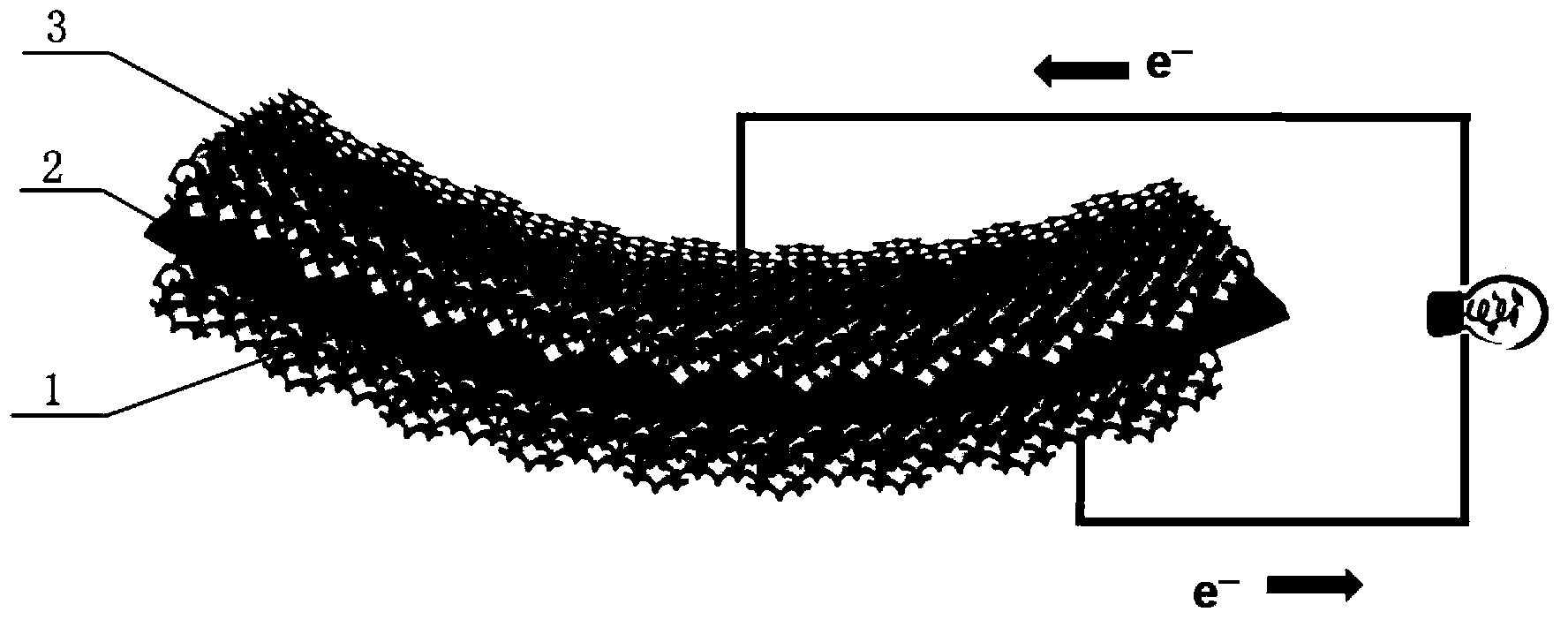
Rapidly charged flexible lithium ion battery and preparation method of electrodes of rapidly charged flexible lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, flexible technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, secondary batteries, battery pack components, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve flexible characteristics such as bendability, achieve mass production, improve rate performance, The effect of low product cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode preparation: 1ml tetraisopropyl titanate was added to the LiOH solution with a molar concentration of 0.4M, and the graphene foam (1×1cm 2 , with a thickness of 100 μm) into the above solution, placed in an 80ml polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and reacted at 130°C for 12 hours. Take out the obtained titanate / graphene foam electrode and calcinate at 550°C for 6 hours under an inert atmosphere to obtain a lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode; during the hydrothermal process, the wrinkles and defects on the graphite foam preferentially become titanate The nucleation site of the final nanosheet-like titanate grows uniformly on the surface of the foamed graphene.
[0047] In the lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode of this embodiment, the proportion of graphene is 12wt%, and the rest is lithium titanate.
[0048] figure 2 Optical photographs of lithium titanate / graphene electrode foams from figure 2 It can be seen that t...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Preparation of lithium iron phosphate / graphene foam electrode: 0.01mol of CH 3 COOLi. 2 h 2 O, Fe(NO 3 ) 3 .9H 2 O and NH 4 h 2 PO was added to 35ml of water respectively, 2.5ml of organic reducing agent ethylene glycol and 2.5ml of isopropanol were added and stirred for 0.5 hours. The graphene foam (1×1cm 2 , with a thickness of 100 μm) into the above solution, placed in an 80ml polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and reacted at 180°C for 6 hours. The obtained phosphate / graphene foam electrode was taken out, and calcined at 720° C. for 12 hours under an inert atmosphere to obtain a lithium ferrous phosphate / graphene foam electrode;
[0054] In the lithium iron phosphate / graphene foam electrode of this embodiment, the proportion of graphene is 12wt%, and the rest is lithium iron phosphate.
[0055] image 3 Scan the photo for the lithium iron phosphate / graphene foam electrode. From the picture, we can see that the lithium iron phosphate particles grow on the surf...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The difference from Example 1 is that in order to increase the loading capacity of the electrode active material, a lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode is prepared by using a perfusion method.
[0058] The preparation method of lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode: Grind commercial lithium titanate particles and conductive carbon black evenly according to the mass ratio of 9:1, add N-methylpyrrolidone (the mass ratio to lithium titanate particles is 1: 1) Grind evenly to make a slurry, drop the above slurry into the graphene foam, and dry at 120°C;
[0059] In the lithium titanate / graphene foam electrode of this embodiment, the proportion of graphene foam is ~2wt%, and the rest is lithium titanate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com