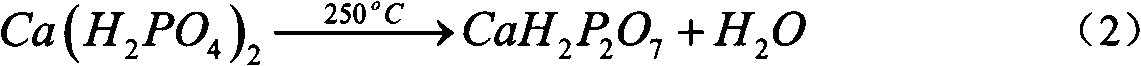Preparation method of calcium metaphosphate porous bioceramic
A technology of calcium metaphosphate and bioceramics, which is applied in the field of preparation of calcium metaphosphate porous bioceramics, and can solve the problem that the porous ceramics method has not been reported.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Step 1: Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 Preparation of O(MCPM) precursor
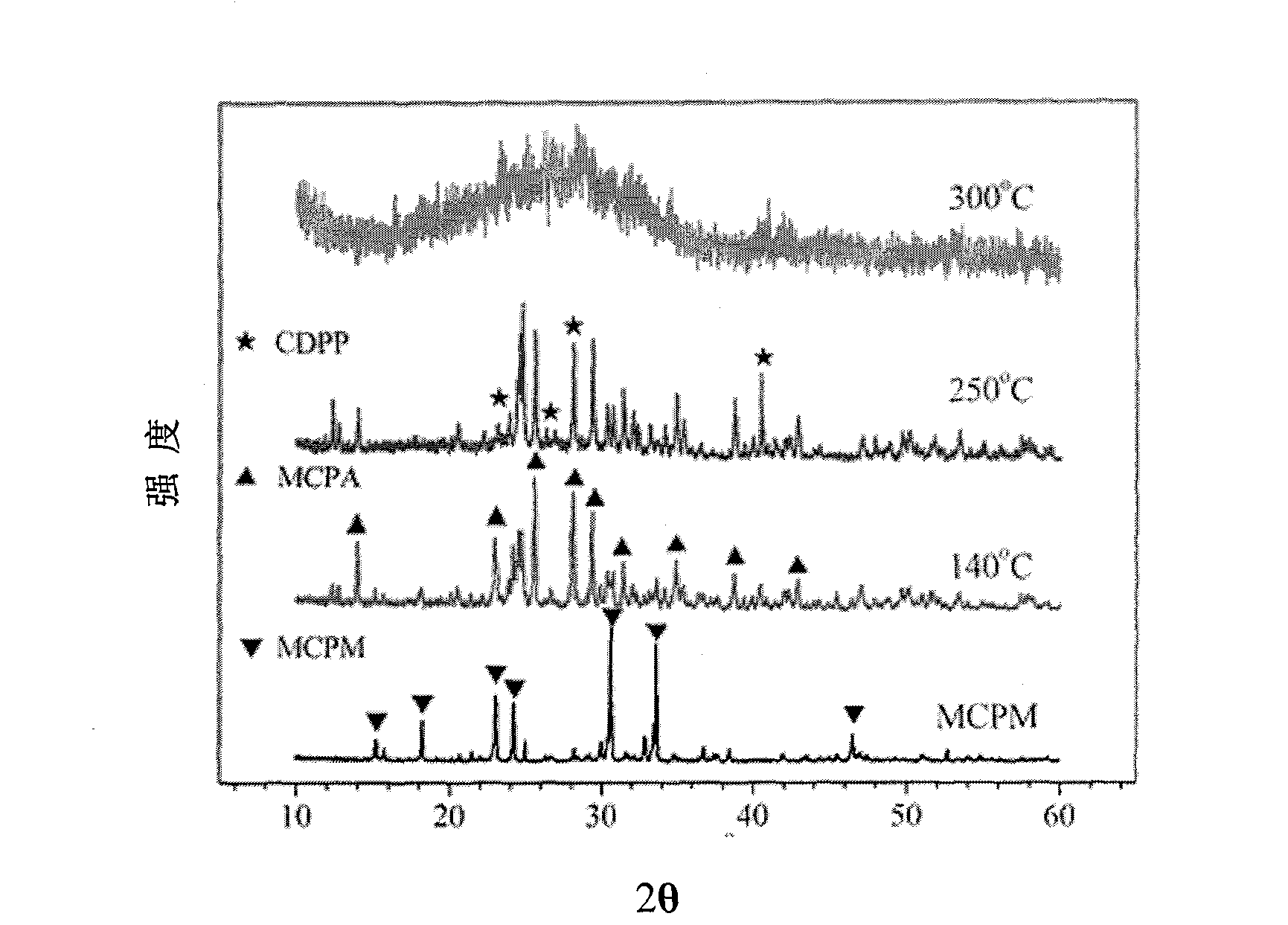
[0033] Add 42.06 g of calcium oxide with a Ca / P mol ratio of 0.5 to 500.0 ml of a phosphoric acid solution with a concentration of 3.0 mol. After stirring the solution for 48 hours with a magnetic stirrer, put the beaker into an electric constant temperature blast drying oven at 60°C Drying under high temperature for 7 days, ball milling the dried powder, passing through a 200-mesh sieve. That is, Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) precursor powder. Product Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) powder X-ray diffraction pattern as attached to the instruction manual figure 1 shown.
[0034] Step 2: Preparation of calcium metaphosphate porous ceramics
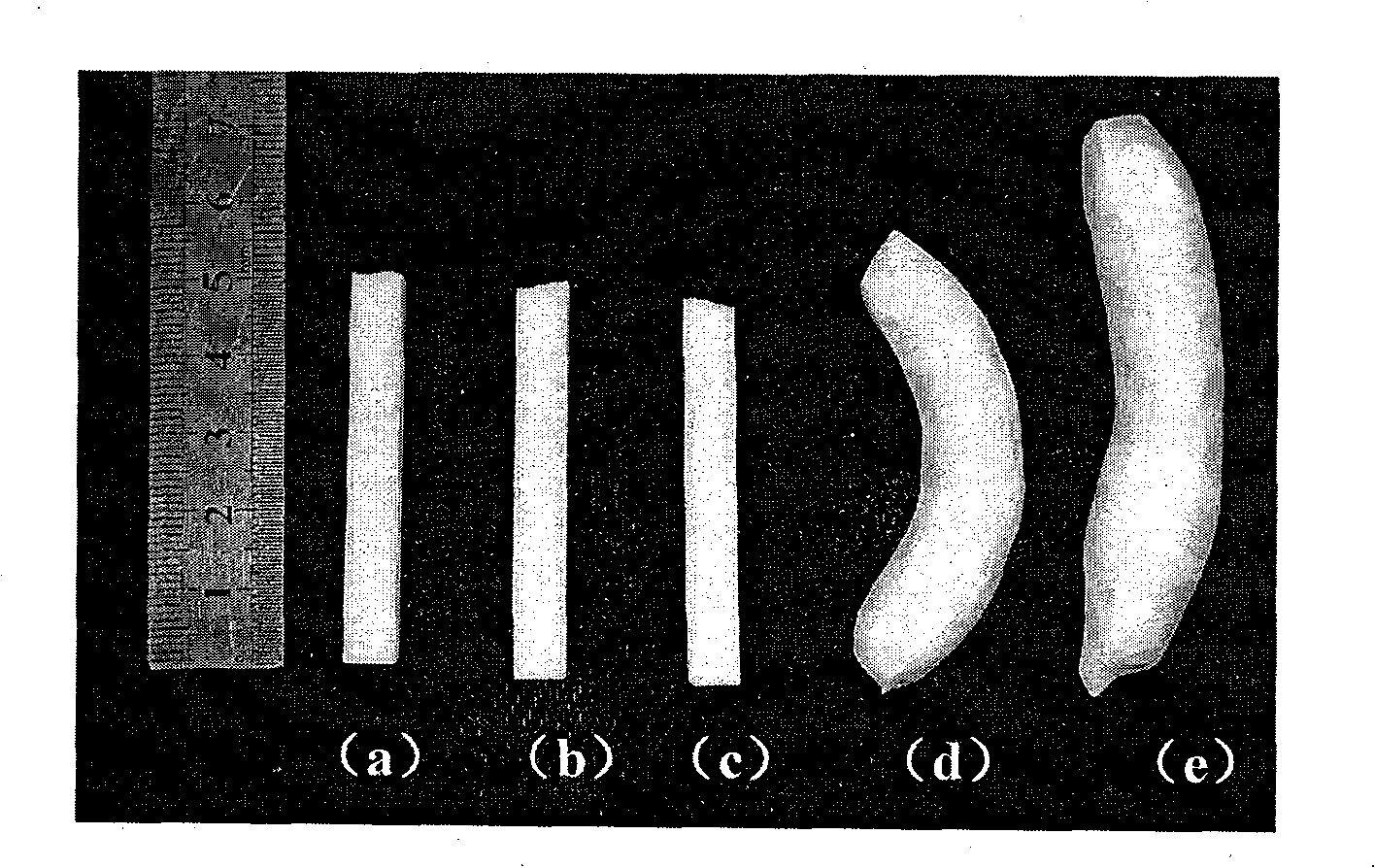
[0035] Take 5.0g of synthesized Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 After mixing O(MCPM) and 5.0wt% PVA binder evenly, granulate and sieve, use dry pressing method to form at 2.0MPa, then heat up to 500°C at 0.5°C / min, and then press 5.0°C / min The heating rate of min wa...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Step 1: Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 Preparation of O(MCPM) precursor
[0038] Add 14.02 g of calcium oxide with a Ca / P mol ratio of 0.5 to 500.0 ml of a phosphoric acid solution with a concentration of 1.0 mol. After stirring the solution for 48 hours with a magnetic stirrer, put the beaker into an electric constant temperature blast drying oven at 60°C Drying under high temperature for 7 days, ball milling the dried powder, passing through a 200-mesh sieve. That is, Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) precursor powder. Product Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) powder X-ray diffraction pattern as attached to the instruction manual figure 1 shown.
[0039] Step 2: Preparation of calcium metaphosphate porous ceramics
[0040] Take 5.0g of synthesized Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 (MCPA). Then Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 (MCPA) mixed with 5.0wt% PVA binder evenly, granulated and sieved, formed by dry pressing at 2.0MPa, then heated at 0.5°C / min to 500°C, and then presse...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Step 1: Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 Preparation of O(MCPM) precursor
[0043] Add 28.04g of calcium oxide with a Ca / P mol ratio of 0.5 to 500.0ml of a phosphoric acid solution with a concentration of 2.0mol. After stirring the solution for 48 hours with a magnetic stirrer, put the beaker into an electric constant temperature blast drying oven at 60°C Drying under high temperature for 7 days, ball milling the dried powder, passing through a 200-mesh sieve. That is, Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) precursor powder. Product Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) powder X-ray diffraction pattern as attached to the instruction manual figure 1 shown.
[0044] Step 2: Preparation of calcium metaphosphate porous ceramics
[0045] Take 5.0g of synthesized Ca(H 2 PO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O(MCPM) was heat-treated at 250 °C for 0.5 h to produce CaH 2 P 2 o 7 (CDPP). CaH 2 P 2 o 7 (CDPP) mixed with 5.0wt% PVA binder evenly, granulated and sieved, formed by dry pressing at 40.0MPa, then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com