Treatment of type II diabetes and diabets-associated diseases with safe chemical mitochondrial uncouplers
A technology for mitochondrial uncoupling and metabolic diseases, applied in the fields of urinary system diseases, metabolic diseases, sensory diseases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0164] The preparation of prodrugs is well known in the art and is described, for example, in Medicinal Chemistry: Principles and Practice, edited by F.D. King, Royal Society of Chemistry (Cambridge, UK) , 1994 noon; Hydrolysis in Drug and Prodrug Metabolism (Hydrolysis in Drug and Prodrug Metabolism), Chemistry, Biochemistry and Enzymology, author: B.Testa, J.M.Mayer, VCHA and Wiley-VCH Press, Zurich, Switzerland, 2003; Practical Medicinal Chemistry (The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry), C. Edited by G Wermuth, Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1999.
[0165] The compounds of the present invention can be prepared by exemplary methods used by those skilled in the art as described in the relevant publications.
Embodiment 1
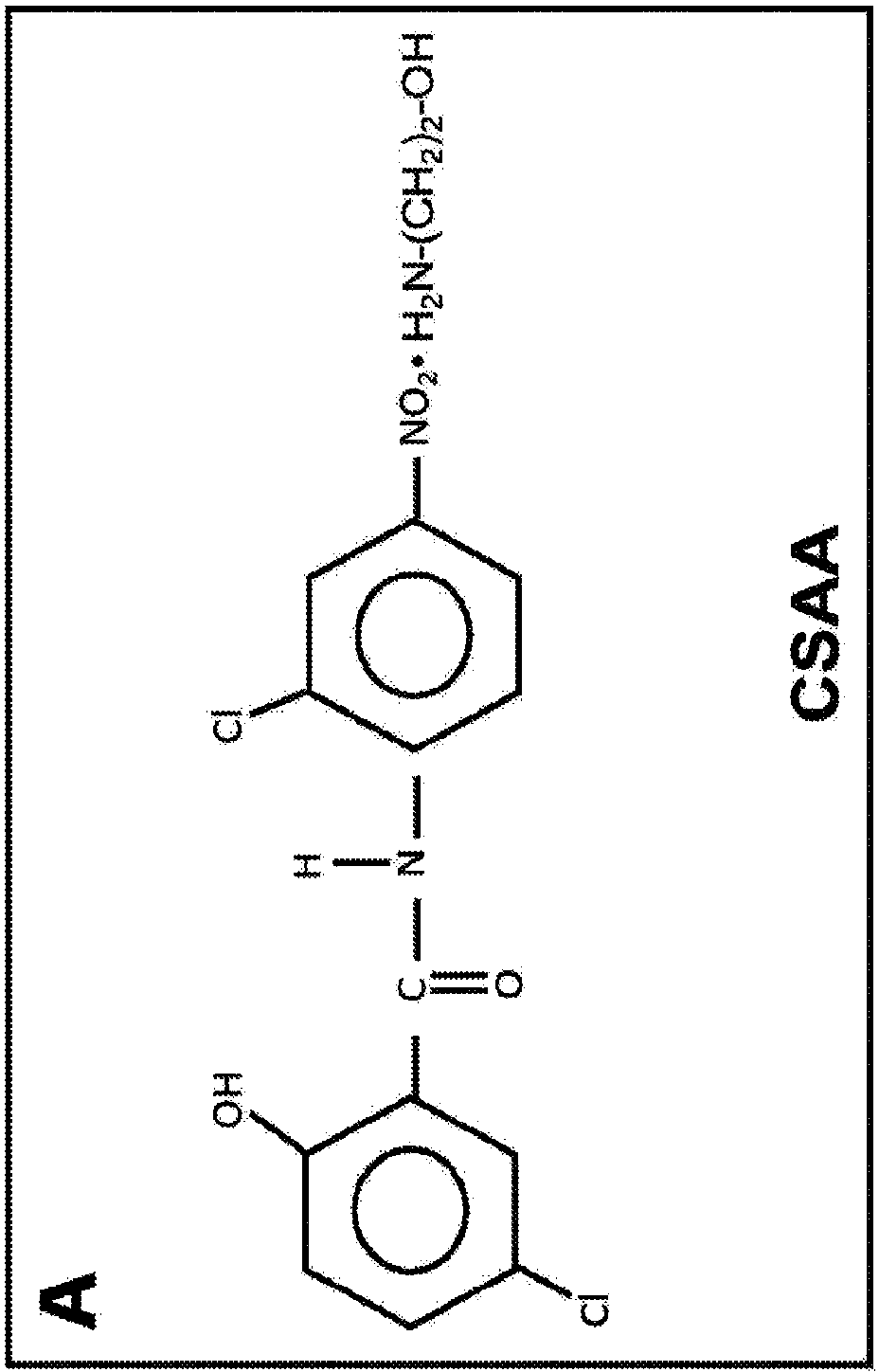
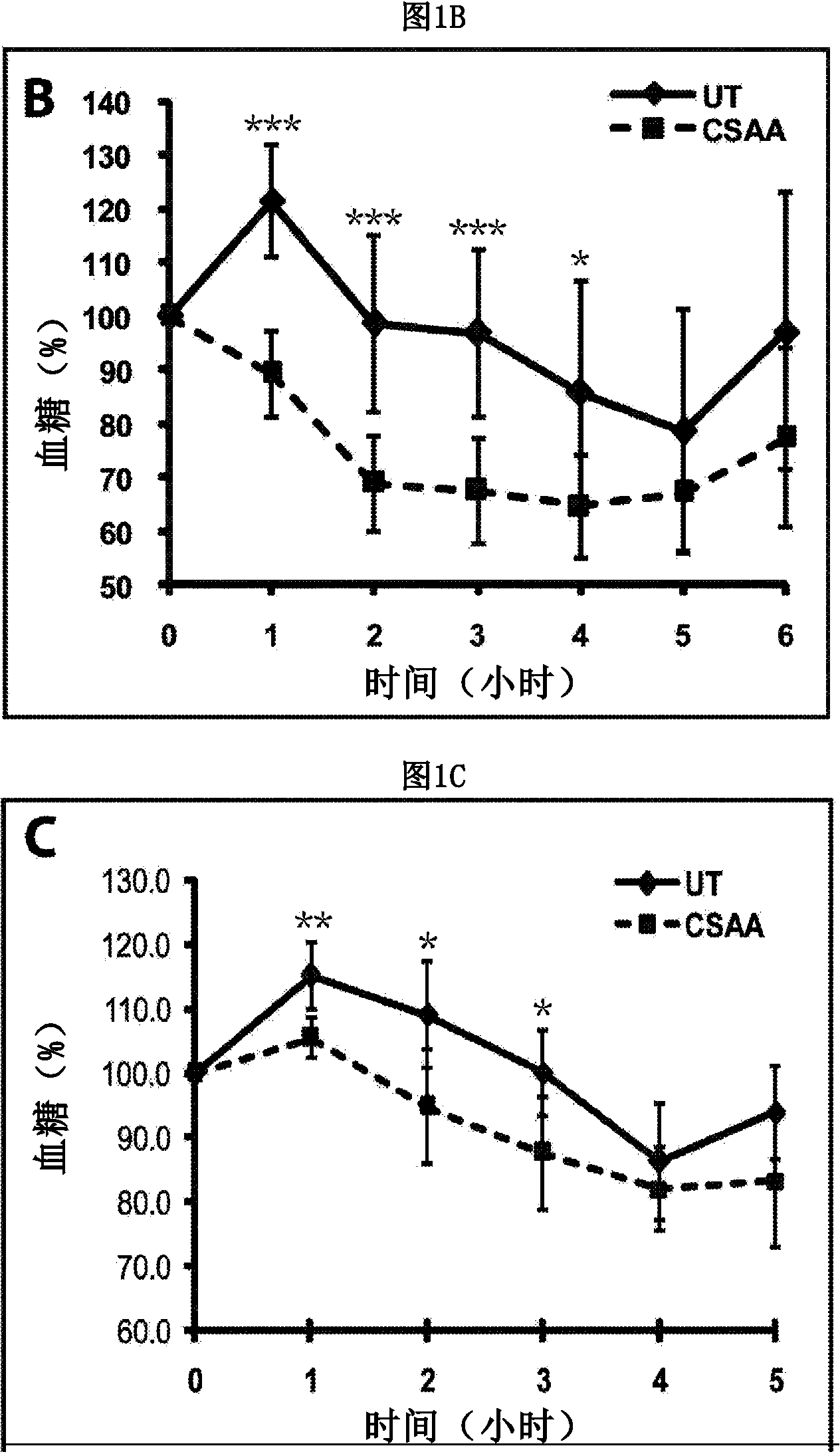
[0185] Acute treatment with 5-chloro-salicyl-(2-chloro-4-nitro)aniline 2-aminoethanol salt (CSAA) effectively reduces blood glucose in diabetic and pre-diabetic mice. The structure of CSAA is shown in Figure 1A middle. To assess the effect of CSAA on glycemic control, we injected saline solution containing CSAA into diabetic db / db mice or pre-diabetic C57 / B16 mice fed a high-fat diet for 10 weeks. As shown in Figure 1, with CSAA treatment, blood glucose concentrations started to decrease about 1 hour after treatment and remained effective for about 4 hours. Significant decreases in blood glucose concentrations were observed in both mouse strains. This was particularly pronounced in db / db mice, which showed a 30% reduction in blood sugar relative to controls. These results indicate that CSAA has an acute effect of lowering blood glucose concentrations in diabetic and pre-diabetic mouse models.
Embodiment 2
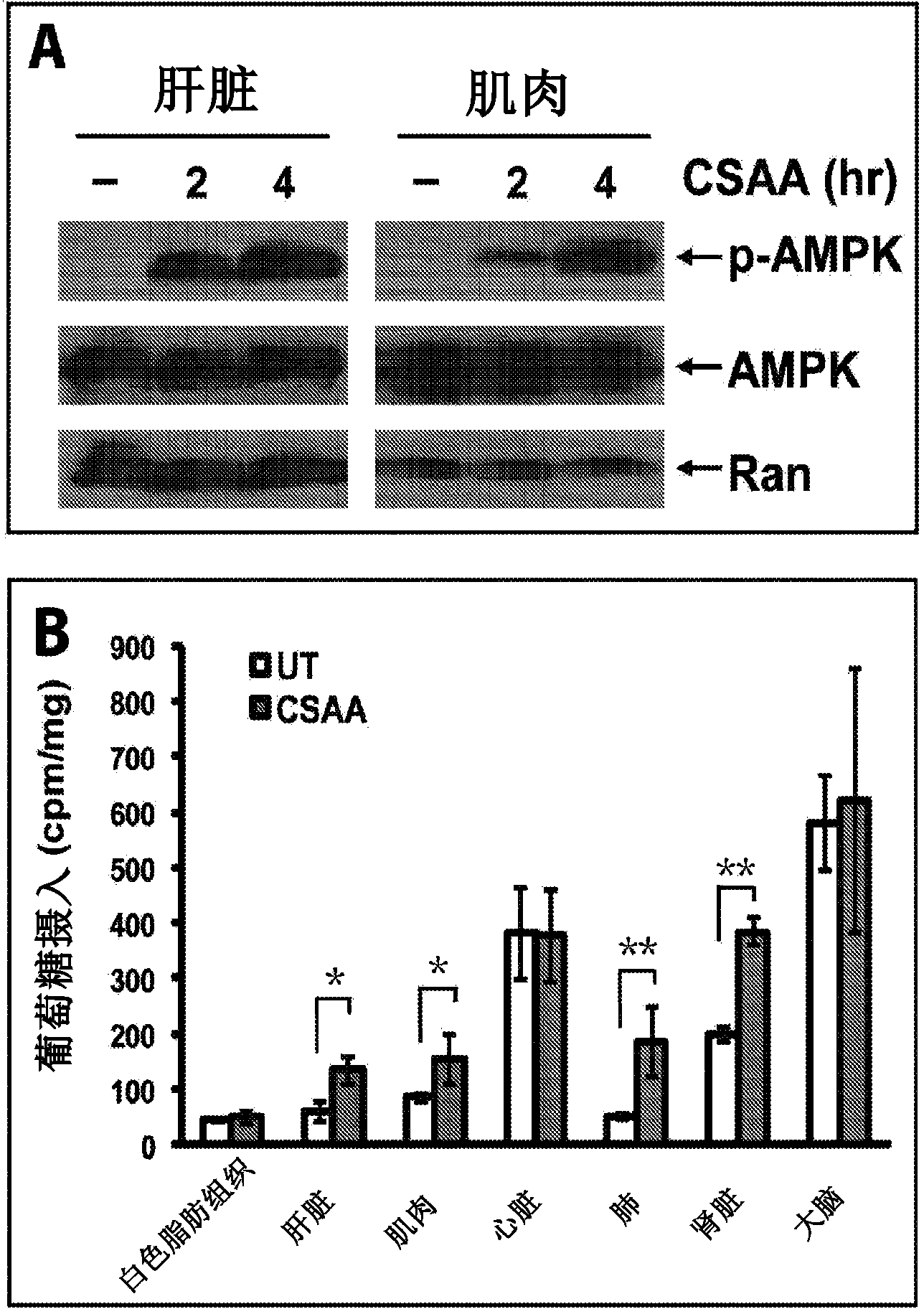
[0187] The acute effect of CSAA on lowering blood glucose concentrations is associated with activation of AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and increased glucose uptake in tissues. Mitochondrial uncoupling reduces the efficiency of ATP production, which in turn induces a compensatory upregulation of glucose uptake. To test this theory, we measured the level of phosphorylated AMPK, which reflects AMPK activity in the liver of mice injected with CSAA. In response to an increase in AMP (adenosine monophosphate), ATP decreases and as a result AMPK is activated. Such as figure 2 As shown in A, indeed, acute treatment with CSAA significantly increased the levels of phosphorylated AMPK. Furthermore, we directly measured the rate of glucose uptake in different tissues of mice acutely treated with CSAA. Such as figure 2 As shown in B, glucose uptake rates were significantly elevated in liver, muscle, kidney, and lung, but not in brain or white adipose tissue (WAT). At the same time, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com