture content to 28%, and compact the soil to a density of 1.3 g cm ?3 , sealed with a rubber stopper with an air inlet and an air outlet, and incubated at 25°C in the dark. 0.5%wt, 1%wt and 2%wt of biochar were added in the same treatment as above, and the treatment without adding biochar was used as the control (0%wt). At the 1st, 2nd, 4th, 8th, 12th, and 24th weeks of culture, airtight trapping devices were used to ventilate. After the aeration was over, the soil was collected, and the total amount of chlorobenzene was extracted and analyzed by n-hexane-accelerated solvent extraction, and extracted by butanol. Bioavailability of chlorobenzenes in soil.
[0041] Such as Figure 7 It was shown that after the addition of biochar, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com