Austempered ductile iron and quenching technology thereof
A technology of austempering nodular iron and austempering, which is applied in the field of heat treatment of metal materials, can solve the problems of easily damaged finished products, high price, long time for nitrate melting and austempering, etc., and achieves the improvement of strength and impact resistance value and processing performance The effect of good and eliminating bad effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] C 3.3 ~ 3.8%
[0083] P 0.01~0.05%
[0084] S 0.005~0.02%
[0085] Mg 0.025 ~ 0.045%
[0086] Re 0.015 ~ 0.03%
[0087] Mn 1.0 ~ 2.5%
[0088] Si 2.3 ~ 3.2%
[0089] Cu 0.3 ~ 1.0%
[0090] B 0.01 ~ 0.08%
[0091] Nb 0.05 ~ 0.2%
[0092] Cr0.1~0.3%
[0093] The rest is Fe.
[0094] Specifically, the matrix structure of the austempered ductile iron is: fine acicular ferrite with a volume percentage of 70-85%, tempered martensite with a volume percentage of 2-20%, and a volume percentage of 5-20%. 28% carbon-rich austenite.
[0095] The austempering ductile iron in this embodiment reduces the cost of austempering ductile iron by replacing the expensive molybdenum (Mo) and nickel (Ni) used in traditional ductile iron with cheap manganese (Mn) and silicon (Si) , to promote the development of the austempering ductile iron industry. At the same time, due to the addition of trace amounts of copper (Cu), boron (B), chromium (Cr), and niobium (Nb) to achieve multi-ele...
Embodiment 2
[0113] C 3.5 ~ 3.7%
[0114] P 0.01~0.03%
[0115] S 0.005~0.01%
[0116] Mg 0.03 ~ 0.04%
[0117] Re 0.015 ~ 0.025%
[0118] Mn 1.0 ~ 2.0%
[0119] Si 2.8 ~ 3.2%
[0120] Cu 0.3 ~ 0.6%
[0121] B 0.01 ~ 0.04%
[0122] Nb 0
[0123] Cr 0.1~0.15%
[0124] The rest is Fe.
[0125] Above, the matrix structure of austempered ductile iron is: fine acicular ferrite with a volume percentage content of 70%, tempered martensite with a volume percentage content of 2%, and carbon-rich austenite with a volume percentage content of 28%. body.
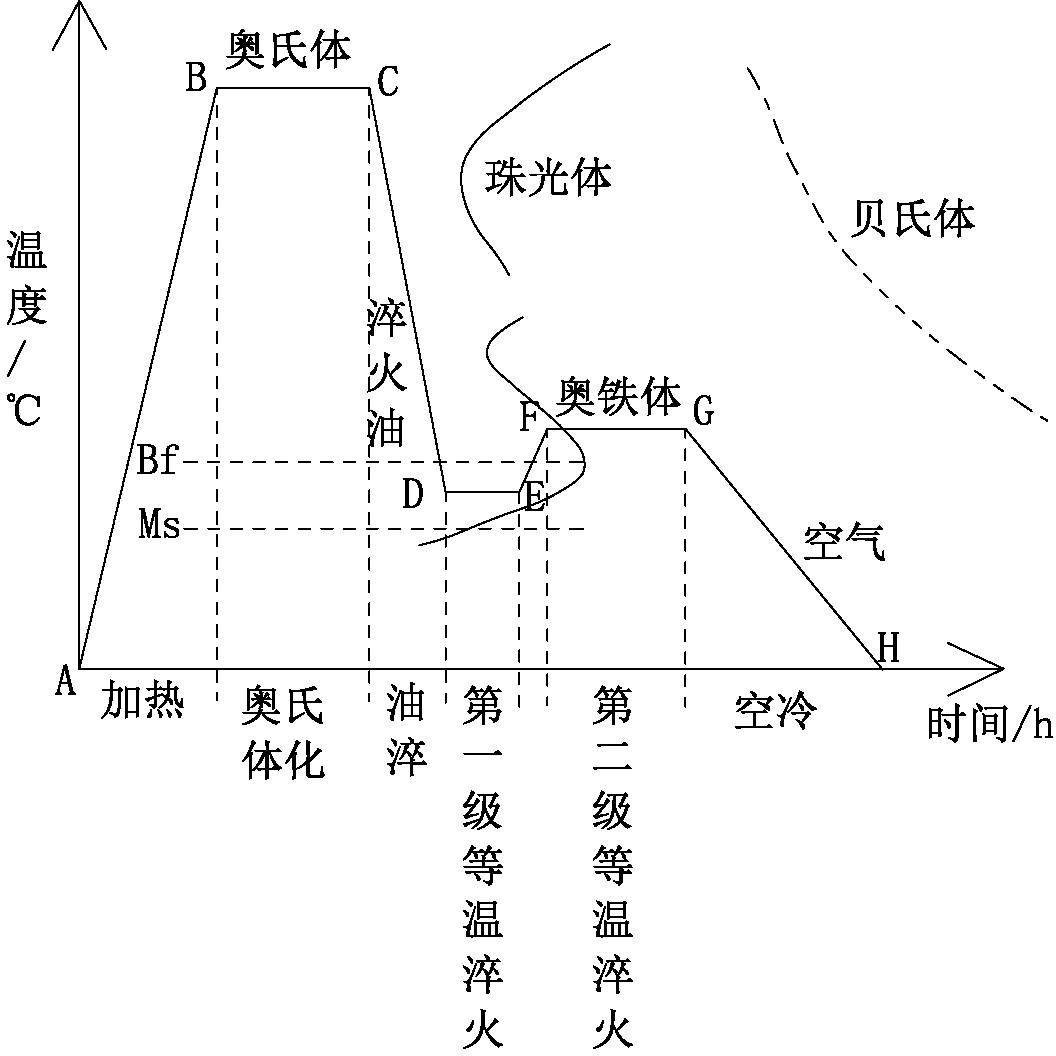
[0126] Simultaneously, a kind of austempering ductile iron quenching process of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0127] (1) Heating the workpiece to the austenitizing temperature of 860~940°C, heat preservation treatment for 1.0~3.5h to saturate the austenite with carbon, and obtain carbon-rich austenite, the carbon content of which is 1.2~ 1.8%;
[0128](2) Put the workpiece treated in step (1) into graded quenchi...
Embodiment 3
[0138] C 3.3%
[0139] P 0.04%
[0140] S 0.015%
[0141] Mg 0.035%
[0142] Re 0.02%
[0143] Mn 1.5%
[0144] Si 3.0%
[0145] Cu 0.8%
[0146] B 0.02%
[0147] Nb 0.1%
[0148] Cr 0.15%
[0149] The rest is Fe.
[0150] Above, the matrix structure of austempered ductile iron is: fine acicular ferrite with 85% by volume, tempered martensite with 10% by volume, and carbon-rich austenite with 5% by volume body.
[0151] At the same time, a quenching process for austenitic ductile iron of the present invention includes the following steps: (1) Heating the workpiece to the austenitizing temperature of 890°C, and performing heat preservation treatment for 1.5 hours to saturate the austenite with carbon to obtain carbon-rich austenite Tenite, the carbon content of the carbon-rich austenite is 1.2%;
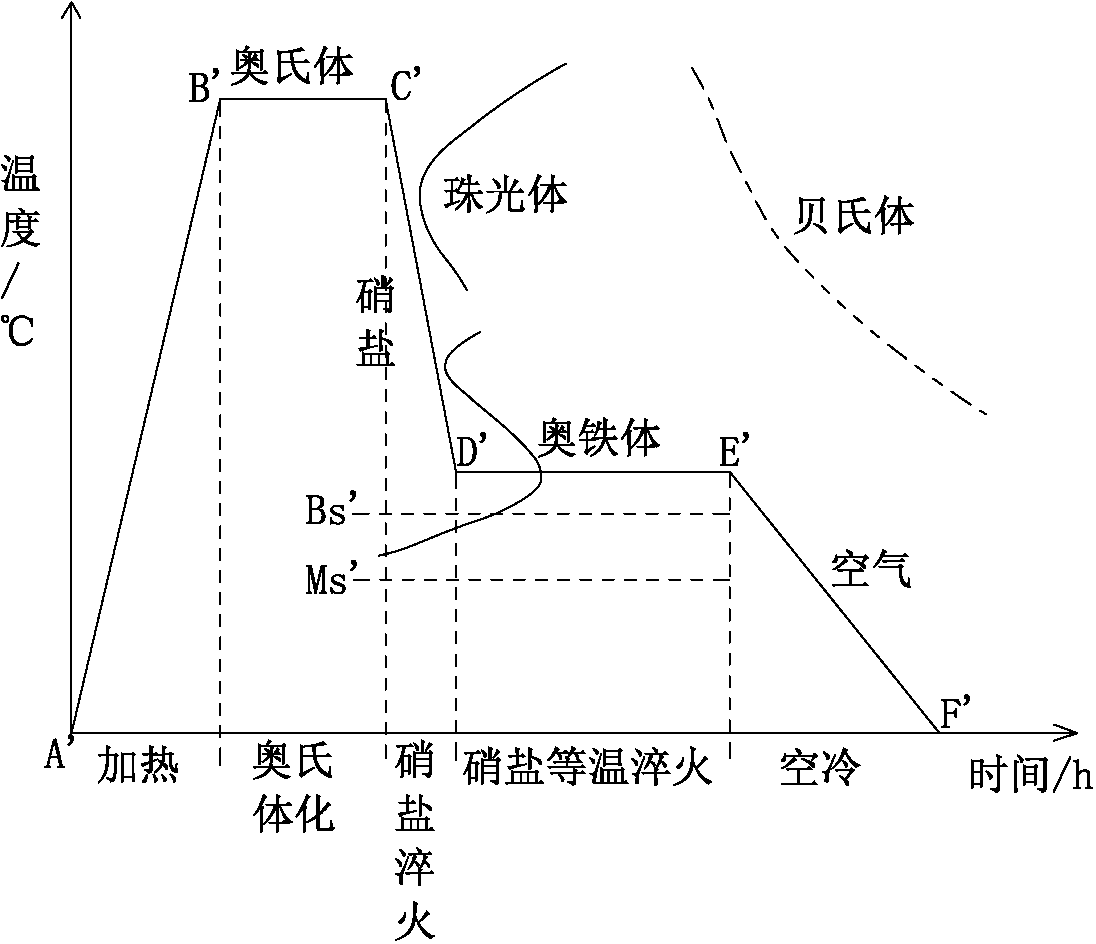
[0152] (2) Put the workpiece treated in step (1) into graded quenching oil, and cool the workpiece to above 180°C in 1 for first-stage austempering 1; wherein, the cooling...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flash point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ignition point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com