Method for preparing ACE inhibitory peptide by enzymolysis of squid viscera with magnetic nanoparticle immobilized cells
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and immobilized cells, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of poor operation stability of tissue enzyme autolysis method, high cost of exogenous enzyme enzymolysis, and high process complexity, so as to improve applicability and flexibility. The effect of improving the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency and reducing the cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
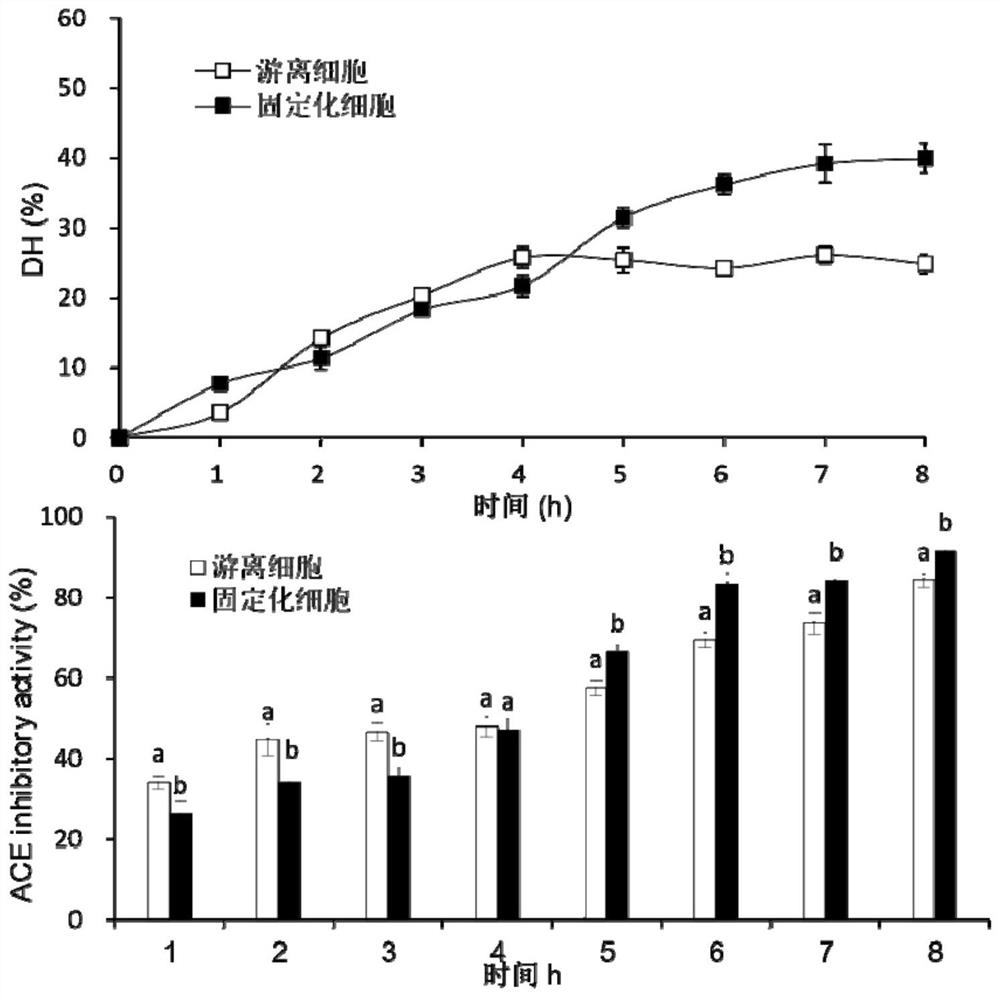
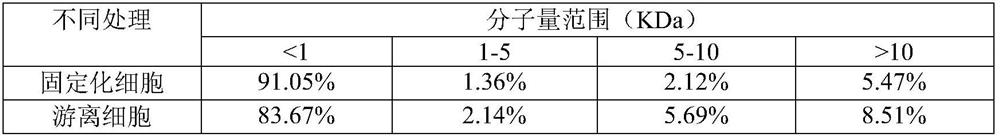
[0042] This implementation illustrates the method and beneficial effects of preparing squid visceral active peptides by using nano-magnetic microspheres to immobilize cells compared with free cells.
[0043] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0044] Step 1: Mix 500g of squid viscera with 500mL of deionized water, heat at 100°C for 30 minutes, remove the massive fish bones, grind the heated slurry in a homogenizer, and then place it in a shallow pan at 80°C Drying for 18 hours, collecting the dried bulk powder, grinding into a fine powder in a pulverizer, and passing through a 60-mesh sieve to obtain a fine powder of the squid viscera extract.
[0045] The second step: the preparation of magnetic ferric iron tetroxide (Fe 3 o 4 ) Nanoparticles: Dissolve 21.6g of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 8g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate in 100mL of deionized water, gradually raise the temperature to 60°C under the protection of nitrogen, and stir at constant temperat...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0070] Step 1: Mix 500g of squid viscera with 1000mL of deionized water, heat at 90°C for 20 minutes, remove the massive fish bones, grind the heated slurry in a homogenizer, and then place it in a shallow pan at 90°C Dry it under the hood for 20 hours, collect the dried bulk powder, grind it into a fine powder in a pulverizer, and pass through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain a fine powder of the squid viscera extract.
[0071] The second step: the preparation of magnetic ferric iron tetroxide (Fe 3 o 4 ) Nanoparticles: Dissolve 25g of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 10g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate in 120mL of deionized water, gradually raise the temperature to 60°C under the protection of nitrogen, and stir at constant temperature for 3 hours. Then add 80 mL of ammonia water with a concentration of 25%, raise the temperature to 80° C. and react for 2 hours, stop stirring and cool to room temperature, and let stand u...
Embodiment 3
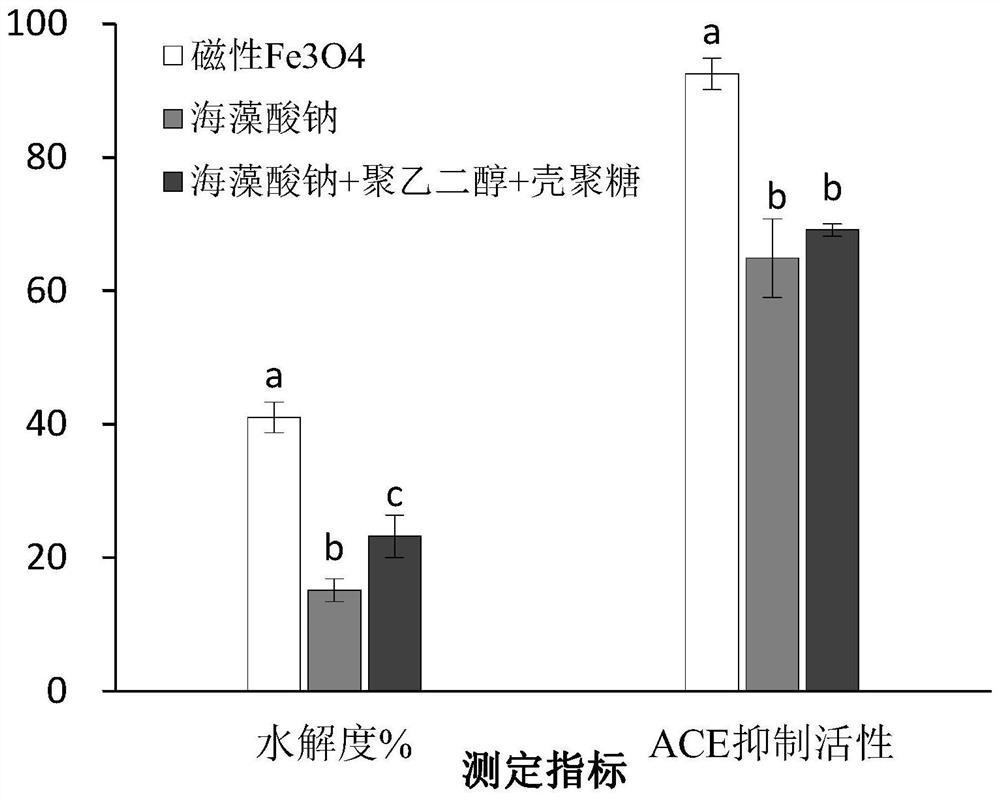
[0080] In this example, magnetic microsphere immobilization and sodium alginate, polyethylene glycol, chitosan and other common media immobilization methods were used to study the effects on proteolysis rate and ACE inhibitory activity.
[0081] The magnetic microspheres were immobilized as described in Example 1, using common media such as sodium alginate, polyethylene glycol, and chitosan to immobilize references (International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics, 25 (2), 681-689. ) method was implemented, the immobilized cells carried out enzymolysis for 8 hours according to the same operation as the enzymolysis process described in Implementation 1, and adopted the same detection method as in Example 1 to measure proteolysis rate and ACE inhibitory activity. The results are as follows figure 2 shown.
[0082] From figure 2It can be seen that the degree of proteolysis after immobilization with magnetic microspheres is significantly higher than that of immobiliza...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com