Recombinant protein for resisting porcine pseudorabies virus reproduction and application thereof
A porcine pseudorabies virus and recombinant protein technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of disease re-epidemic, immunosuppression, unsatisfactory immune protection response of vaccine strains, etc., and achieve a significant inhibitory effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Bioinformatics analysis Design protein molecules and related genes for their synthesis.
[0046] The N-terminal domain of protein kinase R (protein kinase R, PKR) contains two dsRNA binding domains; the C-terminal has a kinase domain. After binding dsRNA, PKR protein phosphorylates eIF-2alpha after autophosphorylation, which then prevents the translation of viral proteins. Apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) can simultaneously bind many procaspases. These procaspases activate themselves by cleavage, which then enzymatically cleaves many cellular proteins, thereby killing the cell. When the dsRNA-binding domains and procaspases-binding domains of these two factors are combined into a fusion protein, cells transfected with the protein can immediately initiate the apoptosis process when encountering dsRNA.
[0047] Retrieve the porcine PKR gene (gi|47523704) and Apaf-1 gene (gi|350584646) on NCBI, analyze their domains, and take the dsRNA binding do...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2 expresses and purifies this protein with prokaryotic expression vector pET-28a
[0051] The gene was amplified using a pair of primers as follows:
[0052] sDRACO-1:GACGGGCCGAAGCTTGCTATG
[0053] sDRACO-2:GATCCGACGTCTTAGGAAGAAG
[0054] The cloned gene was connected to the pMD18-T vector, digested by HindIII and XhoI and then connected to the pET-28a expression vector. After the sequence verification was correct, it was transformed into a BL21 expression strain. After IPTG induced expression, SDS-PAGE confirmed the successful expression ( figure 1 ). Continue to analyze the solubility of the recombinant protein: the recombinant strain was induced to express with IPTG, ultrasonically crushed, centrifuged, the supernatant and precipitate were collected, and the solubility of the protein was analyzed. The results of SDS-PAGE showed that at 34.5KD, both the supernatant and the precipitate had a band ( figure 2 ). Cultivate 350ml of the recombinant strain...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 Cell experiments confirmed that the protein (sDRACO) has the ability to significantly inhibit the proliferation of porcine pseudorabies virus
[0056] Proceed as follows:
[0057] 1) The cells cultured for 48 hours into a good monolayer were digested into single cells by trypsin, spread on a 96-well plate, and the antiviral experiment was carried out when the cells grew to 50-80%;
[0058] 2) Do a series of 10-fold dilutions of the PRV virus;
[0059] 3) Antiviral experiment: the experimental group was added with sDRACO and PRV at the same time, and the control group was added with the same amount of PBS and PRV;
[0060] 4) Observe and record the time of cell lesion and the number of holes;
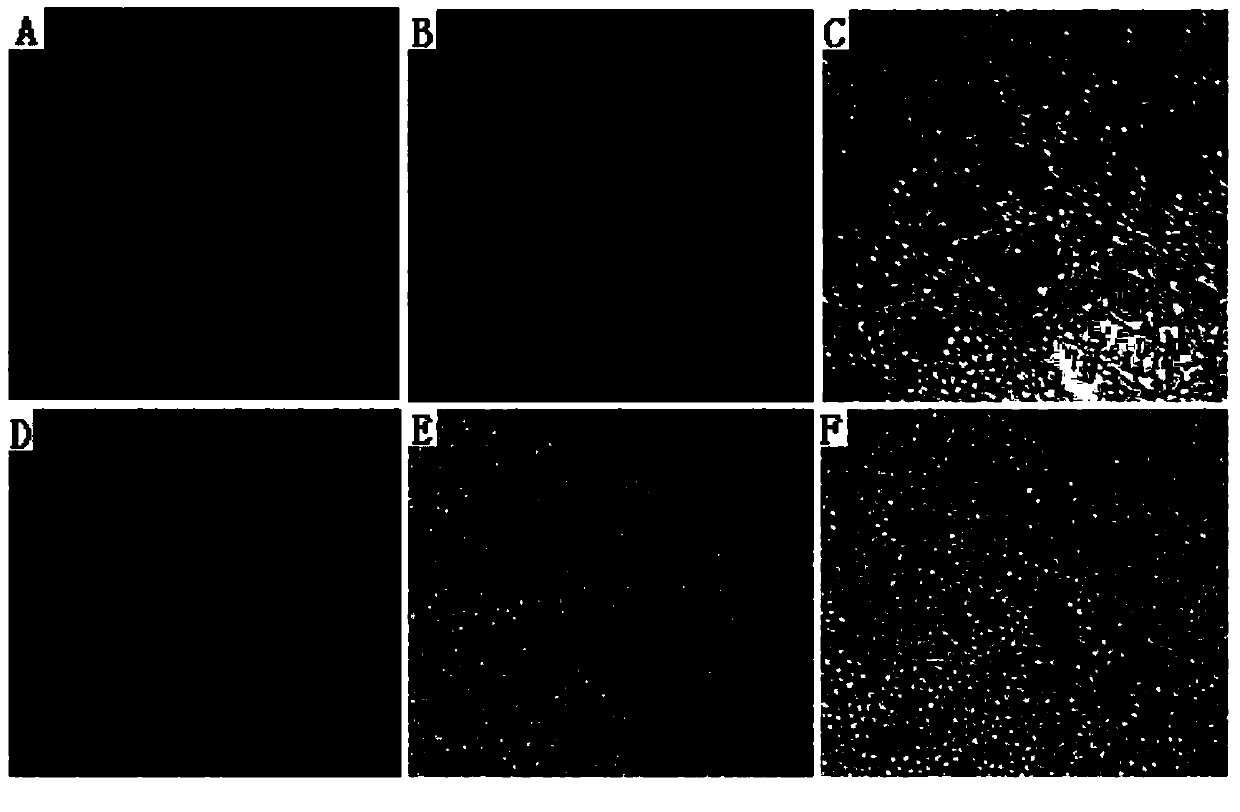
[0061] When the virus was added at a dose of 10 11.5 When TCID50, some cells did not have pathological changes, while all cells in the corresponding control group were pathological ( image 3 ).
[0062] The virus in each well was collected separately, the viral DNA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com