Method through planting, harvest and landfill of fast-growing herbaceous plants to achieve carbon sequestration
A herbaceous plant and plant technology, which is applied in botany equipment and methods, landfill technology, solid waste removal, etc., can solve the problems of no carbon sequestration method, no multiple harvesting, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve enhanced Soil carbon sequestration capacity, increasing soil aggregates, and improving soil structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
[0115] Embodiment A-municipal refuse treatment obtains organic fertilizer
[0116] 1. Sorting out combustibles such as large pieces of wood, cardboard, decorative materials, foam, and construction waste such as cement, bricks, marble, ceramic tiles, and gypsum boards.
[0117] 2. Break open the plastic bag containing domestic garbage to disperse all the items in the bag.
[0118] 3. Use magnetic separation to separate ferrous metals.
[0119] 4. Use the garbage wind sorting system (see CN102601049A) to screen the treated municipal solid waste, screen out the inorganic matter, and crush the remaining organic matter into large particles.
[0120] 5. The crushed organic matter is mixed with human and animal manure, phosphorus fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, etc., and the carbon-nitrogen ratio is 20-30:1;
[0121] 6. Dilute the compound beneficial bacteria powder with water by 50 to 100 times, and cultivate it at room temperature for 8 to 12 hours. After obtaining the b...
Embodiment B
[0125] Embodiment B-Urban Domestic Sewage Treatment, Obtain Treated Sewage Rich in Nutrients
[0126] Urban domestic sewage mainly includes kitchen washing water, toilet flushing wastewater and other domestic miscellaneous water. This type of wastewater contains a large amount of suspended solids, chemically or biologically degradable dissolved or colloidally dispersed organic matter, nitrogen-containing compounds (including ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen and organic nitrogen), phosphate, potassium sodium and heavy metals Ions, fungal biota, etc. If it is discharged into natural water bodies without treatment or with insufficient treatment, it will lead to eutrophication and accumulation of toxicity in the water body. worsen and pollute the environment.
[0127] 1. Sludge and sewage enter the aeration tank at the same time and are fully mixed. The microorganisms in the aeration tank absorb and decompose the organic matter in the sewage to purify the s...
Embodiment 1
[0132] Example 1 - Valley-type landfill or flat-type landfill
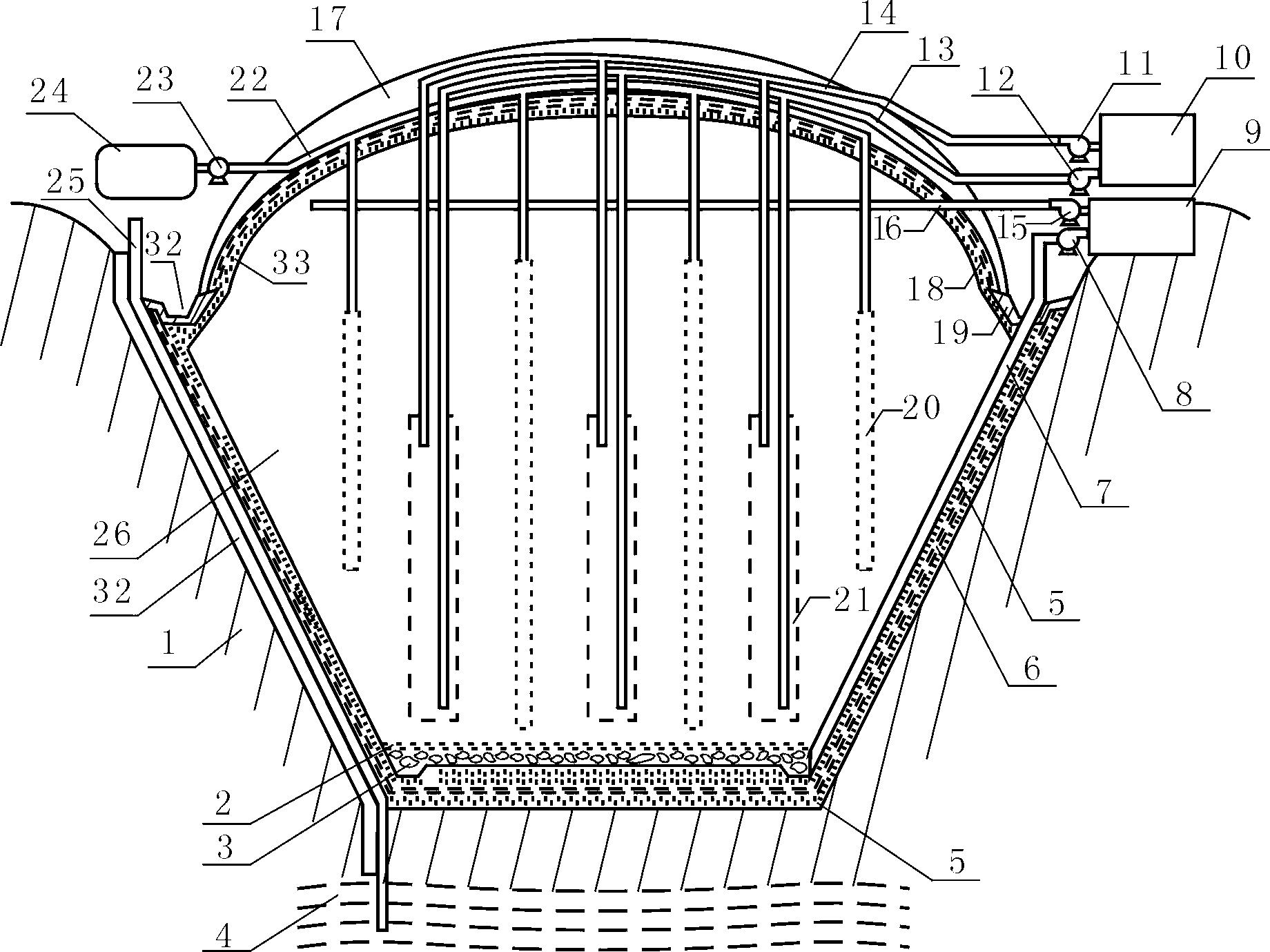
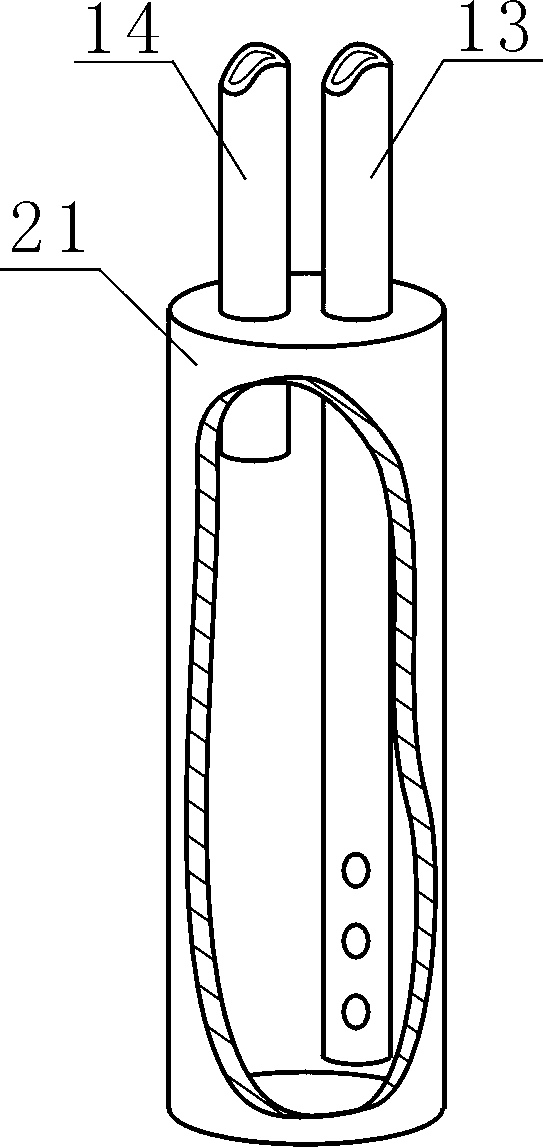
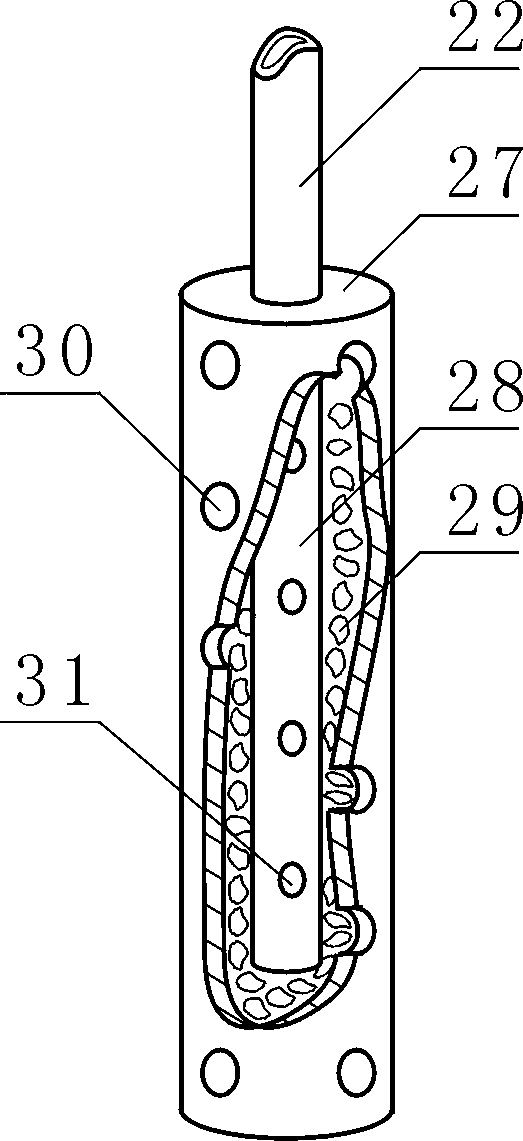
[0133] For a typical landfill see Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the valley type biomass landfill includes a landfill space unit 26, the bottom of the landfill space unit (the bottom of the valley or the bottom of the pit) and the slope 1 are provided with a compacted clay layer 5, the said An anti-seepage liner 6 is provided in the compacted clay layer 5 at the bottom of the pit and the side slope, and a gravel layer 3 is provided on the compacted clay layer 5 at the bottom of the pit, and a soil layer 2 is provided on the gravel layer 3; The landfill space unit 26 fills the valley, the surface layer of the landfill space unit 26 is provided with a B compacted clay layer 33, the B clay layer 33 is provided with a waterproof layer 18, and the waterproof layer 18 is provided with a covering soil layer 17; the edge of the covering soil layer 17 is provided with a lateral drain 19; the landfill space unit 26 is provided ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com