Indirect Dot-ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method and application of blood group antibody
A detection method, blood type antibody technology, applied in the field of blood type identification, can solve the problems of lack of standardization, standardization, difficulty in guaranteeing reagent quality, short storage period, etc., and achieve the effect of easy automatic operation, saving manpower, and reducing human errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
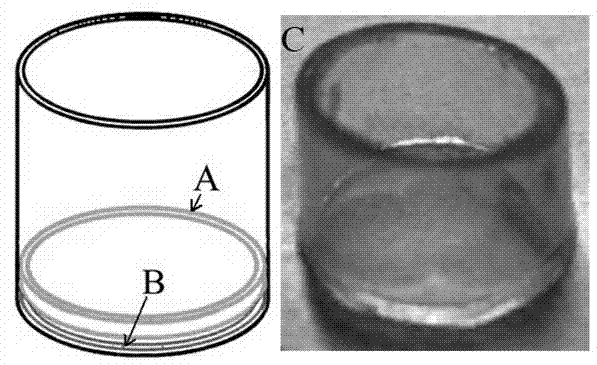
[0029] S1. Preparation of Dot-ELISA 96-well plate: Soak the nitrocellulose membrane with distilled water, then dry it slightly, and use a puncher to make a circular membrane of appropriate size. Put the dried nitrocellulose membrane into a 96-well plate, and press the nitrocellulose membrane on the bottom of the 96-well plate with a fixing ring (Fig. 1). Then put the 96-well plate into a drying oven to dry for 2 h, and store it dry for future use.
[0030] The structure of the retaining ring is as figure 1 As shown in C; the fixed ring is made of plastic material, and the fixed ring is a cylindrical ring with a height of 2-4 mm and a thickness of 0.04-0.08 mm. The outer diameter of the ring matches the inner diameter of the 96-well plate used. The outer diameters of both ends of the fixed ring are divided into small and large ends. It is not easy to slip off, and the outer diameter of the small end is slightly smaller than the inner diameter of the 96-well plate, so that it ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Determination of the amount of antigen: Dilute the cell membrane of the corresponding blood type with 0.01 mol / L PBS solution (pH7.4), dilute the antigen by 2 times, spot 2 μL on the membrane of each Dot-ELISA plate hole, and judge the coating concentration according to the result. The specific steps of the indirect Dot-ELISA detection method for blood group antibodies are the same as in Example 1.
[0038] The criterion for judging is: the greater the concentration of the antigen, the more prone to non-specific binding. Negative antibody serum shows colorless or no spots, and positive antibody serum shows the darkest concentration is the best antigen coating concentration.
[0039] The results of this experiment show that the antigen coating concentration of 1-2 μg (2 μL, 500-1000 μg / ml) can achieve high sensitivity without non-specific binding.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Specificity experiment:
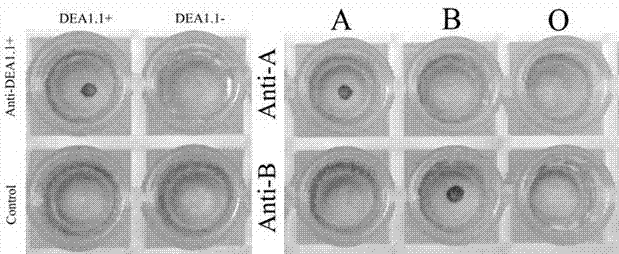
[0042] Different concentrations of canine DEA1.1 positive antigen and ABO antigen were used to react with negative and positive antibody antiserum respectively. Different concentrations of DEA1.1 negative antigen reacted with canine negative and positive antibody antiserum respectively. Observe the specificity of the indirect Dot-ELISA method. The specific steps of the indirect Dot-ELISA detection method are the same as in Example 1.
[0043] The result shows as figure 2 , the erythrocyte membrane with the corresponding antigen reacts with the positive antibody antiserum, the result shows dark brown spots, the result is +++, and the others have no spots, indicating that the indirect Dot-ELISA detection method has high specificity.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com