Organic electroluminescent device and preparation method
An electroluminescent device and luminescent technology, which is applied in the manufacture of organic semiconductor devices, electric solid devices, semiconductor/solid state devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor refractive index, loss of total reflection, low light extraction performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
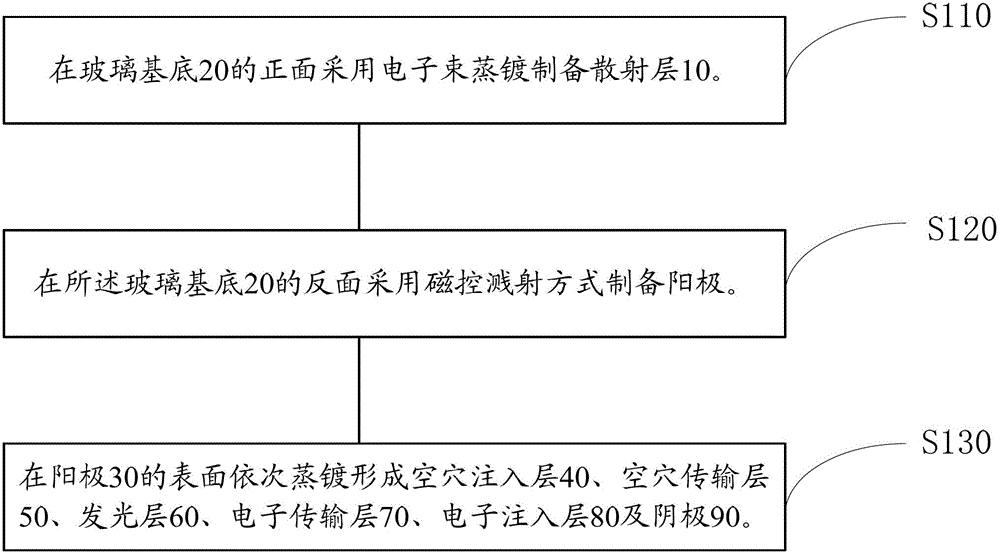
[0037] Please also see figure 2 , the preparation method of the organic electroluminescent device 100 of an embodiment, it comprises the following steps:
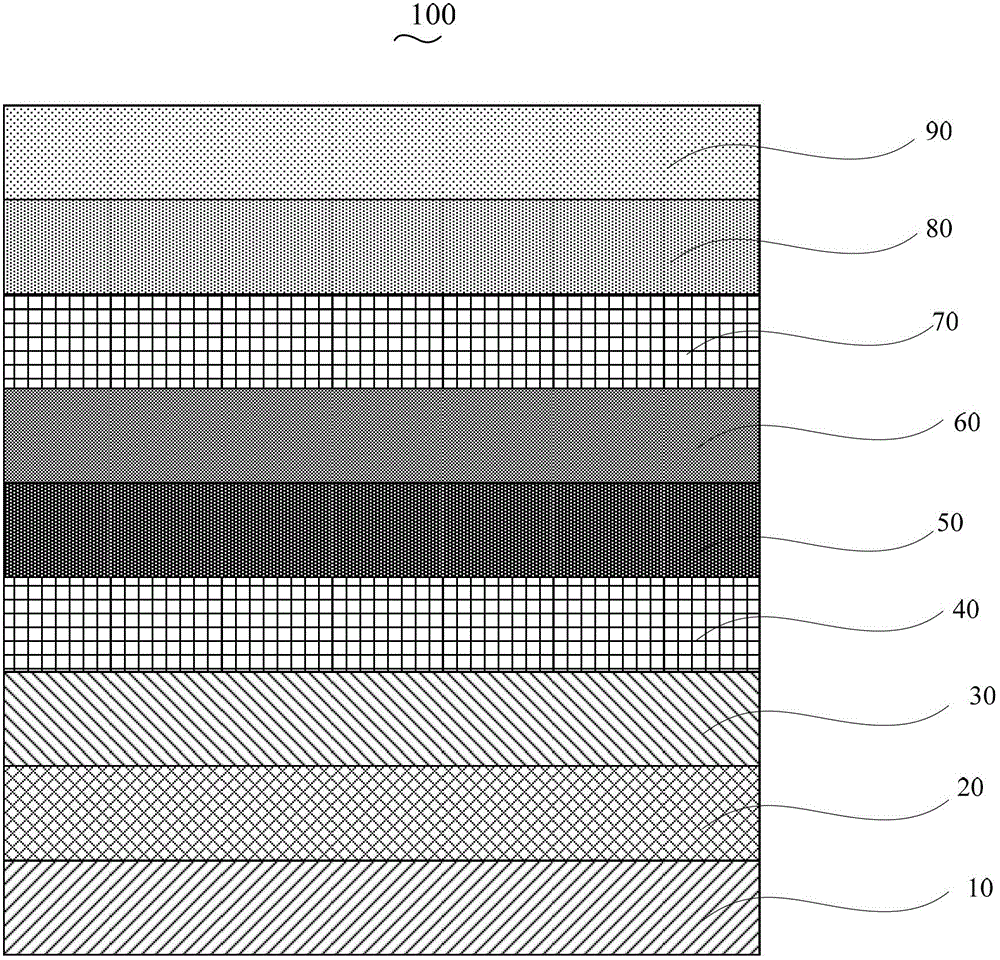
[0038] Step S110 , preparing the scattering layer 10 on the front surface of the glass substrate 20 by electron beam evaporation.
[0039] The scattering layer 10 includes a hafnium compound and a metal oxide doped into the hafnium compound, wherein the metal oxide accounts for 10% to 50% by mass of the hafnium compound, and the hafnium compound The material is selected from at least one of hafnium dioxide and hafnium diboride, and the metal oxide is selected from at least one of tantalum pentoxide, niobium pentoxide and vanadium pentoxide.
[0040] The thickness of the scattering layer 10 is 50 nm to 500 nm.
[0041] Electron beam evaporation at a vacuum pressure of 5 x 10 -5 Pa~2×10-3 Under Pa, the energy density is 10W / cm 2 ~l00W / cm 2 .
[0042] The glass substrate 20 is glass with a refractive index of 1.8-2.2, a...
Embodiment 1
[0059] The structure prepared in this embodiment is Ta 2 o 5 :HfO 2 / Glass Substrate / ITO / MoO 3 / TAPC / BCzVBi / TPBi / LiF / Al organic electroluminescent devices.
[0060] The glass substrate is N-LASF44. After rinsing the glass substrate with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night. The scattering layer was prepared on the front of the glass substrate by electron beam evaporation, and the material of the scattering layer was Ta 2 o 5 and HfO 2 , among them, Ta 2 o 5 accounted for HfO 2 The mass percentage is 15%, and the condition of electron beam evaporation is that the vacuum pressure is 8×10 -4 Pa, the energy density is 25W / cm 2 , the anode was prepared on the reverse side of the glass substrate by magnetron sputtering, the anode material was ITO, and the condition of magnetron sputtering was that the vacuum pressure was 8×10 -4 Pa, the accelerating voltage is 400V, the magnetic field is 100G, and the power density is 200W / cm 2 , and then seq...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The structure prepared in this example is Nb 2 o 5 :HfB 2 / Glass Substrate / AZO / V 2 o 5 / TCTA / ADN / Bphen / CsF / Pt organic electroluminescent devices.
[0066] The glass substrate is N-LAF36. After rinsing the glass substrate with distilled water and ethanol, soak it in isopropanol for one night; use electron beam evaporation to prepare a scattering layer on the front of the glass substrate. The material of the scattering layer is Nb 2 o 5 and HfB 2 , where Nb 2 o 5 accounted for HfB 2 The mass percentage is 50%, and the condition of electron beam evaporation is that the vacuum pressure is 2×10 -3 Pa, the energy density is 100W / cm 2 , the anode was prepared on the reverse side of the glass substrate by magnetron sputtering, the anode material was AZO, and the condition of magnetron sputtering was that the vacuum pressure was 2×10 -3 Pa, the accelerating voltage is 300V, the magnetic field is 200G, and the power density is 40W / cm 2 , and then sequentially vapor-de...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Power density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com