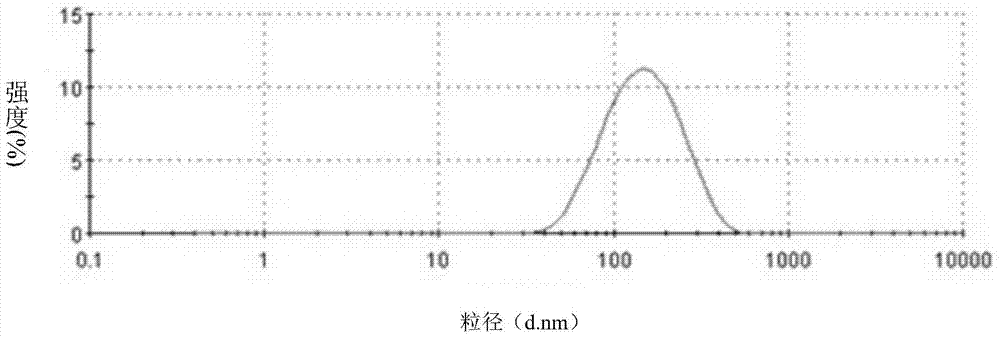
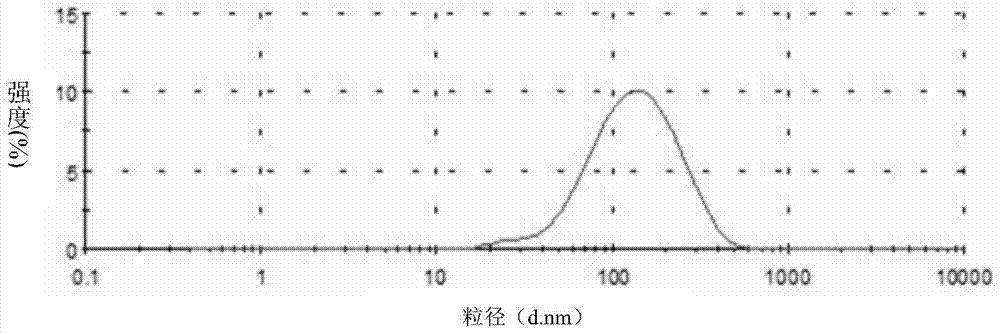
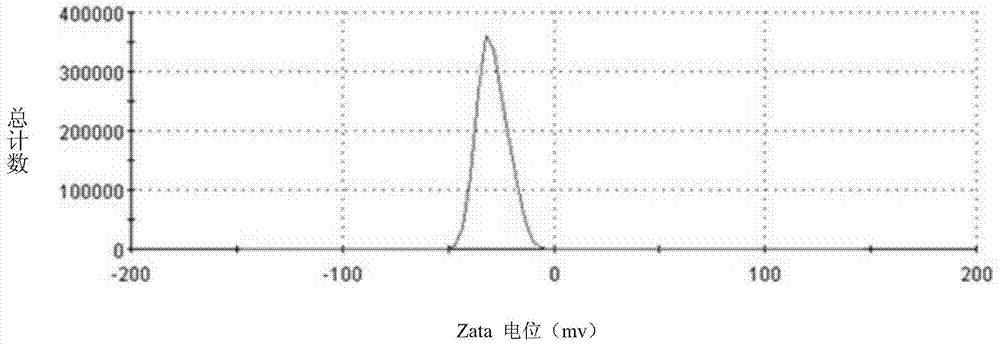
Lactoferrin modified solid lipid nanoparticles, as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of solid lipid nano and lactoferrin, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of less active targeting and difficulty in targeting functional molecules of connexins, and achieve good brain targeting effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1: Preparation of loperamide solid lipid nanoparticles modified by lactoferrin
[0049] Step 1 Synthesis of maleic anhydride-6-aminocaproic acid-polyethylene glycol monostearate (mal-sac-PEG-MS)
[0050] Mal-sac uses dichloromethane as a solvent, adds 1 / 3 mal-sac molar amount of PEG-MS, under ice bath conditions, adds DMAP (5% of PEG-MS), and then adds DCC dropwise (with mal-sac etc. mol), stirred at room temperature for 10 hours, using dichloromethane: methanol (8:2) as the developer, thin layer chromatography analysis to determine the end point of the reaction, ether precipitation, methanol recrystallization, mal-sac-PEG-MS was obtained under low temperature conditions, The melting point is 50-53°C, and the yield is 82%. .
[0051] Step 2 Preparation of loperamide solid lipid nanoparticles (L-SLN) by high-speed shear-melt ultrasonic method
[0052] Weigh the prescribed amount of loperamide and MTS into a test tube, heat and ultrasonically dissolve it as ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2: Preparation of lactoferrin-modified coumarin 6 solid lipid nanoparticles
[0069] Step 1 Synthesis of maleic anhydride-6-aminocaproic acid-polyethylene glycol monostearate (mal-sac-PEG-MS) mal-sac uses dichloromethane as solvent, adding 1 / 3mal-sac molar amount PEG-MS, under ice bath conditions, add DMAP (5% of PEG-MS), then drop DCC (equimolar to mal-sac), stir at room temperature for 10h, dichloromethane: methanol (8:2 ) as developing agent, thin-layer chromatographic analysis to determine the reaction end point, ether precipitation, methanol recrystallization, mal-sac-PEG-MS was obtained under low temperature conditions, melting point 50-53 ℃, yield 82%. .
[0070] Step 2 Preparation of mal-sac-PEGylated coumarin 6 solid lipid nanoparticles (mal-sac-PEG-Co-SLN) by high-speed shear-melt ultrasonic method
[0071] Weigh 61 mg of coumarin, 50 mg of MTS, and 0.5 mg of mal-sac-PEG-MS into a test tube, heat and ultrasonically dissolve it as the oil phase; we...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: Analgesic experiment of Lf-L-SLN
[0077]Step 1 Animal grouping and administration: 110 qualified ICR mice were divided into 11 groups: (1) control group: normal saline 0.15ml / 10g; (2) blank SLN group: 0.15ml / 10g blank solid lipid nanoparticles (not Protein-modified nanoparticles without adding loperamide); (3) blank Lf-SLN group: 0.15ml / 10g, i.e. protein-modified blank solid lipid nanoparticles; (4) positive drug group: morphine hydrochloride 15mg / kg, ( 0.15ml / 10g); (5) Loperamide (L) solution group: 3.6mg / kg (0.15ml / 10g); (6) L-SLN low-dose group: 1.8mg / kg, that is, loperamide solid lipid nanoparticles (0.075ml / 10g); ⑺L-SLN medium-dose group: 2.7mg / kg (0.1ml / mg); ⑻L-SLN high-dose group: 3.6mg / kg (0.15ml / mg); ⑼Lf-L-SLN low-dose Group: 1.8mg / kg, that is, lactoferrin modified loperamide solid lipid nanoparticles (0.075ml / 10g); ⑽Lf-L-SLN medium dose group: 2.7mg / kg (0.1ml / 10g); ⑾Lf- L-SLN high dose group: 3.6mg / kg (0.15ml / 10g). Except for the positive gro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com