A kind of low-temperature partial glyceride lipase derived from marine microorganisms and its application
A technology of marine microorganisms and partial glycerides, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems that lipase cannot meet the use requirements and is limited, and achieve good hydrolytic activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
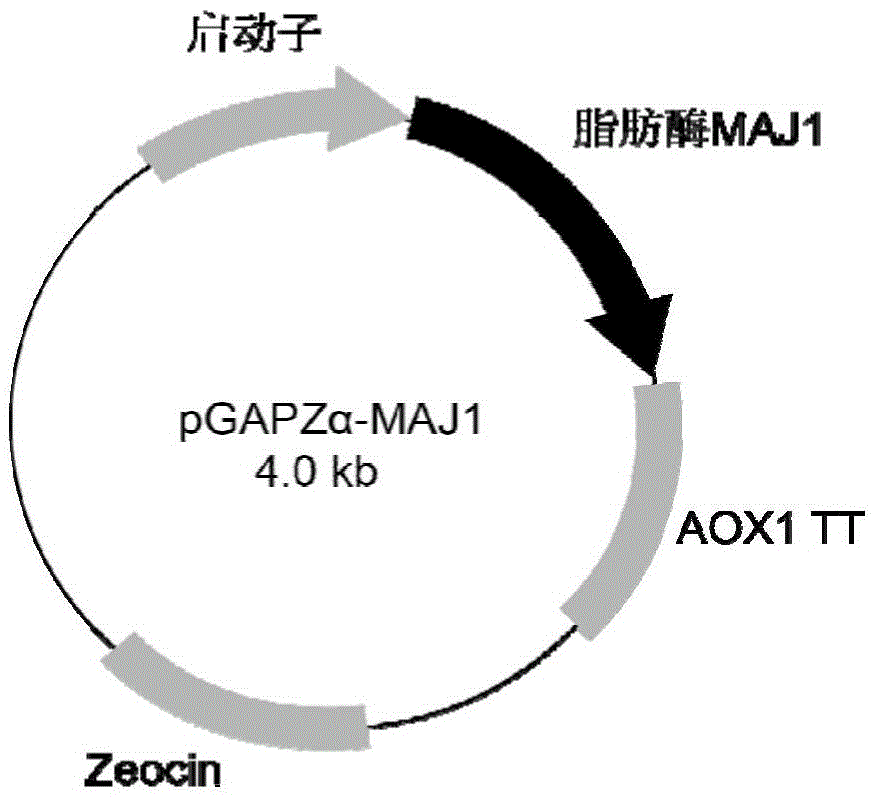
[0048] Construction of expression vector of partial glyceride lipase MAJ1 Pichia pastoris
[0049] According to Genbank's partial glycerol lipase maj1 gene (GenBank accession number: WP_009776835) of the two-faced bacteria HTCC2649, Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. was entrusted to use the method of artificial synthesis, and the sequence was optimized according to the codon preference of Pichia pastoris (sequence SEQ ID NO :1). After gene synthesis, the mature peptide sequence was amplified using the following primers,
[0050]MAJ1For5'-TACTGGTACCGCCACCGTCGCTGCTGATCCCGTTG-3'
[0051] (SEQ ID NO: 3)
[0052] MAJ1Rev5'-AGCTCTCGAGTCAGTGATGGTGGTGATGGTG-3'
[0053] (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0054] PCR amplification conditions: 94°C for 5min; 25 cycles of 94°C for 20s, 53°C for 30s, 72°C for 80s; 72°C for 7min. After the PCR amplification product was purified by a DNA purification kit, the purified gene fragment and plasmid pGAPZαA (purchased from Invitrogen) were digested with ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Recombinant Expression and Purification of Lipase MAJ1
[0057] After the lipase MAJ1 expression plasmid was linearized with the restriction endonuclease BlnI, it was electroporated into competent cells of Pichia pastoris X-33 (purchased from Invitrogen). Spread the transformation solution on a YPD (100ug / mLZeocin) plate, culture it at 30°C for 3 days, pick a single colony on the plate and ferment it in 100mL YPD medium for 72 hours, centrifuge and concentrate the fermentation liquid for SDS-PAGE detection, and obtain the expression Lipase MAJ1 positive recombinant strain.
[0058] The recombinant strain was inoculated into 100mLYPD medium, 30°C, 200rpm shaking culture for 48-72 hours, and the fermentation supernatant was collected (10,000rpm, centrifuged for 20min, 4°C).
[0059] The fermentation supernatant of the MAJ1 recombinant strain was suction-filtered with a 0.45 μm filter membrane. Afterwards, 10kD membranous cells (Vivaflow200, Sartorius, Germany) were used...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Optimal temperature and temperature stability
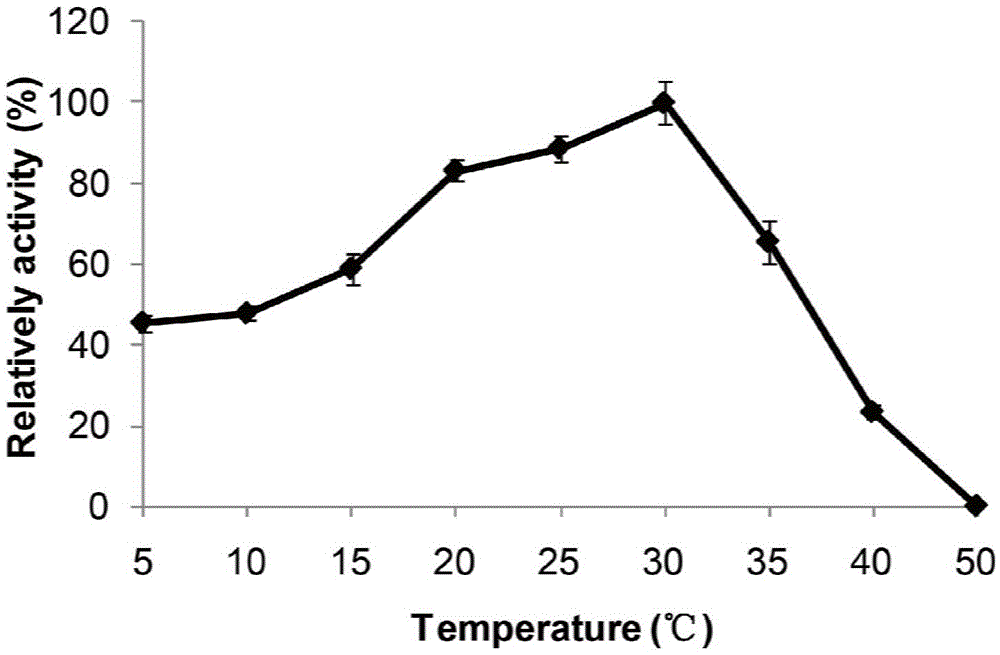
[0062] Effect of temperature on MAJ1 lipase activity: under different temperature (5°C-50°C) conditions, the MAJ1 enzyme activity was determined by colorimetry. The reaction system includes 100mM Na 2 HPO 4 -NaH 2 PO 4 (pH7.0), 1mM p-nitrophenolcaprylate (p-NPc), 10μL enzyme solution, react at each temperature for 5min, measure the absorbance value OD at 405nm 405 . The influence of temperature on MAJ1 enzyme activity is expressed by relative enzyme activity, and the maximum enzyme activity measured is set as 100%. All experiments were repeated three times. The results showed that the optimum reaction temperature of MAJ1 was 30°C, and 80% of the relative enzyme activity was reached at 25°C (see image 3 ).
[0063] When determining the stability of MAJ1 under different temperature conditions, MAJ1 was first incubated at different temperatures (20°C, 30°C, and 40°C), and samples were taken at 0.5h, 1h, 1.5h, 2h, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com