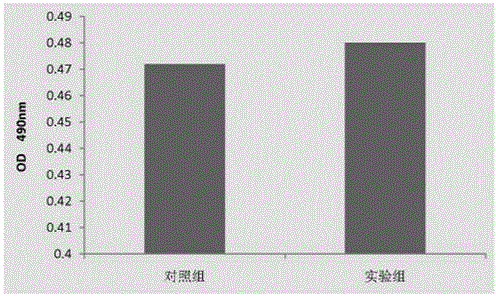
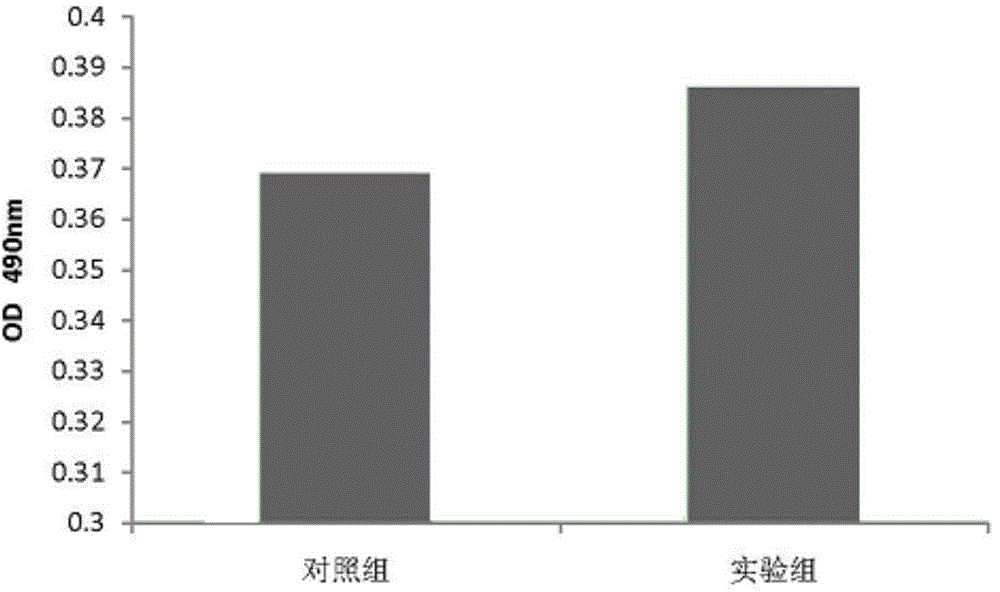
Alginic acid-hyaluronic acid in situ tissue engineering cell scaffold and its preparation method
A technology of hyaluronic acid and tissue engineering, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient tissue support of natural materials, poor histocompatibility of polymer materials and inorganic materials, and rapid degradation, etc., to achieve Avoid toxicity risk, good safety and efficacy, effect of maintaining cell viability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1. Preparation of a kind of alginic acid-hyaluronic acid in situ tissue engineering cell scaffold
[0064] Using sodium alginate and oxidized formylated hyaluronic acid as raw materials, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0065] 1) Preparation of solution
[0066] Preparation of solution 1: Weigh an appropriate amount of sodium alginate powder and prepare a 4% (w / v) solution with physiological saline; the weight-average molecular weight of the sodium alginate is about 150,000 Da, and the M / G ratio is about 0.65 .
[0067] Preparation of solution 2: Weigh an appropriate amount of oxidized formylated hyaluronic acid powder, and prepare a 3.5% (w / v) solution with physiological saline; the weight average molecular weight of the oxidized formylated hyaluronic acid is about 2 million Da , the degree of formylation is about 0.5.
[0068] 2) Preparation before use
[0069] A total of 10 cells to be loaded 6 Mix one with 0.5ml of the above solution 1, and fill ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2. Preparation of an alginic acid-hyaluronic acid in situ tissue engineering cell scaffold
[0072] Using oxidative alginate sodium alginate and sodium hyaluronate as raw materials, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0073] 1) Preparation of solution
[0074] Preparation of solution 1: Weigh an appropriate amount of oxidative alginate sodium alginate powder, and prepare a 4% (w / v) solution with physiological saline; the weight average molecular weight of the sodium alginate is about 150,000 Da, M / G The ratio is about 0.65 and the degree of aldylation is about 0.5.
[0075] Preparation of solution 2: Weigh an appropriate amount of sodium hyaluronate powder and prepare a 3.5% (w / v) solution with physiological saline; the weight average molecular weight of the sodium hyaluronate is about 2 million Da.
[0076] 2) Preparation before use
[0077] Mix the cells to be loaded with the above solution 1, and fill it into a sterile syringe; fill the above solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3. Preparation of an alginic acid-hyaluronic acid in situ tissue engineering cell scaffold
[0080] Using oxidative alginate sodium alginate and sodium hyaluronate as raw materials (the weight average molecular weight of the raw materials is the same as in Example 2), the preparation steps are the same as in Example 2, except that:
[0081] The concentration of solution 1 is 3.0% (w / v); the concentration of solution 2 is 2.5% (w / v);
[0082] Mix solution 1 and solution 2 with a volume ratio of 1:2 through a three-way syringe, and equilibrate at room temperature for 4 minutes to form the desired mixture of alginic acid-hyaluronic acid in situ tissue engineering cell scaffolds and cells to be loaded.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com