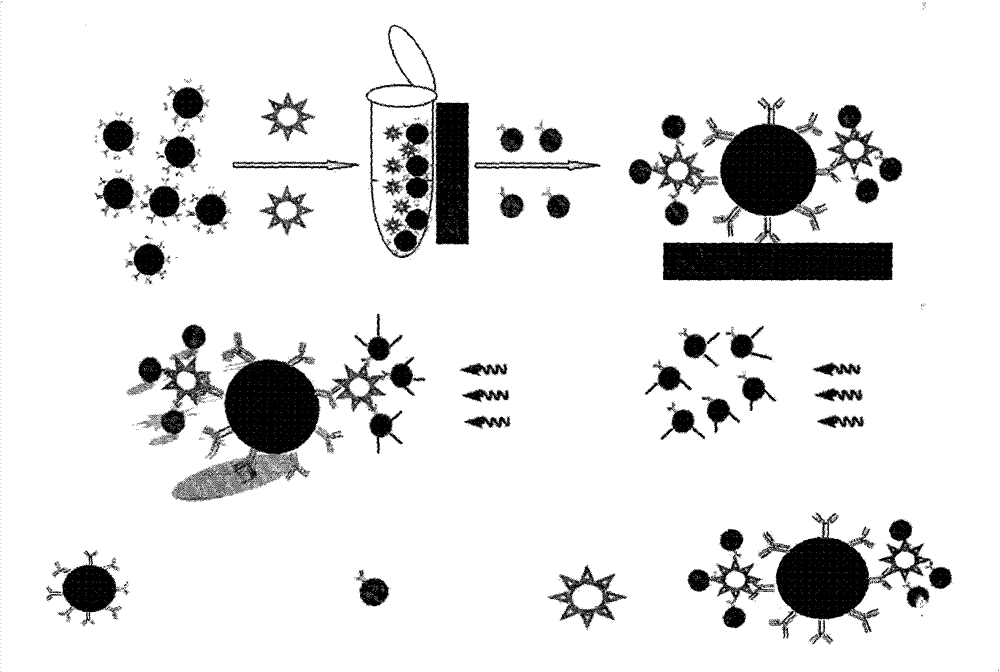
Method for detecting biomacromolecule based on magnetic separation-quantum dot immunofluorescence sensing and reagent preparation method
A biomacromolecule and immunofluorescence technology, applied in the field of detection of biomacromolecules, can solve the problems of fluorescence background interference, loss of fluorescence signal, and the inability of fluorescence to be effectively excited.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: the preparation of simulated sample
[0032] Take the detection of the content of Fusarium wilt in the sample as an example.
[0033] Take 15 corn seed samples in a 50mL centrifuge tube, soak and disinfect with 30mL 3-5% NaCl0 for 5min-15min, and rinse with 10mL sterile water for 3 times. Soak with 40mL PBS buffer solution (0.01mol / L, pH 7.4), overnight at 4°C. Transfer the soaking liquid into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 1000r / min for 10min, take the supernatant and transfer it to another centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 10000r / mmin for 15min, discard the supernatant, suspend and precipitate with 100mL of the above PBS buffer solution, and prepare corn seed matrix liquid. Use this matrix solution as diluent to prepare different content corn blight bacteria (10 7 , 10 6 , 10 5 , 10 4 , 10 3 , 10 2 , 10 and 0 cfu / mL) of serial positive samples. Negative samples were prepared according to the above steps without adding corn wilt bacteria.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Preparation of immunomagnetic bead reagent
[0035] Take the detection of the content of Fusarium wilt in the sample as an example.
[0036] 1. Preparation of phosphate buffer solution: disodium hydrogen phosphate (0.2mol L -1 ) and sodium dihydrogen phosphate (0.2mol L -1 ) according to (Na 2 HPO 4 / NaH 2 PO 4 =4:1 ratio) mixed to prepare 0.01mol L -1 Phosphate buffer solution, pH=7.4.
[0037] 2. Preparation of blocking solution: use a molar concentration of 0.01mol L -1 Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was dissolved in PBS of PH=7.4 so that the concentration by weight was 0.5%.
[0038] 3. Activation of supercisive nano-magnetic beads: Take 2mg of supercisive nano-magnetic beads with a particle diameter of 1000nm carboxyl group in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, place it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 30s, put it into a vortex oscillator and vibrate for 10s, and use Separation of magnetic separation rack to obtain solid superparasitic nano-magnetic beads, the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: quantum dot fluorescent probe (QDs-Ab 2 )(2) Preparation
[0041] Take the detection of the content of Fusarium wilt in the sample as an example.
[0042] 1. Activation of carboxyl groups on the surface of QDs: Take 100 μL of QDs solution in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, place it in an ultrasonic cleaner for 30 s, place it in a vortex shaker for 10 s, then add 10 μL of EDC with a mass concentration of 10 mg / mL and 5 μL of NHS with a mass concentration of 10mg / mL was activated by shaking for 15 minutes;
[0043] 2. QDs-Ab 2 Preparation of fluorescent probe (2): Add 0.3 mg of Fusarium wilt monoclonal antibody (protein content 5 mg / mL) to the above-mentioned activated QDs solution, react at room temperature for 2 h, and then add 50 μL of BSA at a concentration of 1 % PBS buffer solution, blocking reaction for 0.5h, then transferred to an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube with a molecular weight of 100kd, centrifuged at a centrifugal force of 8000g for 15min, rem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com