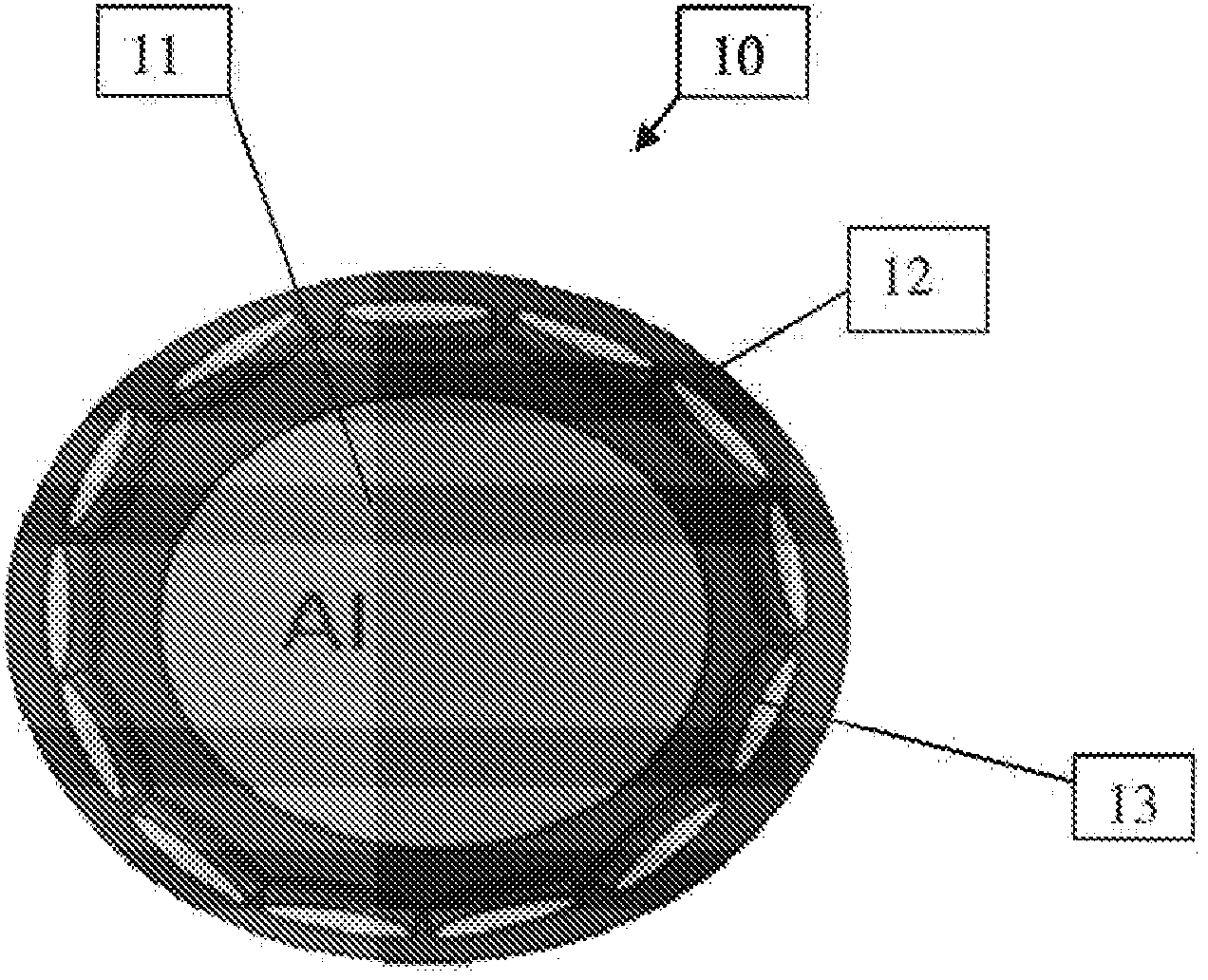
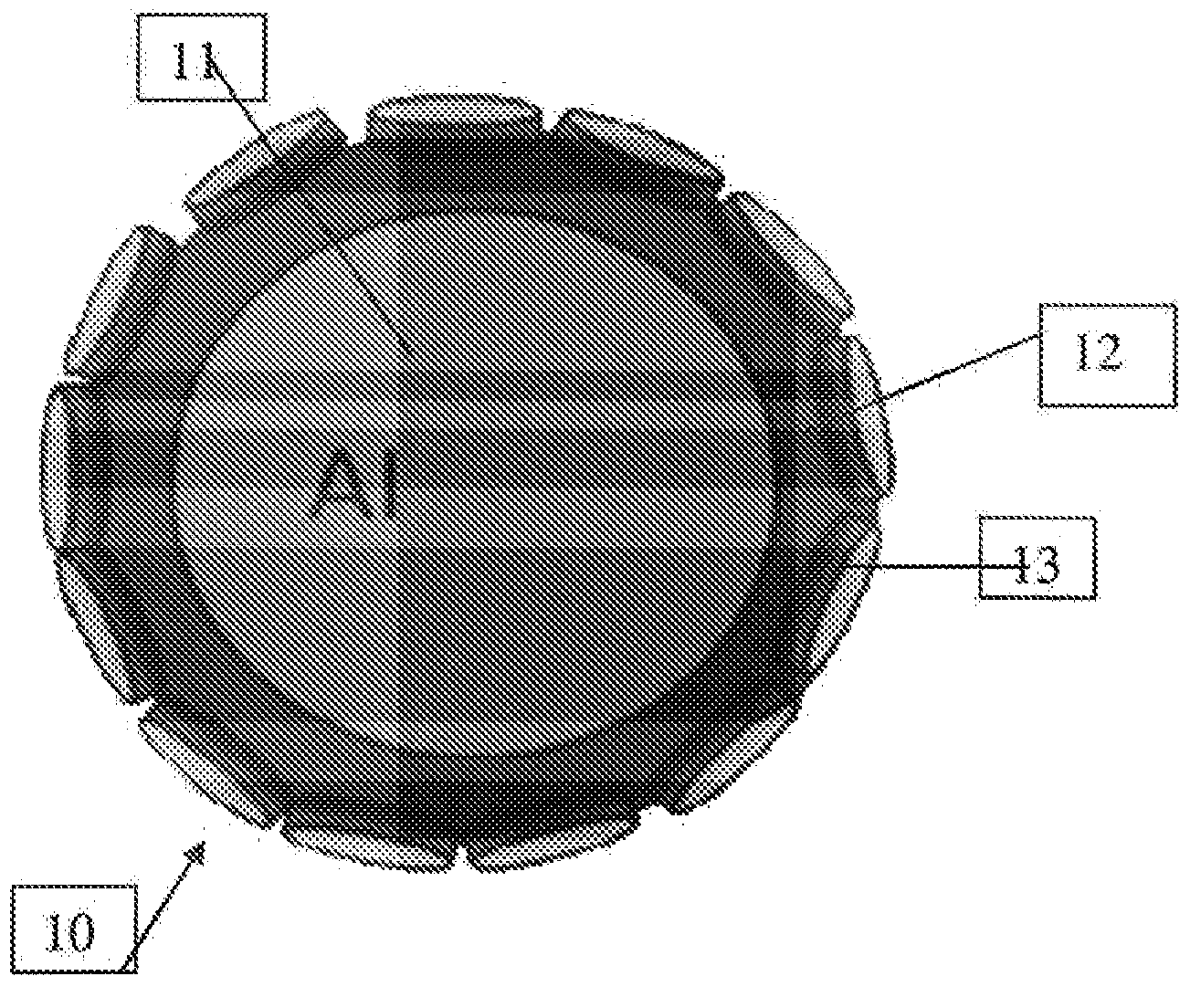
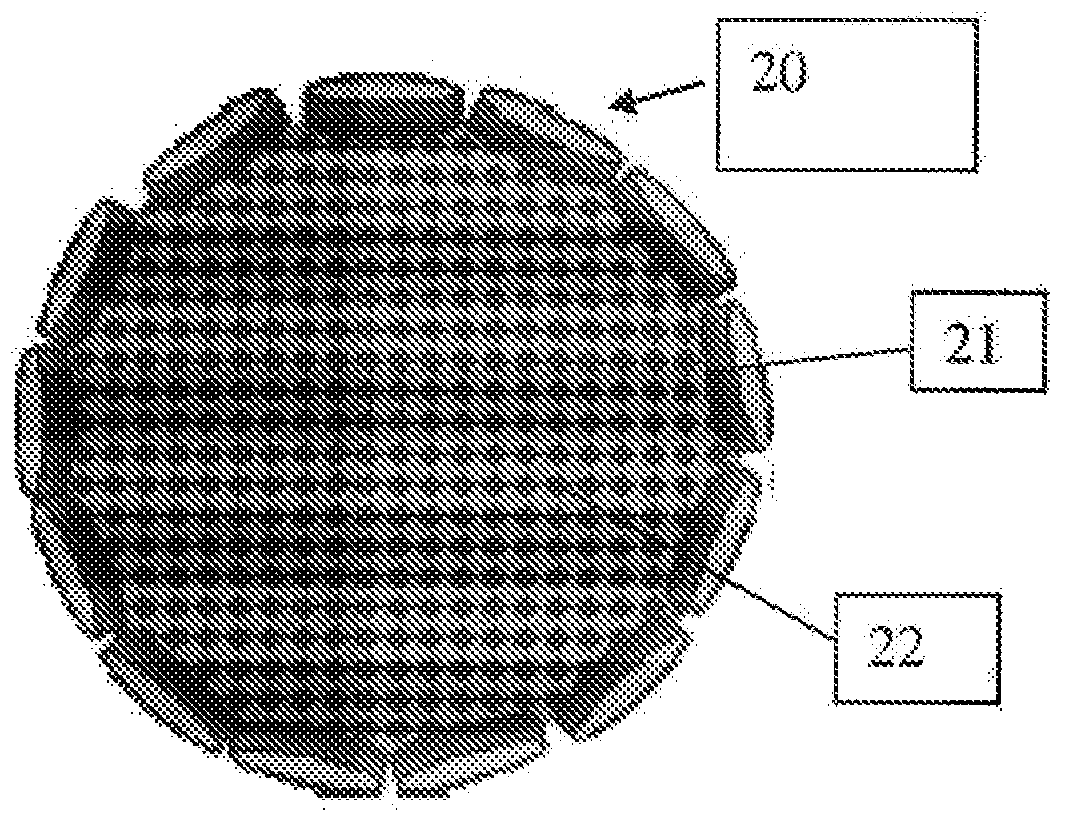
Encapsulated polar materials and methods of preparation
An active substance, polar technology, applied in the field of encapsulated polar substances and preparation, can solve the problem of inapplicability of active substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] Once a stable emulsion or suspension is formed, the emulsion or suspension is subjected to polymerization conditions to form a polymer, preferably a polymer shell around the highly polar liquid droplets. Polymerization conditions depend on the choice of the polymer used. Any polymer system and associated preparation method that forms a polymer or deposit or that forms the polymer as a shell around a droplet may be used. Exemplary methods include interfacial polymerization, in situ polymerization, anionic polymerization, precipitation of polymers from polar or non-polar phases, and electrostatic deposition, eg, by coacervation or layer-by-layer deposition. Exemplary starting materials for such polymers include: where coacervation methods are used, anionic substances (e.g., gum arabic, sodium alginate, styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer, vinylmethyl ether-maleic anhydride copolymer , starch phthalates, and poly(acrylic acid)); in the case of anionic polymerization, cyano...
Embodiment 1 to 23
[0038] Encapsulation preparation procedure
[0039] Add 1.3pph (percentage) of polyisobutylene (weight average molecular weight 500,000 Daltons) in xylene (30g), 5pph of quaternary ammonium-modified nanoclay in xylene to a 120mL (ml) flat bottom bottle with a magnetic stir bar (0.6g), and a premixed solution of diethylenetriamine (3g) and water (6g). Mix well and then sonicate (4x5 sec) at 50% power (Sonics VCX 500 watt model). The prepared emulsion was stirred at 1500 rpm for 2 minutes. A solution of 0.5 g polymeric methylene diisocyanate in 5.5 g xylene was added using a large pipette. The addition was done quickly (-1 ). This peak was stable overnight, indicating that a barrier had formed between the isocyanate and amine. To dispose of cysts, samples were repeatedly decanted and treated with fresh xylene until no isocyanate peaks were visible by ATR-IR. Figure 4 An optical micrograph of the formed capsule 30 is shown. Nanoclay suspensions were prepared as 5 pph suspe...
Embodiment 23-28
[0050] Examples 23-28 Cyanoacrylate Polymers
[0051] Capsules of the present invention were prepared from cyanoacrylate monomers using the ingredients listed in Table 4 and the procedure outlined below.
[0052] Table 4
[0053] ingredients, in order of addition
[0054] Weigh the solvent into a 60 mL bottle and add a stir bar. An aqueous buffer solution was added and the stir bar stirred at 500 rpm to dissolve or disperse the buffer. The particles were added and the mixture was sonicated at 50% power (4x5 seconds with bottles closed and shaken between cycles). The mixture was stirred at 500 rpm after sonication. The monomers are added. The mixtures were studied using light microscopy and in all examples the morphology of the capsules was visible.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com