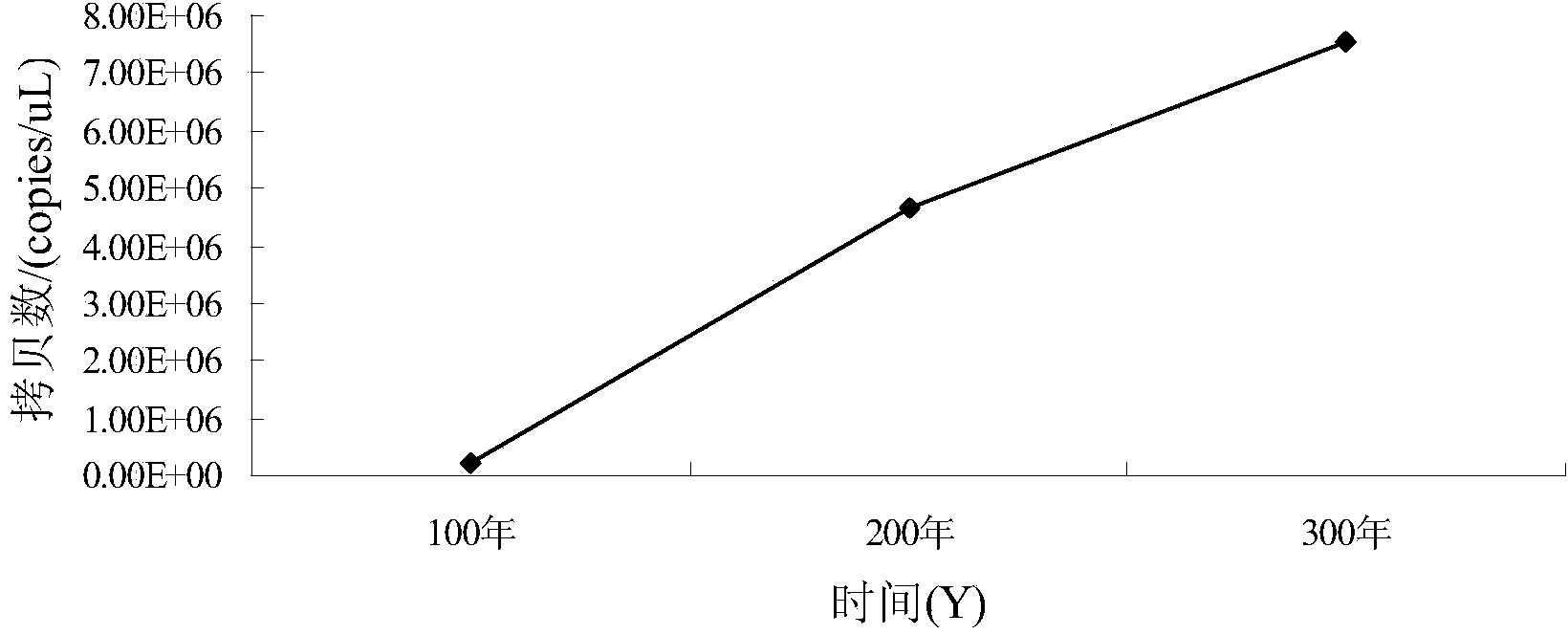Method for quantitatively analyzing clostridia, lactobacilli, bacilli and methanobacteria in pit mud
A Bacillus, quantitative analysis technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, lack of stability and reliability of detection results, and achieve the effect of strengthening monitoring, simple operation, and simplifying detection procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The preparation of embodiment 1 standard curve
[0038] 1. Synthesize specific primers for Clostridium, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus and methanogens, and specifically amplify the screened Clostridium, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus and methanogens
[0039] Clostridium-specific primer sequence (5′→3′):
[0040] Clost-F: AAAGGRAGATTAATACCGCATAA;
[0041] Clost-R: TTCTTCCTAATCTCTACGCA.
[0042] Lactic acid bacteria specific primer sequence (5'→3'):
[0043] Lacto-F: AGAACACCAGTGGCGAAGG;
[0044] Lacto-R: CAGGCGGAGTGCTTAATGC.
[0045] Bacillus-specific primer sequence (5′→3′):
[0046] Bacil-F: ATGGCTGTCGTCAGCT;
[0047] Bacil-R: ACGGGCGGTGTGTAC.
[0048] Methanogen-specific primer sequence (5′→3′):
[0049] Metha-F: GGTGGTGTMGGATTCACACARTAYGCWACAGC;
[0050] Metha-R: TTCATTGCRTAGTTWGGRTAGTT.
[0051] R in the above primers is A or G; W is A or T; M is A or C; Y is T or C.
[0052] 2. Screening of Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Bacillus and Methanogen in pit mud and...
Embodiment 2
[0090] The preparation of embodiment 2 standard samples
[0091] 1. Collection of pit mud samples
[0092] Pit mud samples were collected (100-year-old, 200-year-old, and 300-year-old pit mud were collected respectively). If DNA cannot be extracted in time after sample collection, it should be stored in a -80°C refrigerator immediately.
[0093] 2. Extraction method of microbial total DNA in pit mud
[0094] Weigh 1g of pit mud sample into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 5mL of PBS buffer solution pH7.64 and 8-9 sterilized glass beads to the centrifuge tube, vortex for 5min, centrifuge at 200×g for 5min, and absorb the supernatant. Add 5mL PBS buffer solution to the precipitate and repeat washing twice, combine the three supernatants (operated on ice), centrifuge at 12000rpm for 5min, and take the precipitate. Add 1mL CTAB extract (2%CTAB, 5mol / L NaCl, 1mol / LTris-HCl(pH8.0), 0.5mol / L EDTA) and 20μL mercaptoethanol to the centrifuge tube, shake at 65°C for 30min , add 5 μL of pr...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Quantitative analysis of Clostridium, lactic acid bacteria, bacillus and methane bacteria in the pit mud microbial community of embodiment 3
[0097] Quantification of Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Bacillus and Methanogen in the pit mud sample: using the total DNA of the pit mud obtained in Example 2, and specific primers for Clostridium, Lactobacillus, Bacillus and Methanogen in Example 1. Daqu fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis was performed according to the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system and PCR program in Example 1.
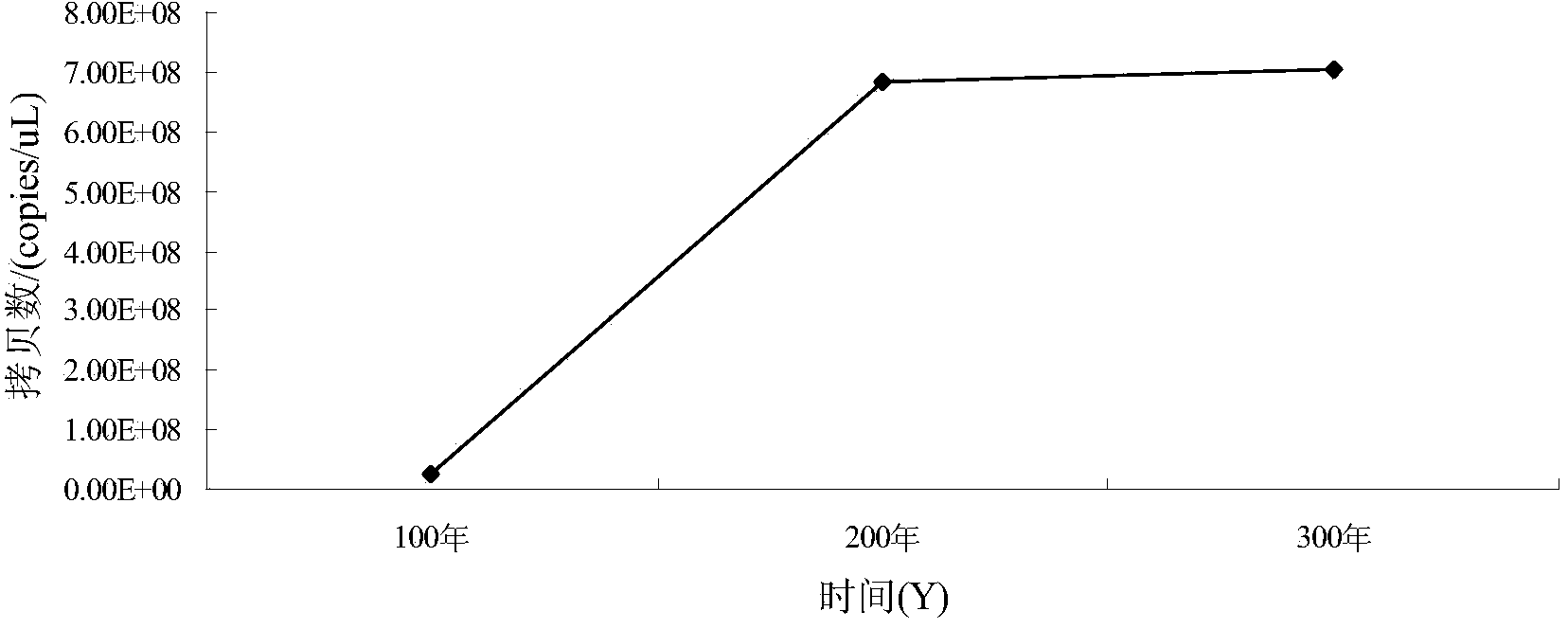
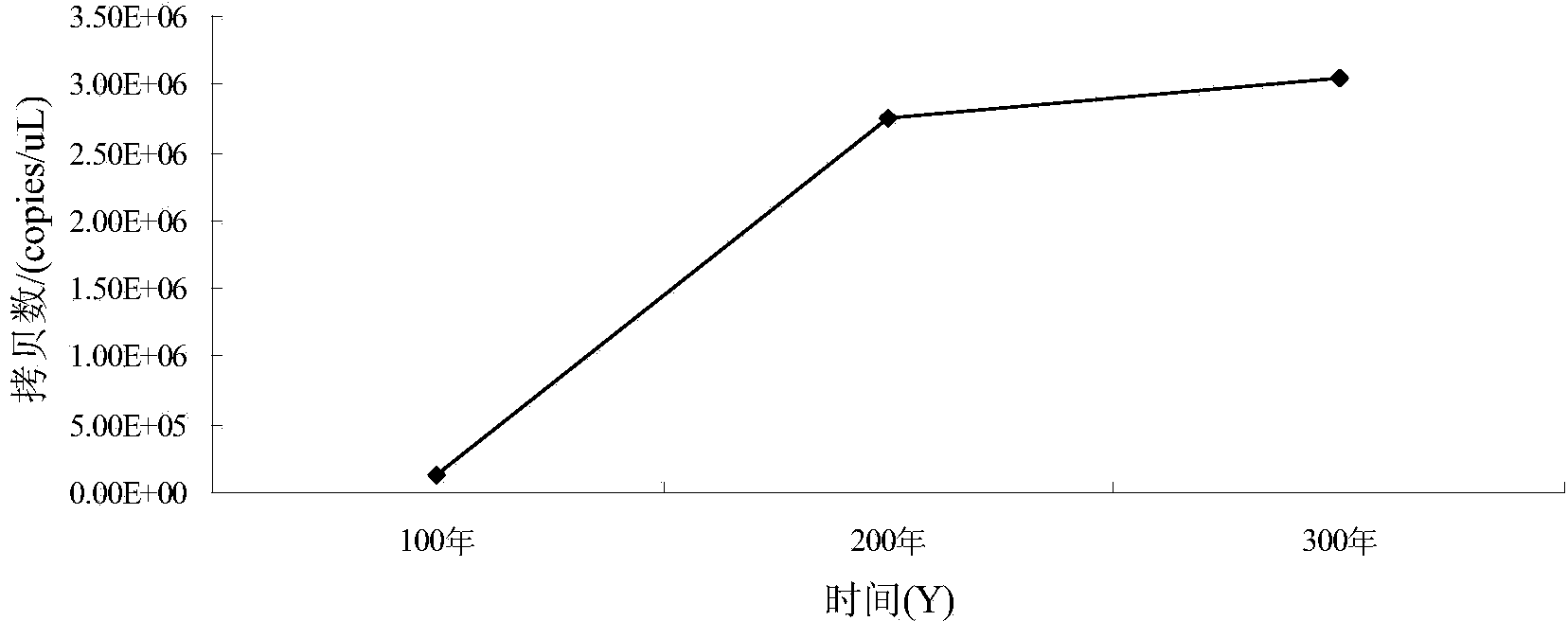
[0098] Quantification of Clostridia in pit mud samples: according to the linear equation y=-0.3303x+13.137(R 2 =0.9978) to calculate the copy number of Clostridia in pit mud samples of different ages, so as to obtain the change trend of Clostridium biomass in different pit ages (such as figure 1 shown).
[0099] Quantification of lactic acid bacteria in the pit mud sample: according to the linear equation y=-0.3411x+14.07(R 2 =0.9978)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com