Method and device for removing ronidazole in water
A technology for ronidazole and water removal, applied in the field of antibiotic wastewater and ronidazole removal, can solve problems such as ineffective removal and degradation, complex chemical structure, etc., and achieves improved feasibility and operability, simple operation, and reduced Effects of Hazardous Substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
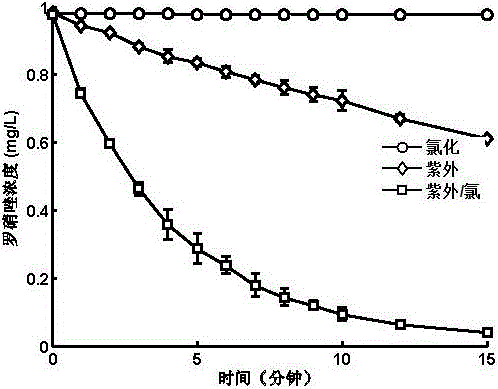
[0043] The initial concentration of ronidazole was prepared with ultrapure water at 5 μM (1 mg / L), and the degradation experiments of ronidazole under the three processes were carried out respectively. The experimental operation for the degradation of ronidazole in the chlorine-only process is as follows: the initial pH of the ronidazole solution is adjusted to 7 with an acid-base solution, and chlorine is added to the ronidazole solution so that the dosage of chlorine is [HOCl] 0 =50μM (as Cl 2 The reaction temperature was controlled to be 25 °C; the experimental operation of the degradation of ronidazole under the single ultraviolet process was as follows: the initial pH of the ronidazole solution was adjusted to 7 with an acid-base solution, and the ronidazole solution was subjected to ultraviolet irradiation, and the intensity of the ultraviolet irradiation was controlled to be 10.6μW / cm 2 , the reaction temperature was controlled to be 25 °C; the experimental operation o...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The initial concentration of ronidazole was prepared with ultrapure water to 5 μM (1 mg / L), the initial pH of ronidazole solution was adjusted to 7 with acid-base solution, and chlorine was added to the ronidazole solution, and the amount of chlorine added was controlled to [HOCl] 0 =0, 125, 25, 50, 100, 150 μM (as Cl 2 meter), and UV irradiation was carried out at the same time, and the UV intensity was controlled to be 5.4 μW / cm 2 , in the reaction process, the reaction temperature was controlled to be 25 °C, and the removal rates of ronidazole were 37.7%, 67.6%, 95.8%, 97.3%, and 98.6% after the reaction for 15 minutes. Figure 4 .
[0047] The increase of chlorine dosage increases the concentration of matrix reactants, increases the driving force of the reaction, and effectively improves the rate of the reaction and the removal rate of RNZ.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The initial concentration of RNZ was 5 μM (1 mg / L) prepared with ultrapure water, the initial pH of the ronidazole solution was adjusted to 7 with an acid-base solution, and chlorine was added to the ronidazole solution, and the amount of chlorine added was [HOCl] 0 =50μM (as Cl 2 meter), and UV irradiation was performed at the same time, and the UV intensity was controlled to be 0, 3.0, 5.4, 8.3, and 10.6 μW / cm, respectively. 2 , under the experimental conditions where the reaction temperature was controlled at 25 °C, the removal rates of ronidazole were 0% (15min), 78.9% (15min), 95.8% (15min), 98.9% (15min), 98.4% (8min). See Figure 5 .
[0050] The increase of UV intensity increased the generation rate of hydroxyl radicals, increased the driving force of the reaction, and effectively improved the rate of the reaction and the removal rate of RNZ.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com