Method for preparing raw material for manganese series ferroalloy from waste zinc-manganese dry batteries
A zinc-manganese dry battery and ferroalloy technology, applied in the field of raw materials for the preparation of manganese-based ferroalloys, can solve the problems of unfeasible economy, complex procedures, and high costs, and achieve the effects of low overall cost, simple process flow, and high recycling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
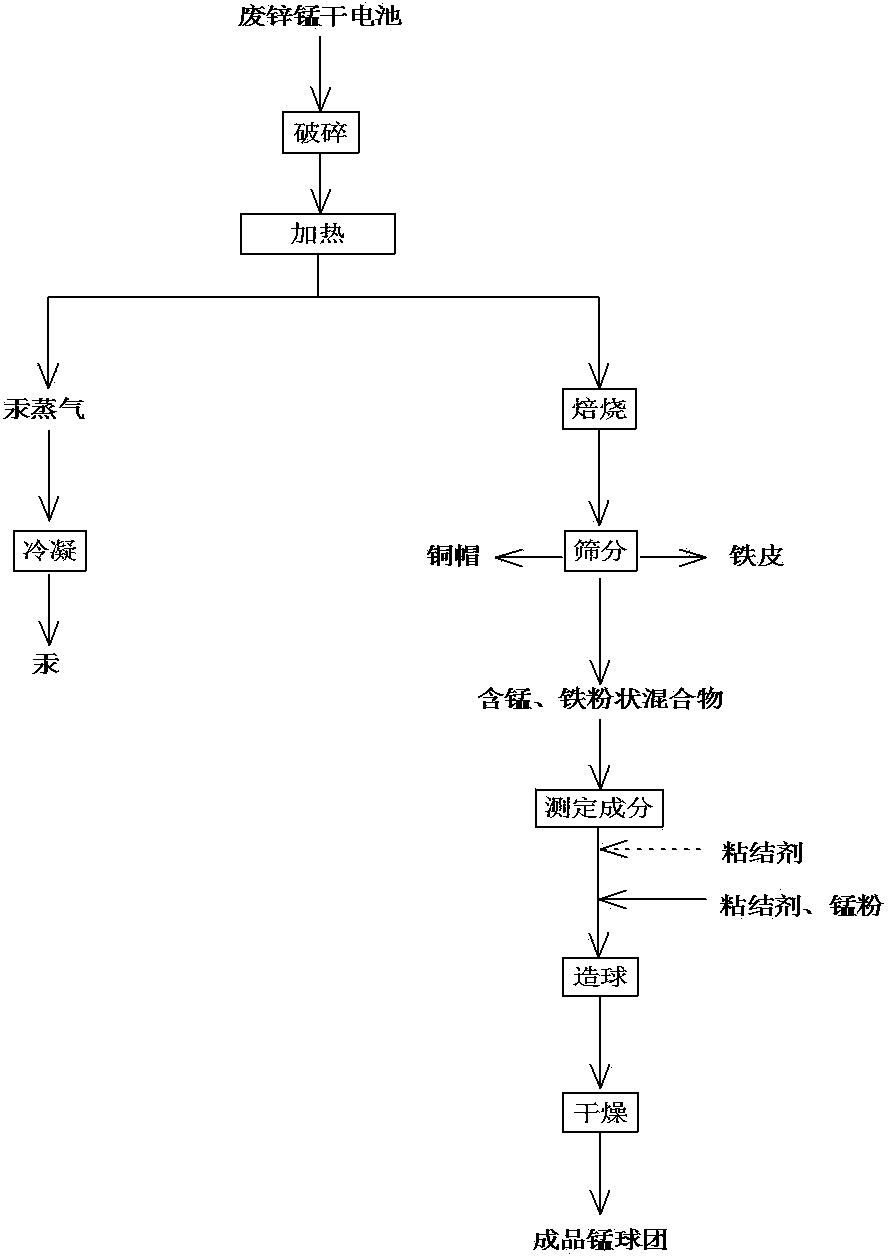
[0026] Embodiment 1: Do not reclaim the zinc in the waste zinc-manganese dry battery
[0027] (1) Regardless of ordinary zinc-manganese dry batteries and alkaline zinc-manganese dry batteries, use a hammer crusher to crush waste zinc-manganese dry batteries.
[0028] (2) Put the mixture treated in step (1) into a vacuum heating furnace, set the pressure to 500Pa, raise the temperature to 280~320°C, keep it for 2~3 hours, exhaust the furnace gas and remove dust, and then use the condenser to cool Below 100°C, the mercury vapor condenses into metallic mercury particles on the inner wall of the condenser, which is recovered by regular water washing.
[0029] (3) Return the system pressure to normal pressure and continue heating for 1 hour to decompose and evaporate other volatile substances.
[0030] (4) Cool the residue in the vacuum heating furnace to room temperature with the furnace, and sieve the residue mixture. The mixture contains iron sheets, copper sheets and mangan...
Embodiment 2
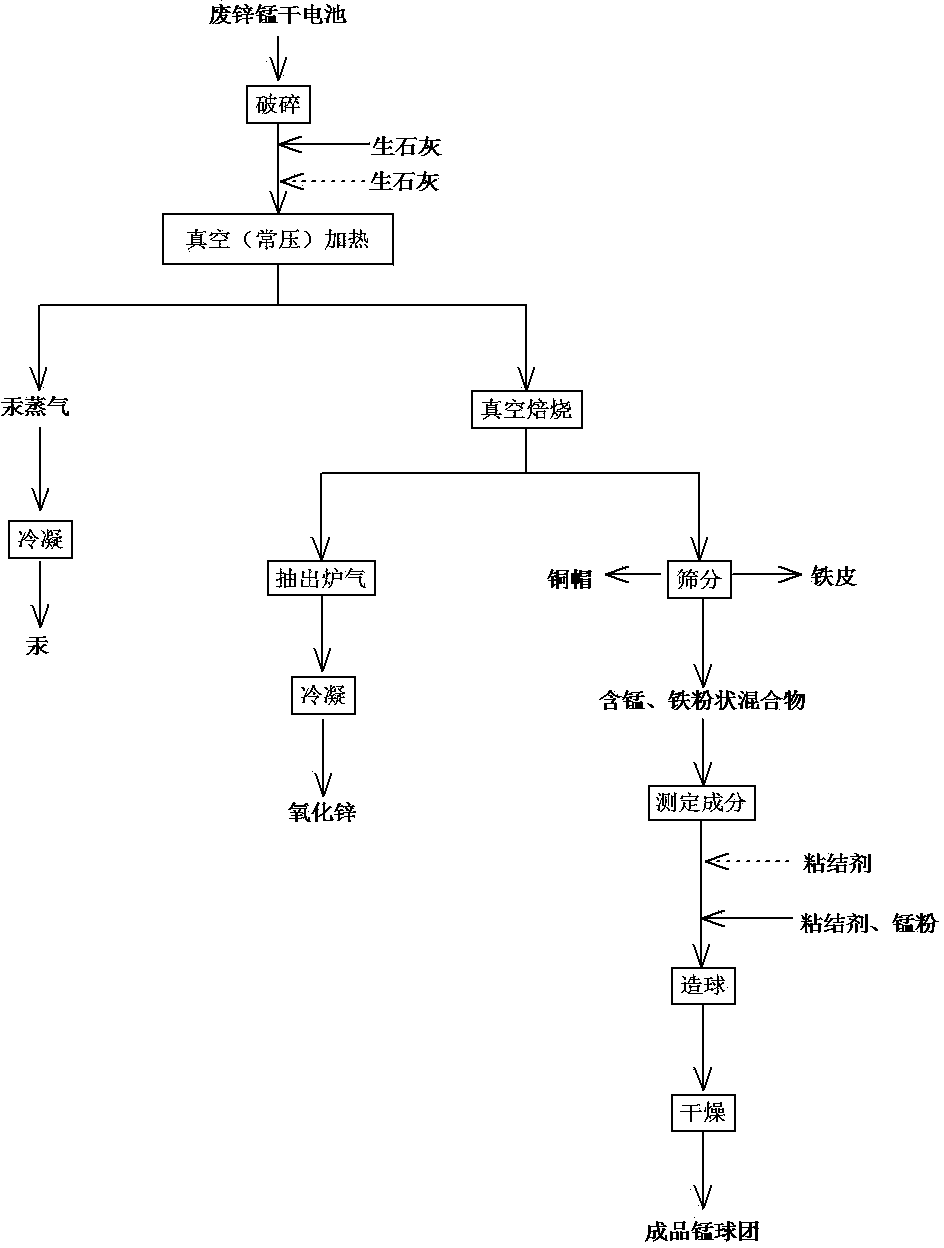
[0034] Embodiment 2: Recycling of zinc in waste zinc-manganese dry batteries without adding quicklime under normal pressure
[0035] (1) Regardless of ordinary zinc-manganese dry batteries and alkaline zinc-manganese dry batteries, use a hammer crusher to crush waste zinc-manganese dry batteries.
[0036] (2) Send the mixture treated in step (1) into a vacuum heating furnace, set the pressure to 500Pa, raise the temperature to 280~320°C, keep it for 2~3 hours, exhaust the furnace gas and cool it to 100°C with a condenser Below ℃, the mercury vapor condenses into metal mercury particles on the inner wall of the condenser, which is recovered by regular water washing.
[0037] (3) Return the system pressure to normal pressure, raise the temperature to 950~1050°C, and keep it for 2 hours to decompose and evaporate zinc and other volatile substances.
[0038] (4) Extract the furnace gas, remove dust, and cool down to below 500°C through the condenser to condense the zinc oxide. ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Vacuum treatment does not add unslaked lime to the recovery of zinc in waste zinc-manganese dry batteries
[0044] (1) Regardless of ordinary zinc-manganese dry batteries and alkaline zinc-manganese dry batteries, use a hammer crusher to crush waste zinc-manganese dry batteries.
[0045] (2) Put the mixture treated in step (1) into a vacuum heating furnace, set the pressure to 500Pa, raise the temperature to 280~320°C, keep it for 2~3 hours, exhaust the furnace gas and cool it down to 100°C with a condenser Next, the mercury vapor is condensed into metal mercury particles on the inner wall of the condenser, which is recovered by regular water washing.
[0046] (3) Increase the pressure of the system to 250-300Pa, raise the temperature to 850-950°C, and keep it for 1.5 hours to decompose and evaporate zinc and other volatile substances.
[0047] (4) Extract the furnace gas, remove dust, and cool down to below 500°C through the condenser to condense the zin...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap