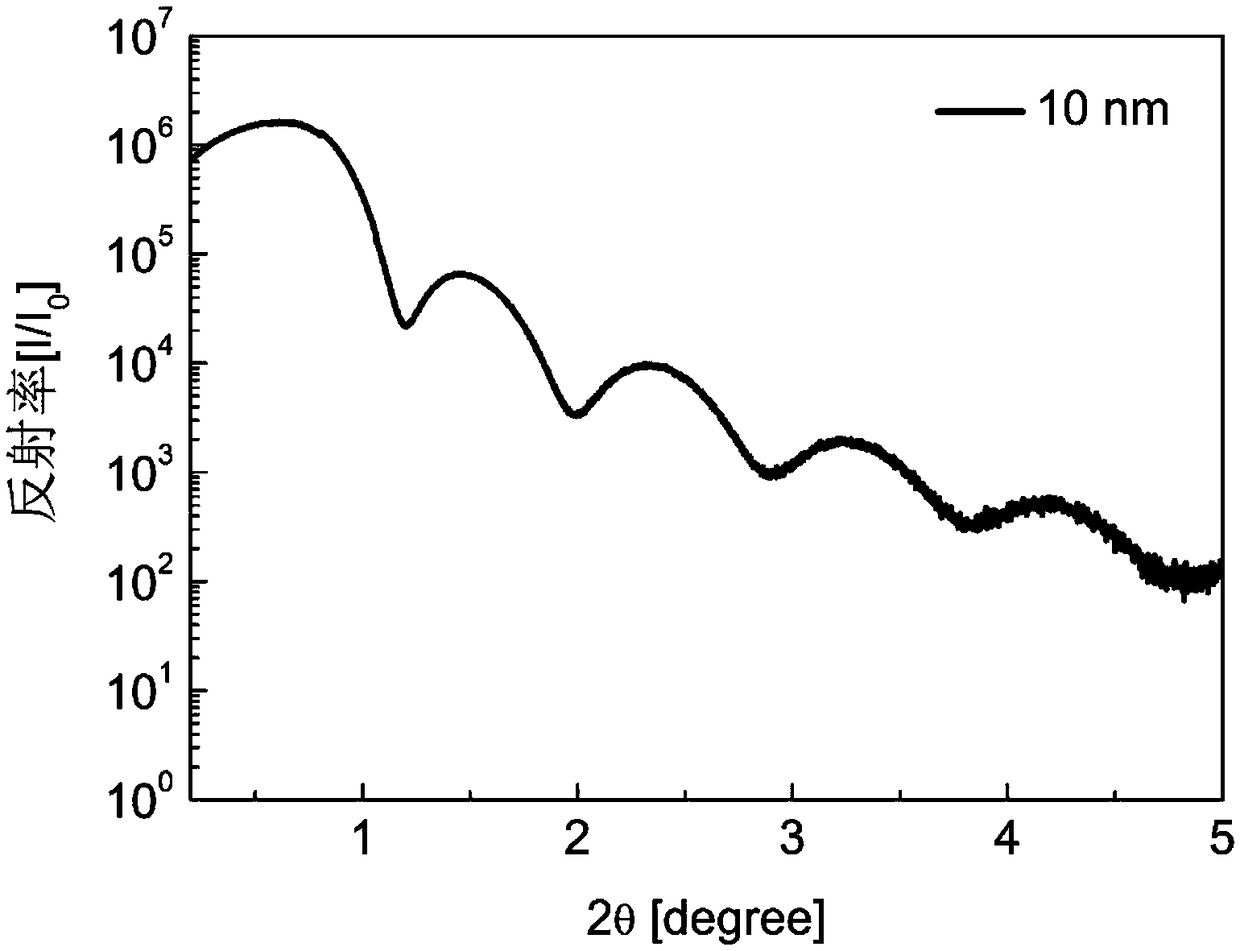
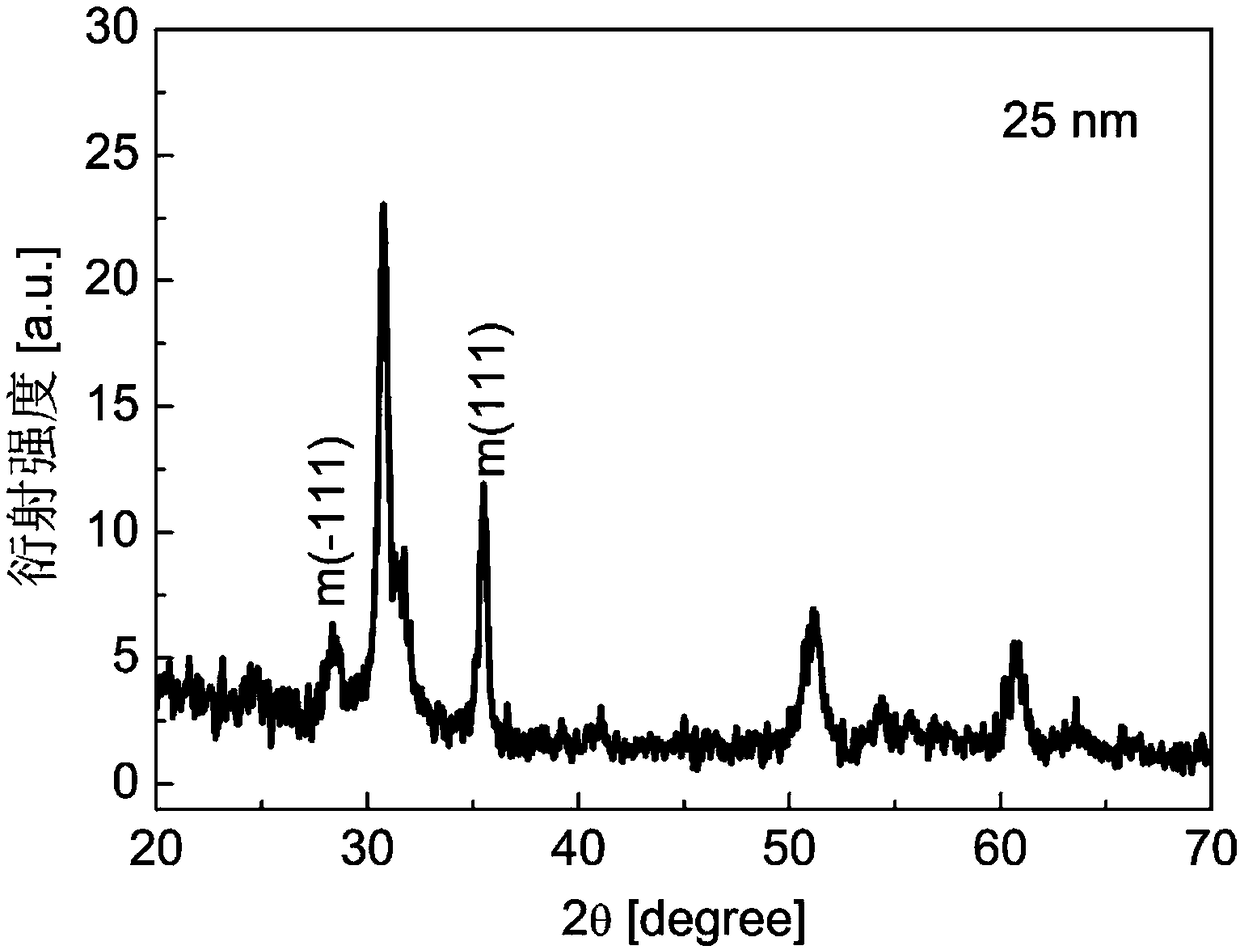
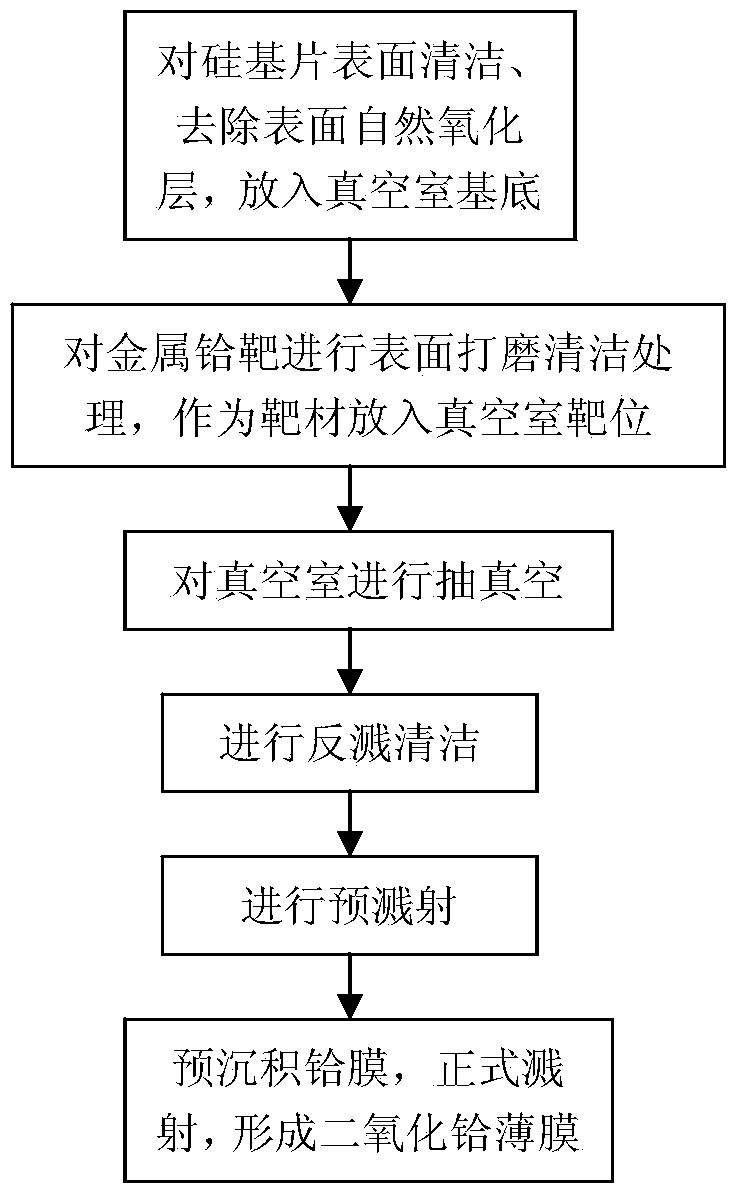
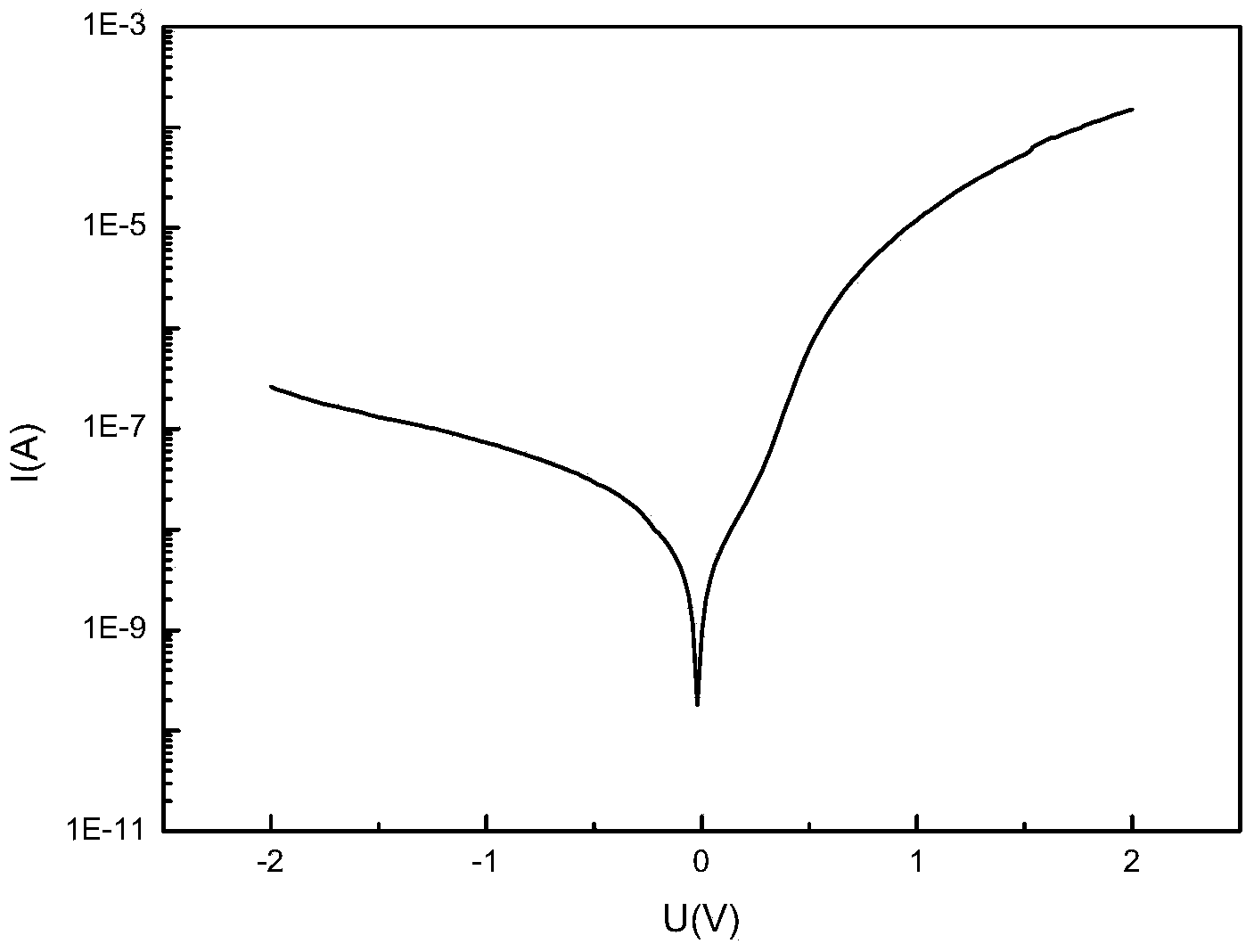
Patents
Literature
137 results about "Hafnium dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
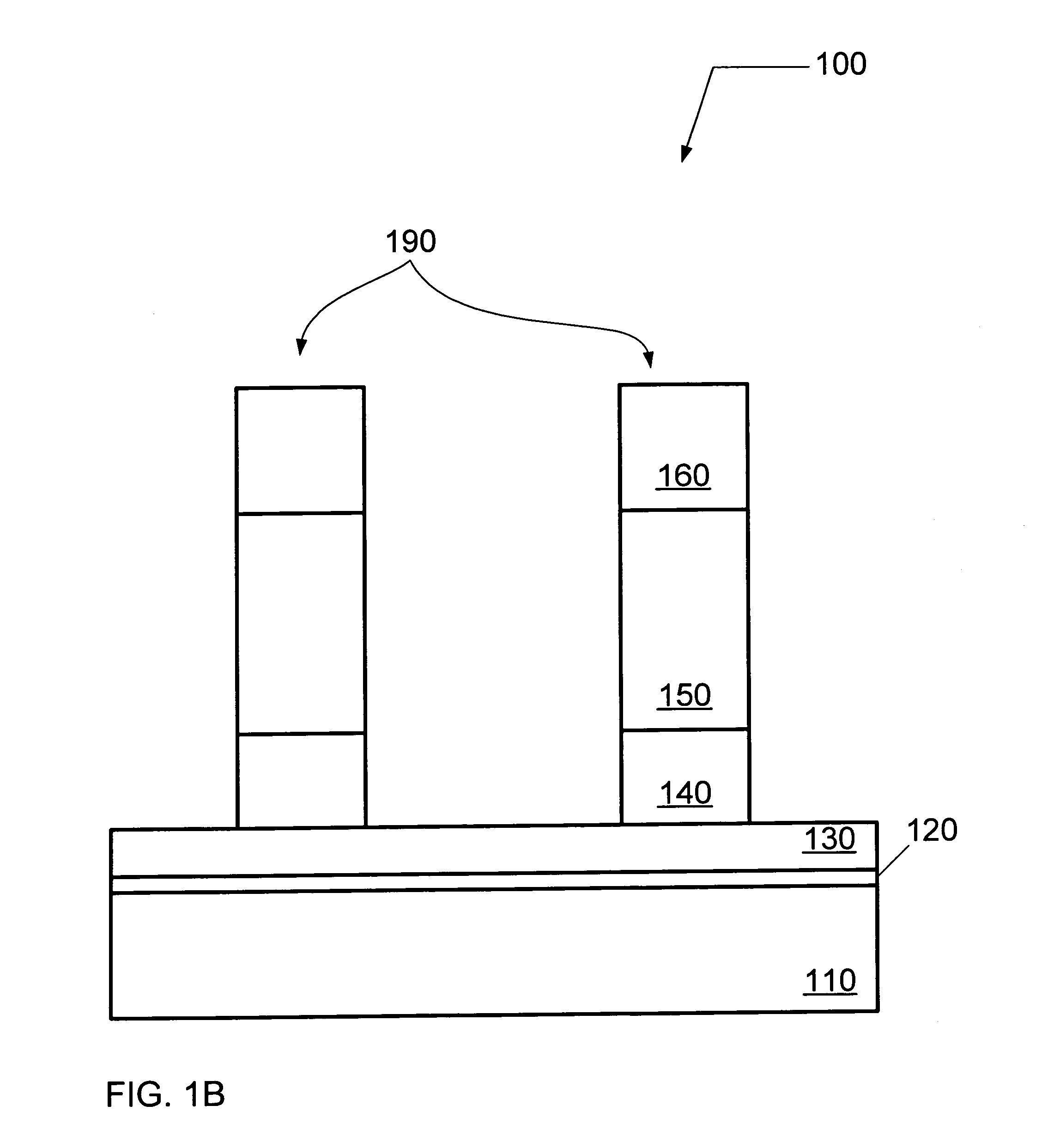
Hafnium(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula HfO₂. Also known as hafnia, this colourless solid is one of the most common and stable compounds of hafnium. It is an electrical insulator with a band gap of 5.3~5.7 eV. Hafnium dioxide is an intermediate in some processes that give hafnium metal.
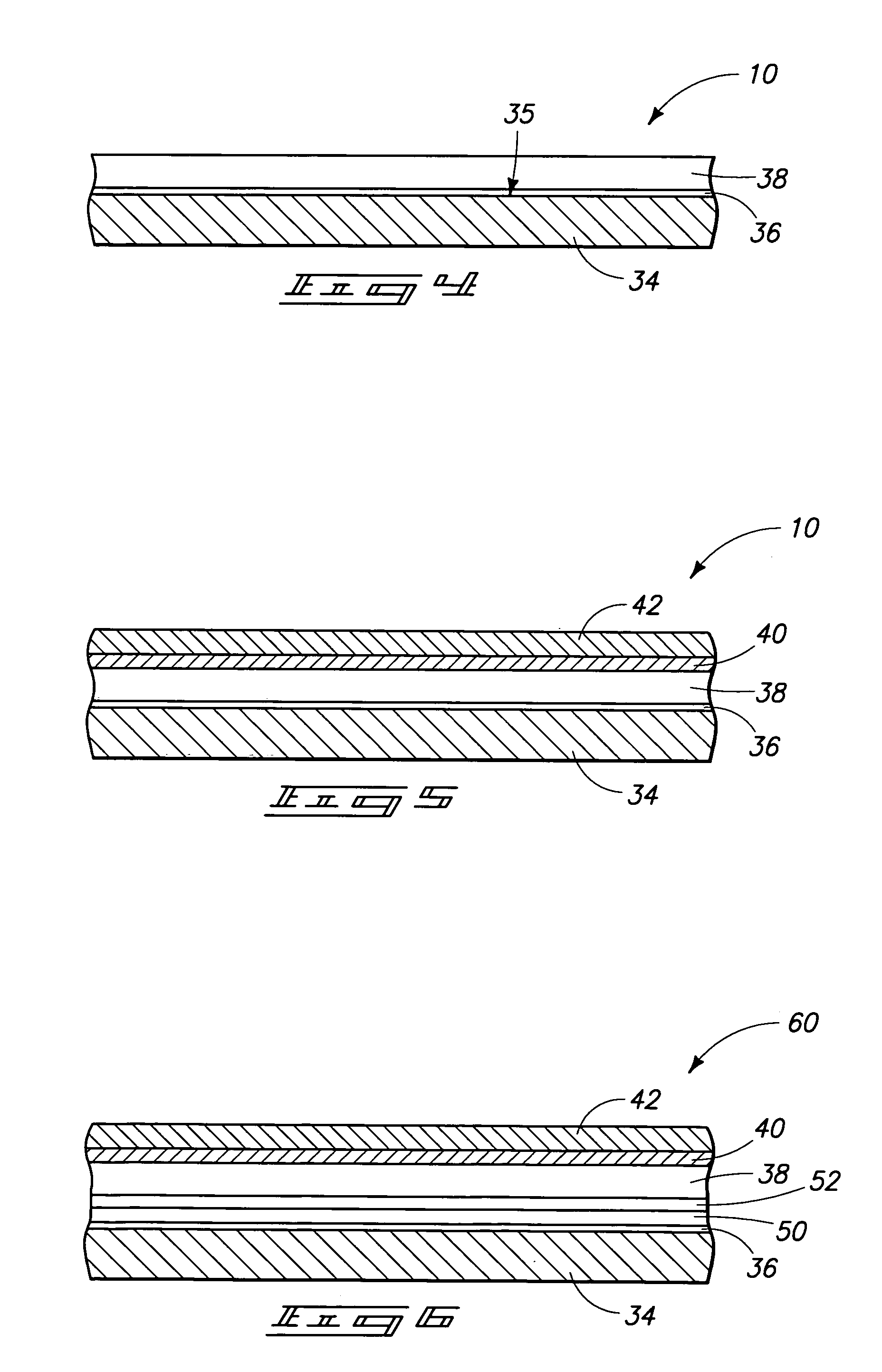
Sintering resistant, low conductivity, high stability thermal barrier coating/environmental barrier coating/environmental barrier coating system for a ceramic-matrix composite (CMC) article to improve high temperature capability
ActiveUS20060121295A1Sufficient thermalSufficient environmental protectionLiquid surface applicatorsBlade accessoriesCoating systemThermal barrier coating
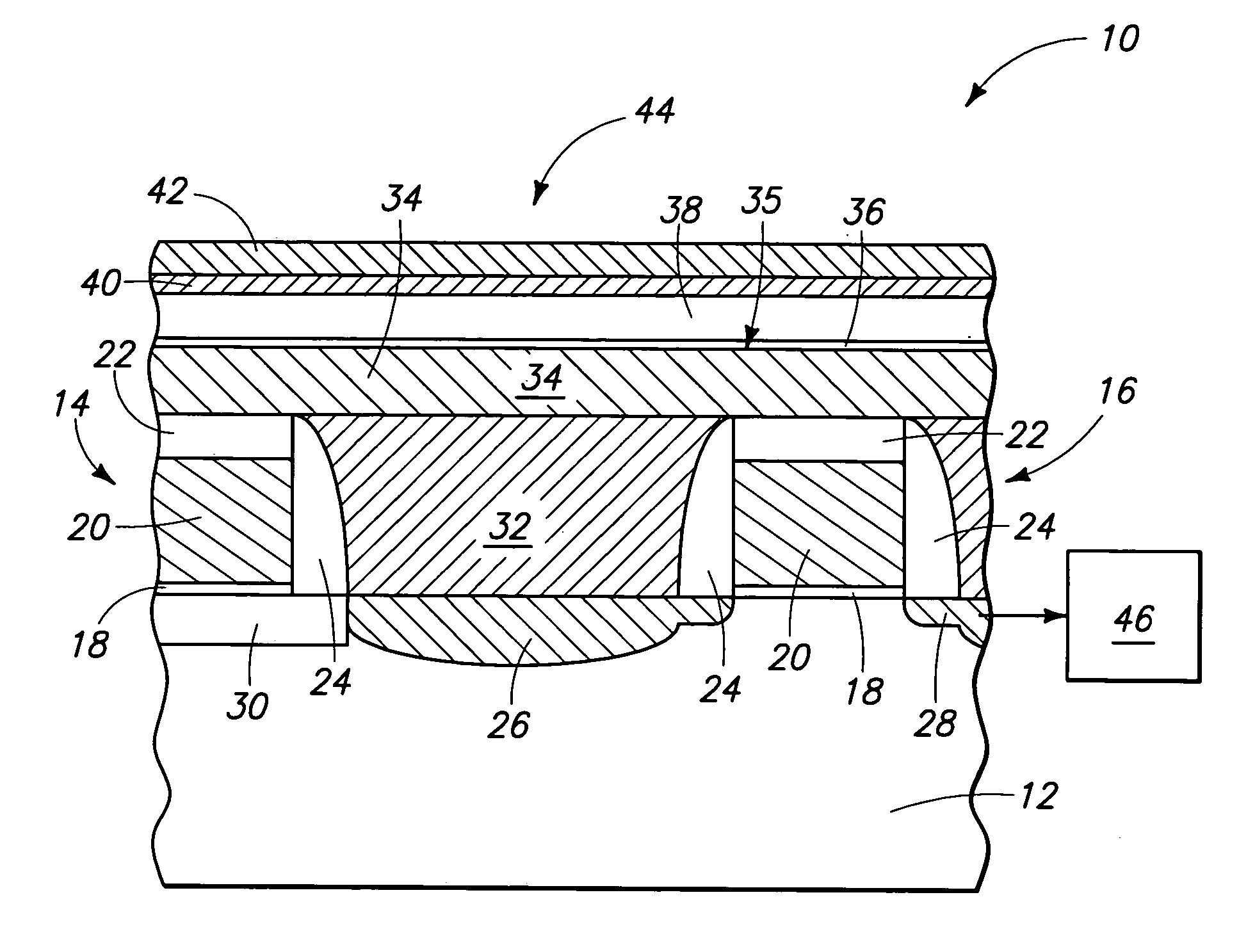
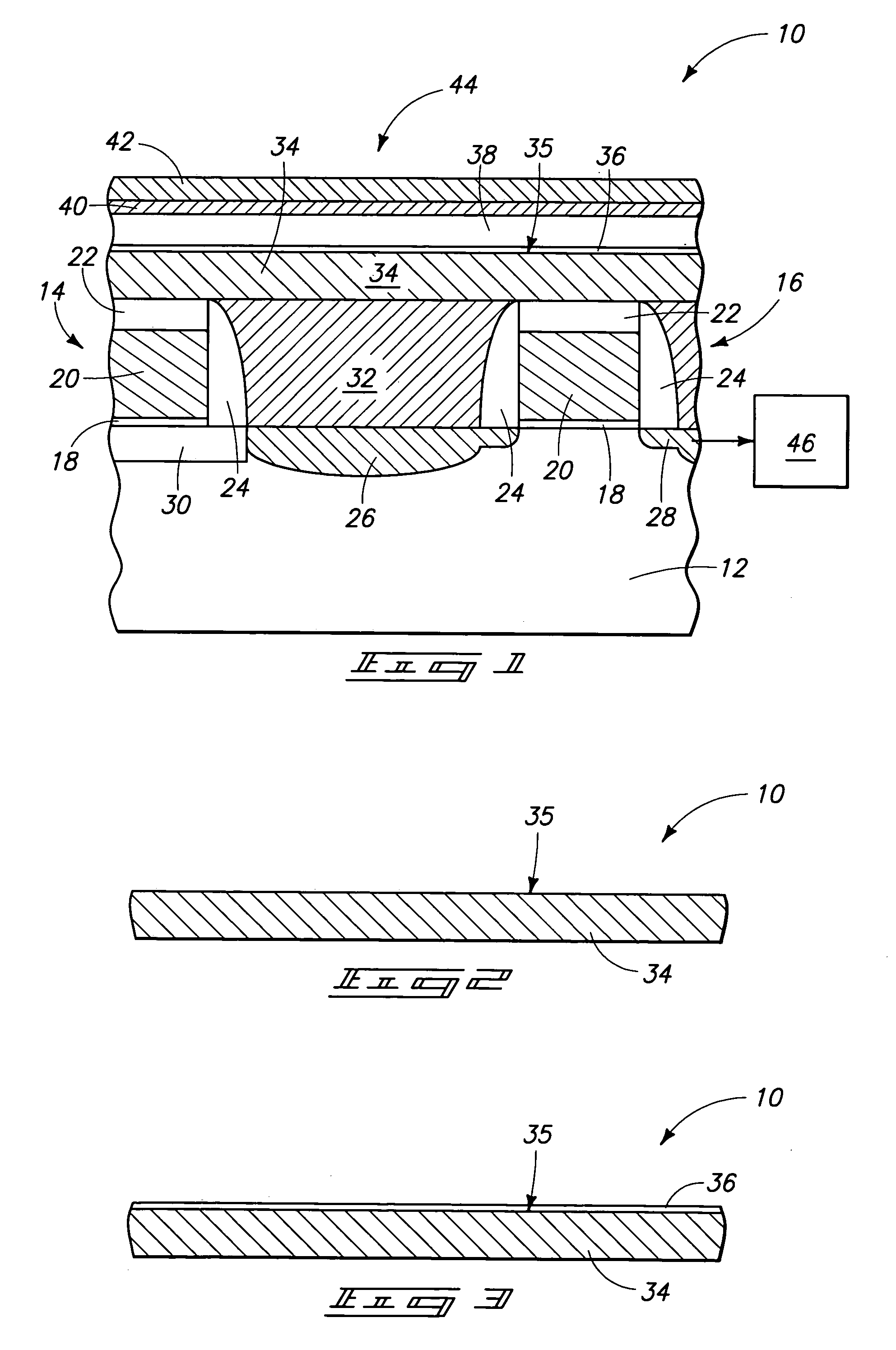
In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, a thermal barrier coating (TBC) for inclusion in a thermal barrier coating / environmental barrier coating system (TBC / EBC system) for use on a silicon containing material substrate is provided. The TBC comprises a compound having a primary constituent portion and a stabilizer portion stabilizing said primary constituent. The primary constituent portion of the TBC comprises hafnia present in an amount of at least about 5 mol % of the primary constituent. The stabilizer portion of said thermal barrier coating comprises at least one metal oxide comprised of cations with a +2 or +3 valence present in the amount of about 10 to about 40 mol % of the thermal barrier coating.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Basic glaze for ink jet printing, preparation method of basic glaze, and ceramic tile
The invention discloses a basic glaze for ink jet printing, a preparation method of the basic glaze, and a ceramic tile. The basic glaze for the ink jet printing comprises the following chemical components by weight percentage: 2.0-3.0% of igloss, 13.0-17.0% of aluminium oxide, 64.0-69.0% of silicon dioxide, 0.05-0.2% of ferric oxide, 0.3-0.9% of calcium oxide, 3.0-6.0% of magnesium oxide, 1.4-2.0% of potassium oxide, 1.4-2.0% of sodium oxide, 0.03-0.10% of titanium oxide, 5.0-10.0% of zirconium dioxide and hafnium oxide, 0.01-0.2% of lithium oxide, and 0.1-2.0% of zinc oxide. The basic glaze for the ink jet printing is free from such defects as deformation, bubbles, pin holes, sewage suction and poor color when an ink jet printing technique is used, and a fabricated product has good color, the surface of a glazed tile is fine and smooth, and the product quality and effect can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG KITO CERAMICS GROUP CO LTD
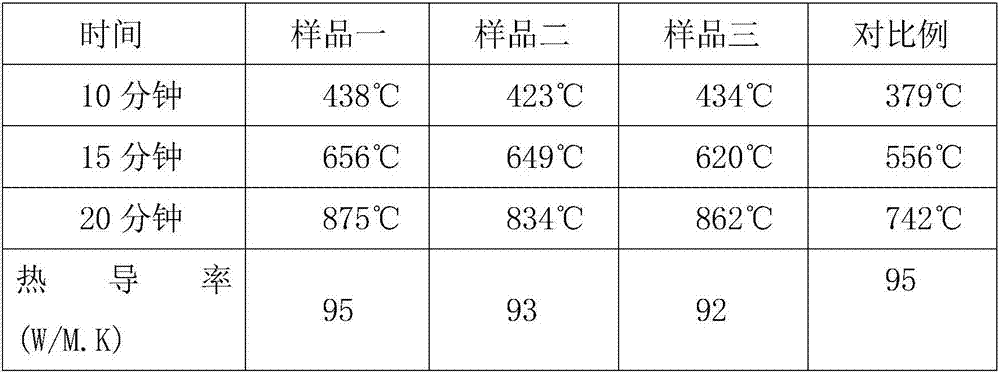
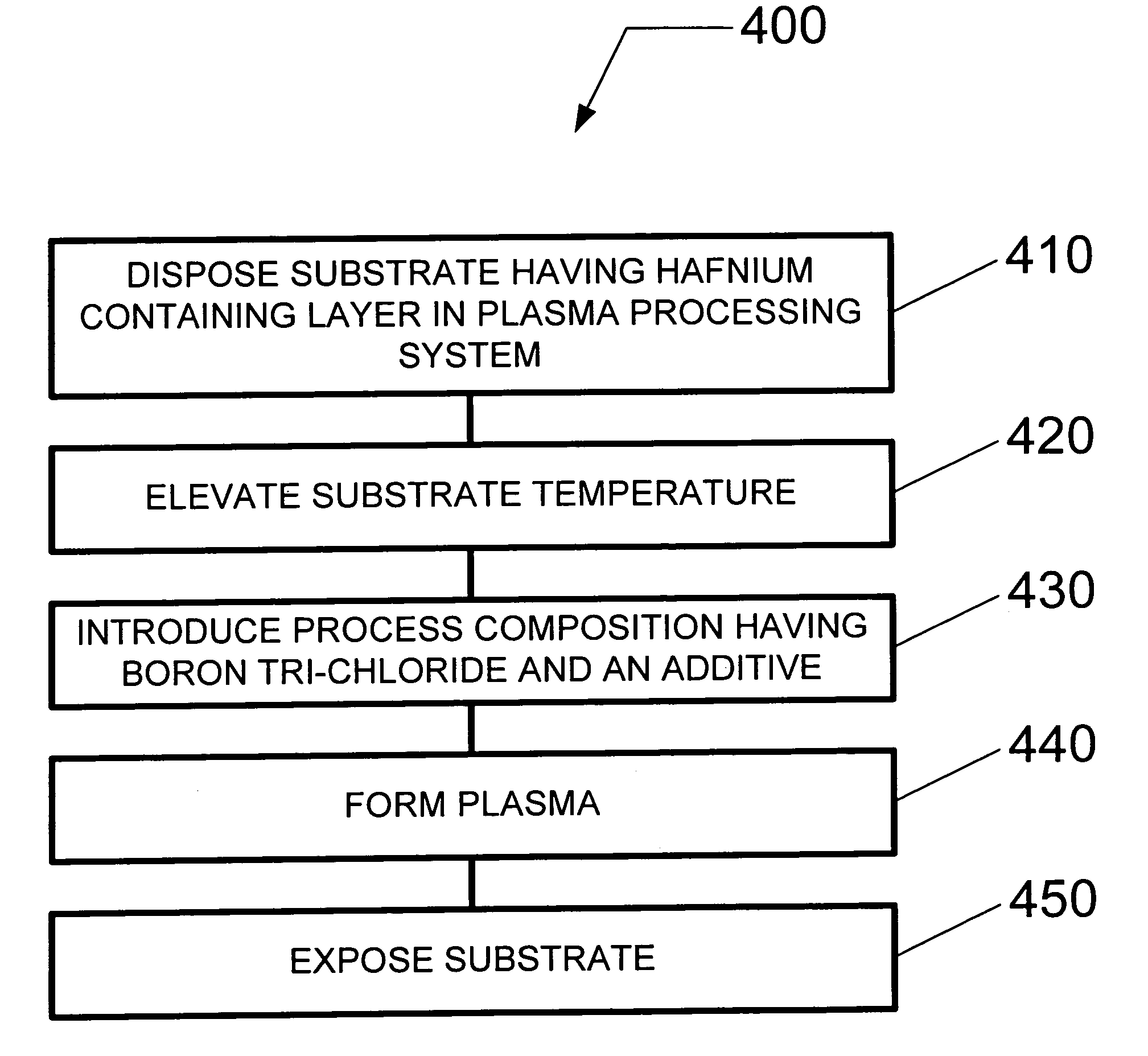
Method and system for dry etching a hafnium containing material
ActiveUS20080064220A1Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsProcess chemistryBoron trichloride
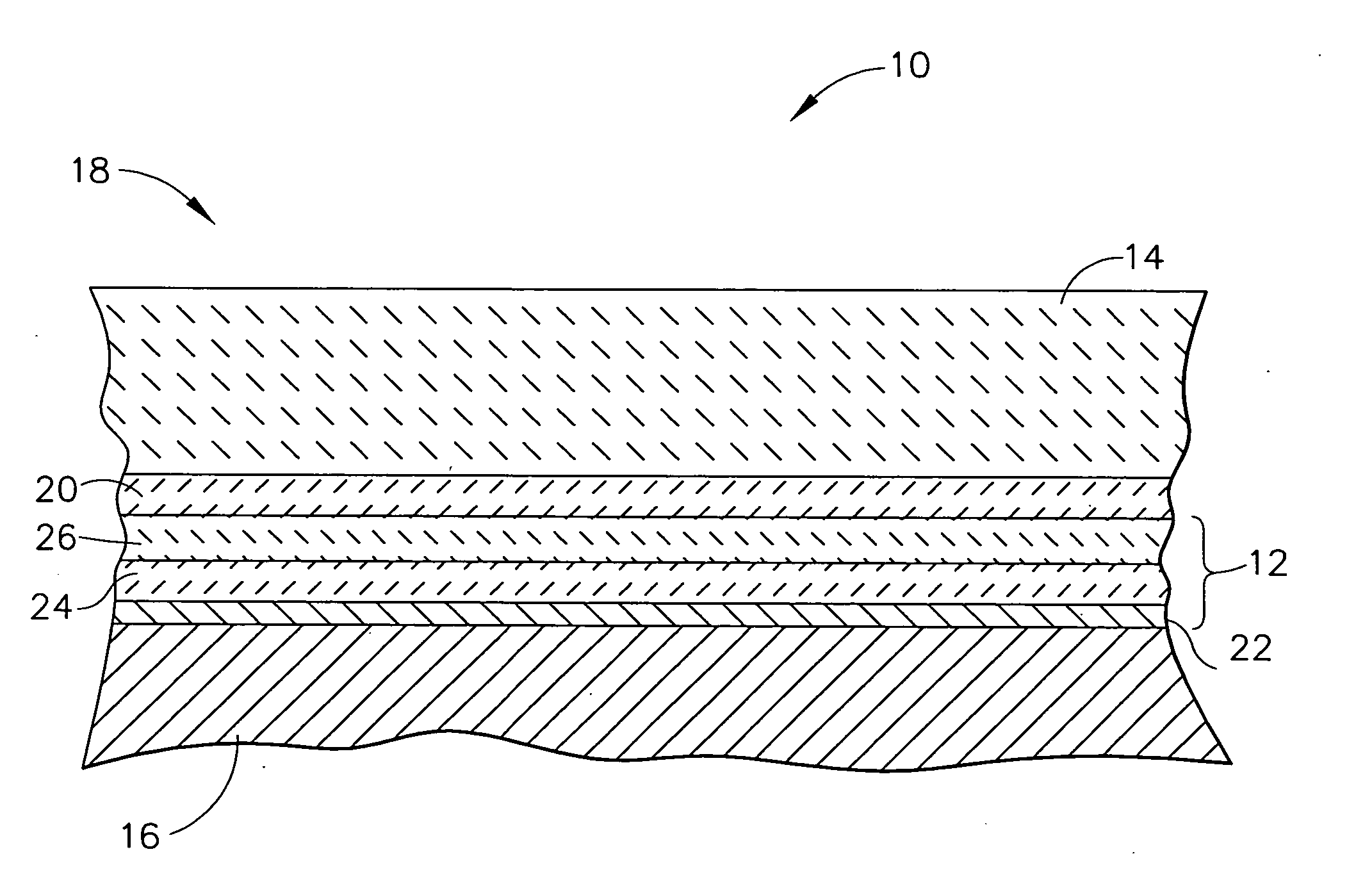
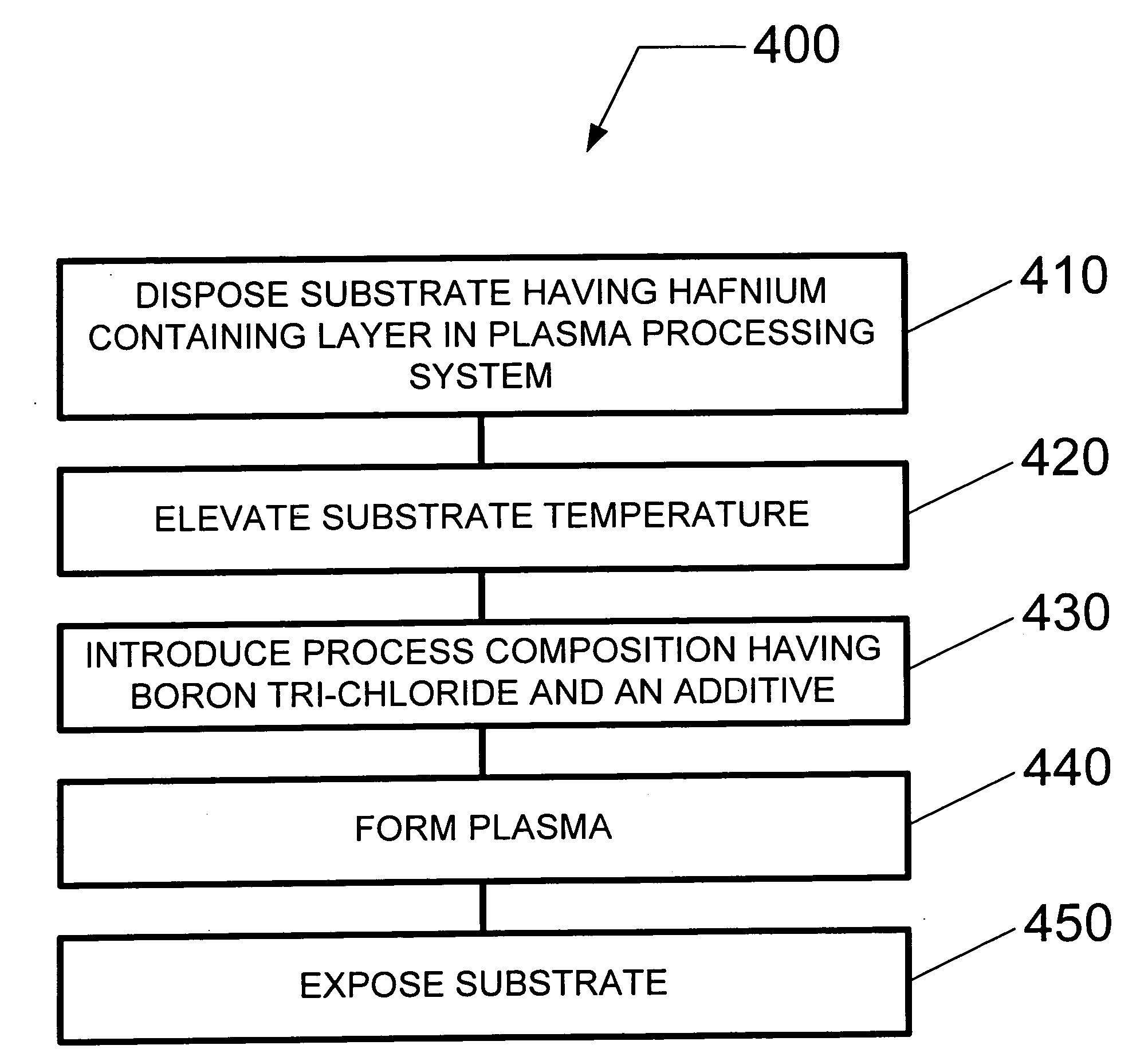
A method and system for etching a hafnium containing material using a boron tri-chloride (BCl3) based process chemistry is described. A substrate having a hafnium containing layer, such as a layer of hafnium dioxide (HfO2) is subjected a dry etching process comprising BCl3 and an additive gas including: an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2; or a nitrogen-containing gas, such as N2; or a hydrocarbon gas (CxHy), such as CH4; or a combination of two or more thereof.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
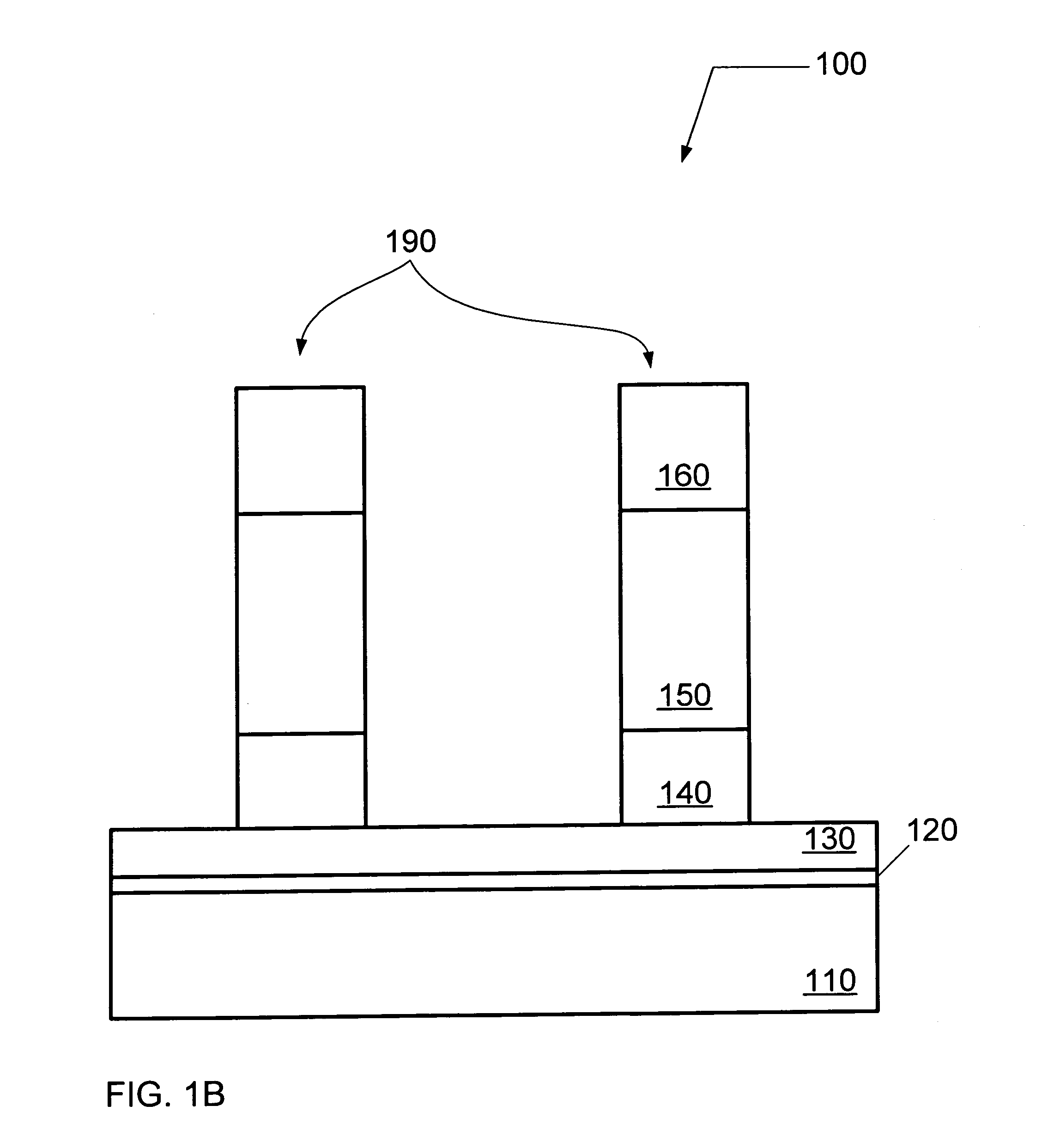
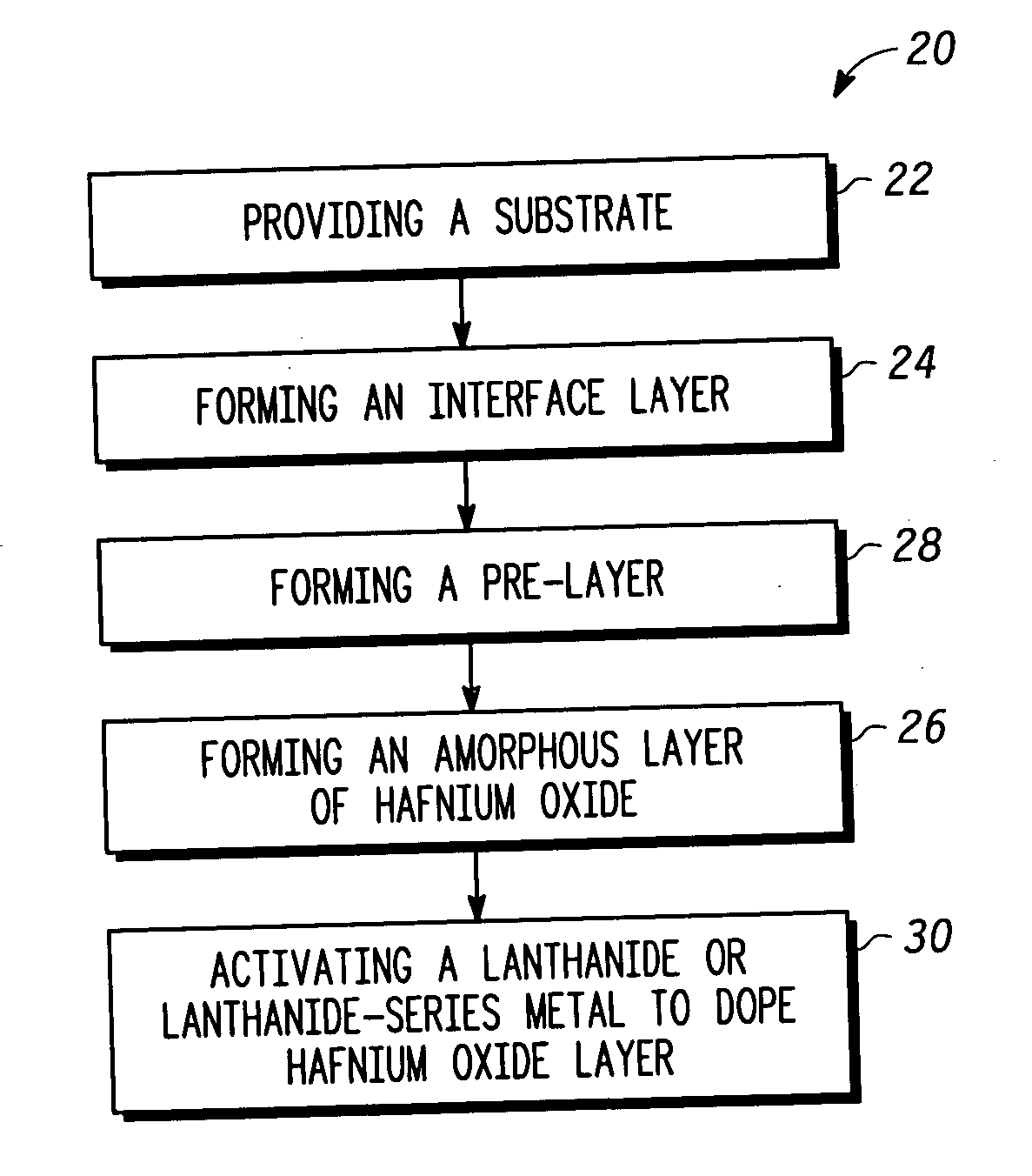
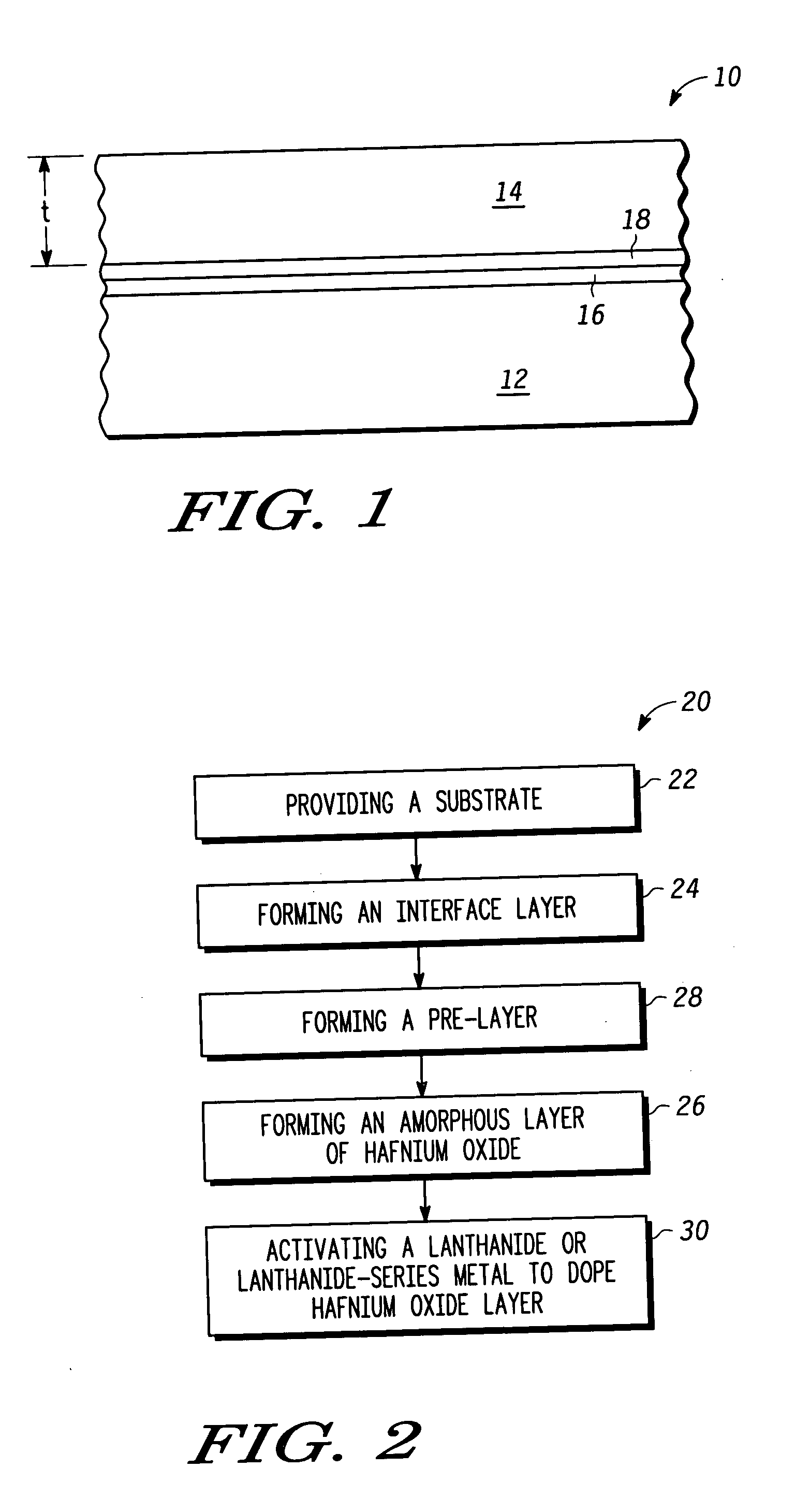
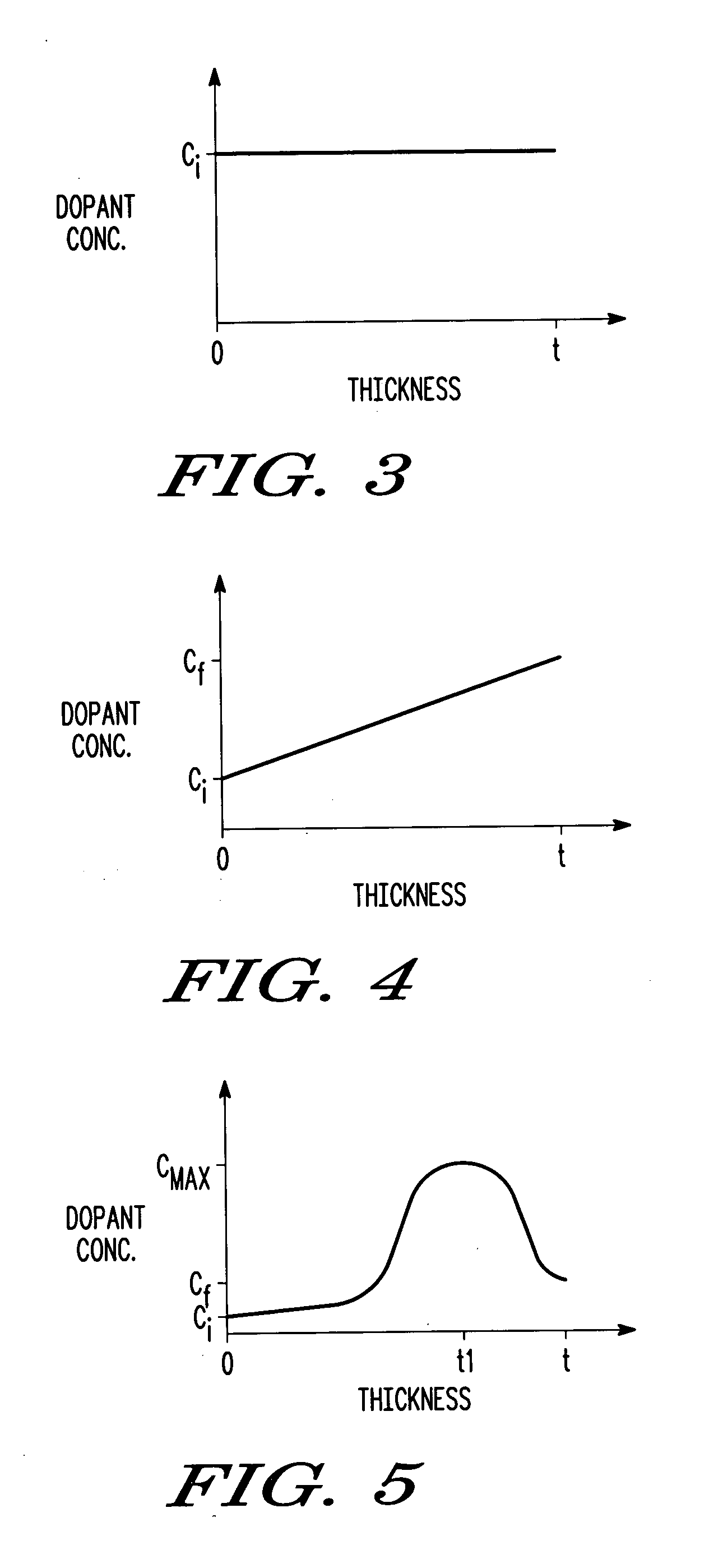
Semiconductor structures and methods of fabricating semiconductor structures comprising hafnium oxide modified with lanthanum, a lanthanide-series metal, or a combination thereof
Semiconductor structures and processes for fabricating semiconductor structures comprising hafnium oxide layers modified with lanthanum oxide or a lanthanide-series metal oxide are provided. A semiconductor structure in accordance with an embodiment of the invention comprises an amorphous layer of hafnium oxide overlying a substrate. A lanthanum-containing dopant or a lanthanide-series metal-containing dopant is comprised within the amorphous layer of hafnium oxide. The process comprises growing an amorphous layer of hafnium oxide overlying a substrate. The amorphous layer of hafnium oxide is doped with a dopant having the chemical formulation LnOx, where Ln is lanthanum, a lanthanide-series metal, or a combination thereof, and X is any number greater than zero. The doping step may be performed during or after growth of the amorphous layer of hafnium oxide.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Tank for melting solder glass
InactiveUS20050022560A1Efficient designGlass furnace apparatusGlass pressing apparatusMelting tankIridium
A melting tank for melting solder glass powders typically comprised of PbO and B2O3 and other minor ingredients. The tank contains surfaces exposed to the atmosphere and surfaces in contact with the molten solder glass. The surfaces of the tank that are in contact with the melt are comprised substantially entirely of iridium. Preferably, the surfaces exposed to the atmosphere contain a coating thereon of a metal or metal oxide such as palladium, ruthenium, rhodium, aluminum oxide, calcium oxide, cerium dioxide, dichromium oxide, hafnium dioxide, magnesium oxide, silicon dioxide, thorium dioxide, zirconia, mullite, magnesia spinel or zircon. It is also preferred that the cavity of the tank have a generally circular shape. The melting tank may be readily fabricated by wrought metallurgical processes or by electroforming.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
IVB-family element modified CaCu3Ti4O12-based pressure-sensitive material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101880158AReduce leakage currentLower intrinsic conductanceChemical compositionChemical element
The invention discloses an IVB-family element modified CaCu3Ti4O12-based pressure-sensitive material and a preparation method thereof. The general formula of a chemical composition of the pressure-sensitive material is CaCu3Ti4-xAxO12, wherein A is one or the composition of several of IVB-family elements in the periodic table of chemical elements and is not Ti, and x is equal to 0.002-2. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: proportioning calcium carbonate, copper oxide, titanium dioxide, zirconium dioxide and hafnium dioxide in a stoichiometric ratio of the CaCu3Ti4-xAxO12, wherein, x is equal to 0.002-2; A is one or the composition of several of the IVB-family elements in the periodic table of chemical elements and is not Ti; then carrying out the processes of ball milling, calcining, secondary ball milling, pelleting, shaping, rubber discharging and high-temperature sintering to finally prepare CaCu3Ti4O12-based ceramic with good pressure-sensitive characteristic. The invention effectively improves the pressure-sensitive characteristic of the ceramic, reduces the leakage current thereof, and simplifies the preparation process while holding the high dielectric performance of the pressure-sensitive ceramic, thereby making the ceramic meet commercial demands.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Novel silane nano trivalent chromium passivation solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103898496AImprove uniformityImprove compactnessMetallic material coating processesChromium CompoundsTitanium zirconium
The invention relates to a novel silane nano trivalent chromium passivation solution and a preparation method thereof, and especially provides a technology and a preparation process of the passivation solution. The formula of the passivation solution is a complex formulation comprising the following raw materials: 3-10 parts of a trivalent chromium compound, 3-8 parts of a titanium zirconium (zirconium silicon) compound, 0-2 parts of zirconium oxide (hafnium dioxide), 0-3 parts of a silane coupling agent, 0-2 parts of a surface wetting agent, 1-5 parts of inorganic acid, 0-0.5 part of an antifoaming agent and 70-90 parts of water. The nano silane trivalent chromium passivation solution prepared by the preparation process has good stability, can be applied to surface treatment of steel, zinc and aluminum to form a nano oxide conversion coating on the workpiece to be processed, and can greatly enhance the uniformity and compactness of a passivation film, so as to improve corrosion resistance of the passivation film. The additional silane coupling agent can improve the adhesion of the film, and hardness and wear resistance of the passivation film, so as to increase the salt fog time of the passivation film.
Owner:苏州禾川化学技术服务有限公司
Electron beam aligning mark based on hafnium oxide and manufacturing method of mark
InactiveCN102969302AReduce manufacturing costHigh melting pointSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectron resistsResist
The invention discloses an electron beam aligning mark based on hafnium oxide, which belongs to the field of micro and nano fabrication of a semi-conductor device. The electron beam aligning mark based on hafnium oxide comprises a substrate and a hafnium oxide thin film mark plated on the substrate. The invention further provides a manufacturing method which specifically comprises the steps of: (1) cleaning the substrate; (2) carrying out spin coating of an electronic resist on the substrate and forming a pattern array with an aligned mark in the electronic resist through an electron beam photolithography technique; (3) evaporating hafnium oxide thin films on the electronic resist and the substrate; and (4) peeling the hafnium oxide thin films attached to the positive electronic resist to obtain the hafnium oxide mark. The aligned mark obtained by the electron beam lithography is prepared by using hafnium oxide which is high temperature resistive, good in adhesion and low in cost. Compared with the conventional 'titanium+gold' marks, the process cost is reduced, the problem that the gold mark and the Si substrate are not adhered well is solved, the adhesion and high temperature bearing capacity of the aligned mark to the substrate are improved, and the higher aligning precision is maintained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for making a refractory ceramic material having a high solidus temperature
ActiveUS20090315227A1Improve homogeneityImprove air tightnessCeramic shaping apparatusCeramicwarePolyvinyl alcoholPolyethylene glycol
A powder metallurgy process for the manufacture of powders of a refractory ceramic material, comprising the consecutive steps of:(i) obtaining a dry mixture of a hafnium dioxide HfO2 powder and an yttrium oxide Y2O3 powder;(ii) step of granulation by pelletization of the dry mixture under stirring in order to obtain a granulated mixture, this granulation step comprising the spraying, into the dry mixture, of an aqueous solution comprising polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG);(iii) drying of the granulated mixture;(iv) filling of a mold with said granulated mixture;(v) isostatical or semi-isostatical pressing of the granulated mixture in order to obtain a compact mixture;(vi) sintering of the compact mixture in order to obtain a refractory ceramic material at a solidus temperature in the range between 2500° C. and 2800° C.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Vacuum coating preparation method of aviation organic glass and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102677002ASolve Adhesion ProblemsSolve the problem of impatienceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAviationEvaporation
The invention relates to a vacuum coating preparation method of an aviation organic glass (polymethylmethacrylate). A set of electronic beam evaporation and ion assisted vacuum coating device is used for continuously preparing a structure of three layers of (auxiliary-main-auxiliary) deposition film series, wherein two auxiliary film layers are respectively located on the bottom layer and the upper layer of a main film layer. The two auxiliary film layers are obtained by heating polytetrafluoroethylene resin liquid, evaporating and vaporizing, spraying into a vacuum chamber, ionizing under ion bombardment, and respectively depositing on the surface of the substrate and above the main film layer. The main film layer is deposited on a bottom layer film by film material (one of zirconium dioxide or hafnium oxide) under electronic beam evaporation and ion assisted bombardment so as to form an optical antireflection film. According to the invention, the structure of three layers of films, which is continuously prepared in vacuum, has the characteristics of high adhesion, high light transmissivity, low haze, friction resistance, weak acid and weak base corrosion resistance and the like. The preparation method provided by the invention is further suitable for vacuum coating of polycarbonate (PC) resin, and can be widely applied in industries of aviation, automobiles, car light outer covers and the like.
Owner:宫杰 +2
Semiconductor constructions comprising aluminum oxide and metal oxide dielectric materials
The invention includes constructions having two dielectric layers over a conductively-doped semiconductive material. One of the dielectric layers contains aluminum oxide, and the other contains a metal oxide other than aluminum oxide (such metal oxide can be, for example, one or more of hafnium oxide, tantalum oxide, titanium oxide and zirconium oxide). The layer containing aluminum oxide is between the layer containing metal oxide and the conductively-doped semiconductive material. The invention includes capacitor devices having one electrode containing conductively-doped silicon and another electrode containing one or more metals and / or metal compounds. At least two dielectric layers are formed between the two capacitor electrodes, with one of the dielectric layers containing aluminum oxide and the other containing a metal oxide other than aluminum oxide. The invention also includes methods of forming capacitor constructions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Bilayer gate dielectric with low equivalent oxide thickness for graphene devices
A silicon nitride layer is provided on an uppermost surface of a graphene layer and then a hafnium dioxide layer is provided on an uppermost surface of the silicon nitride layer. The silicon nitride layer acts as a wetting agent for the hafnium dioxide layer and thus prevents the formation of discontinuous columns of hafnium dioxide atop the graphene layer. The silicon nitride layer and the hafnium dioxide layer, which collectively form a low EOT bilayer gate dielectric, exhibit continuous morphology atop the graphene layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microwave silicon carbide ceramics heating element and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106966733AImprove absorbing performanceImprove high temperature resistanceCeramic shaping apparatusCeramicwareLanthanumSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a microwave silicon carbide ceramics heating element and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of the ceramic material. The microwave silicon carbide ceramics heating element is formed by sintering after mixing and pressing microwave absorbing ceramic powder and a bonder. The microwave absorbing ceramic powder comprises the following raw materials by weight percentage: 68%-73% of silicon carbide, 1%-5% of aluminum oxide, 1%-6% of zirconium oxide, 18%-23% of ferroferric oxide, 1%-6% of hafnium oxide, 1%-6% of silicon dioxide, 1%-5% of yttria, and 2%-5% of lanthanum trioxide. The ceramics heating element is capable of rapidly warming under the microwave function, and has the characteristics of high thermal efficiency, stable performance, and energy-saving.
Owner:顼吉君
Method and system for dry etching a hafnium containing material
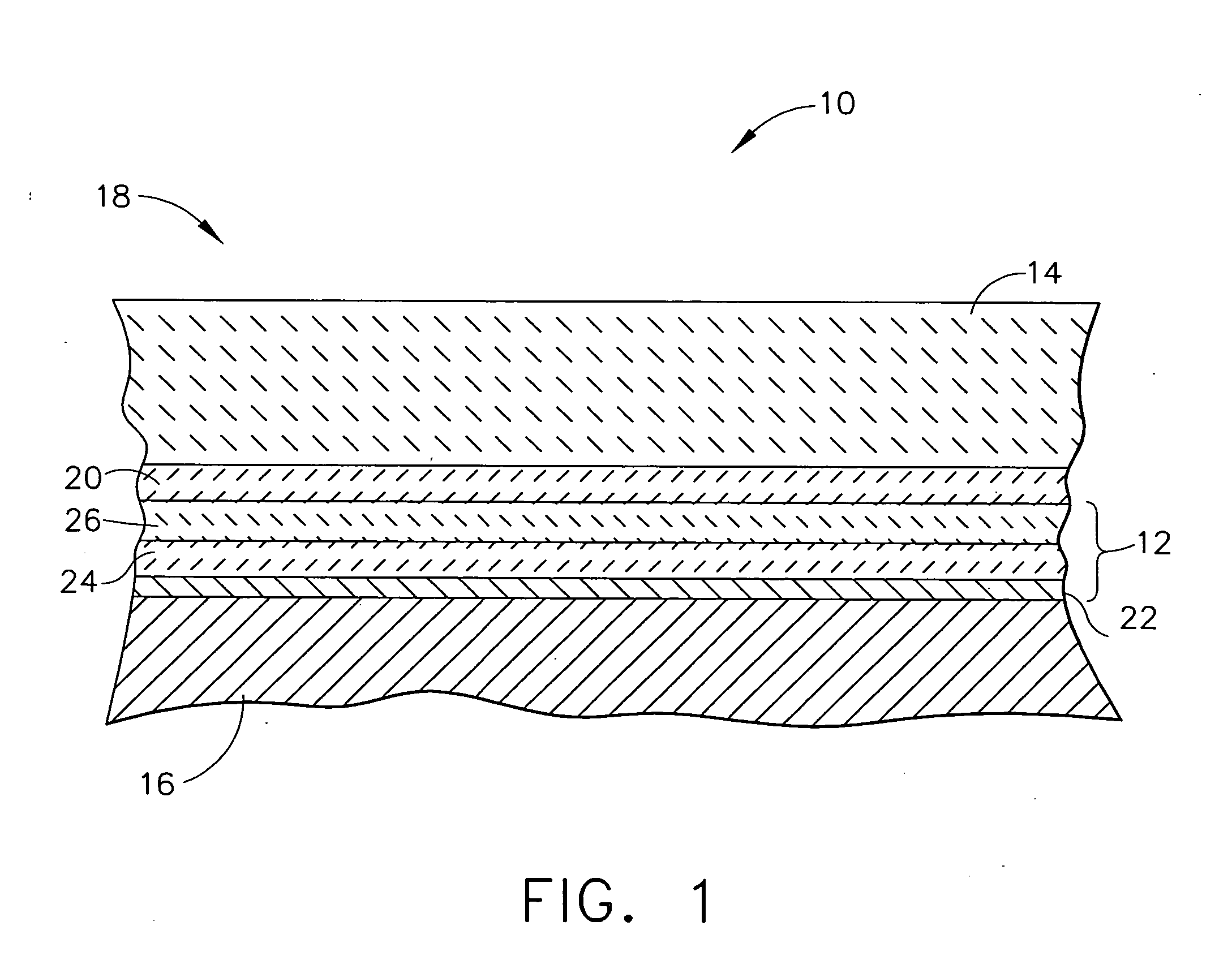
ActiveUS8183161B2Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsProcess chemistryBoron trichloride
A method and system for etching a hafnium containing material using a boron tri-chloride (BCl3) based process chemistry is described. A substrate having a hafnium containing layer, such as a layer of hafnium dioxide (HfO2) is subjected a dry etching process comprising BCl3 and an additive gas including: an oxygen-containing gas, such as O2; or a nitrogen-containing gas, such as N2; or a hydrocarbon gas (CxHy), such as CH4; or a combination of two or more thereof.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Multilayer structure used especially as a material of high relative permittivity
InactiveUS20030129446A1Improved performance characteristicsImprove cohesionTransistorThin/thick film capacitorAlloyRelative permittivity
Multilayer structure, used especially as a material of high relative permittivity, characterized in that it comprises a plurality of superposed elementary layers, each with a thickness of less than about 500 Å, among which there are two layers based on an alloy of titanium dioxide (TiO2) and tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5), these layers being separated by an interlayer of an alloy based on at least hafnium dioxide (HfO2) an alumina (Al2O3).
Owner:SAKURATECH
Electric field assisted quick sintering method of ultrafine-grained hafnium oxide ceramic
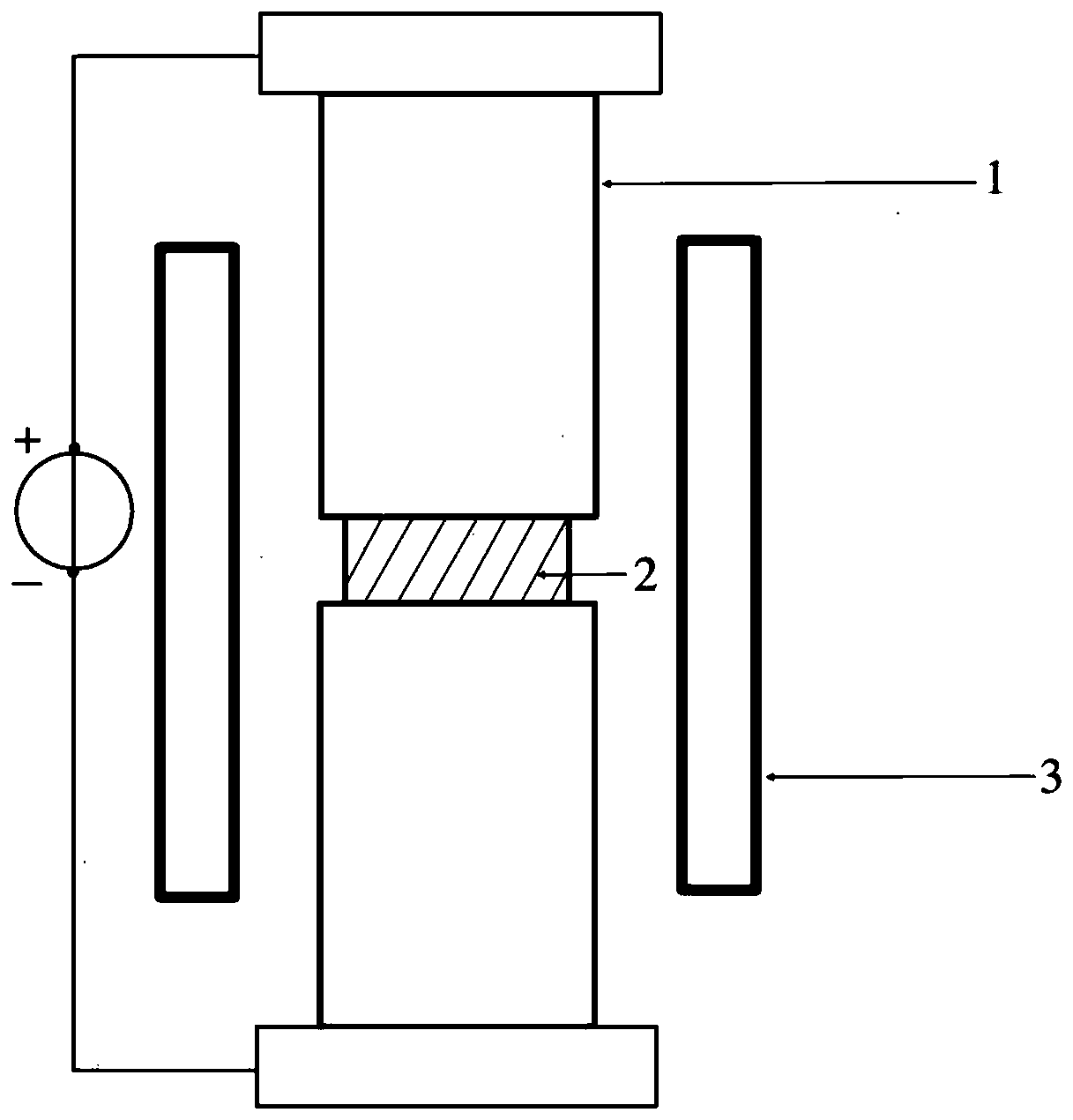
InactiveCN109734445ASolve the problem that it is difficult to sinter densely with traditional sintering methodsDense and fastMaterials scienceElectric field
The invention provides an electric field assisted quick sintering method of ultrafine-grained hafnium oxide ceramic, which is characterized by comprising the steps of 1) weighing HfO2 powder, and pressing to obtain a blank; 2) providing an electric field assisted sintering device; 3) placing a sample between an upper electrode and lower electrode of the electric field assisted sintering device, heating the sample to 800-1300 DEG C through at least two radiation heaters, and starting to enter a temperature holding phase; 4) upon entry to the temperature holding phase, raising voltages of the two ends of the sample in multiple phases, disabling the voltages of the ends of the sample, and closing the radiation heaters so that the sample naturally cools to room temperature to obtain the ultrafine-grained hafnium oxide ceramic. The direct-current electric field assisted sintering technique is utilized herein to quickly produce hafnium oxide ceramic; the hafnium oxide ceramic with high compactness and uniform grain size is produced by controlling the process conditions, such as threshold temperature, field intensity, and current.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of high K hafnium dioxide amorphous film
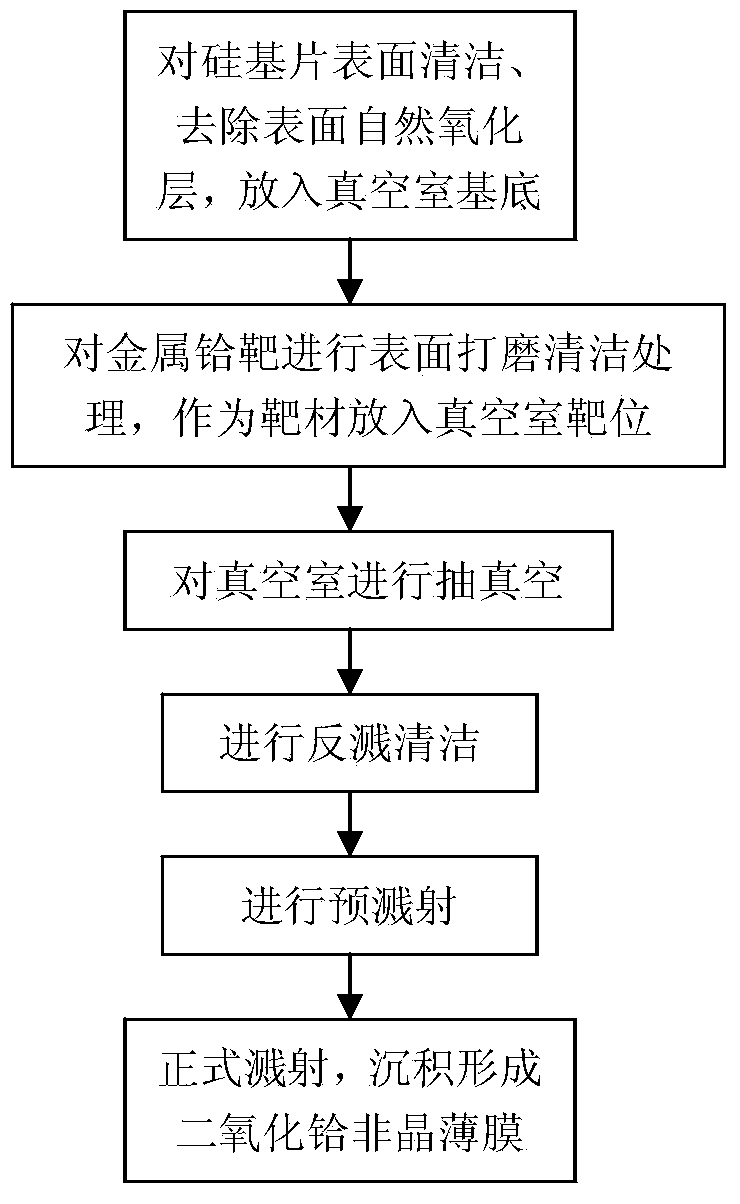
InactiveCN103451612AOptimize tissue ratioImprove compactnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHafniumOxygen
The invention relates to a semiconductor technology, and provides a preparation method of a high K hafnium dioxide amorphous film, which solves the problem that preparation processes of existing HfO2 film materials adopt a doping or heating mode to prepare the HfO2 film materials so that amorphous films can not be entirely generated. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly putting a silicon substrate into a vacuum chamber base after the surface of the silicon substrate is cleaned and a natural oxidation layer on the surface is removed, secondly putting a metal hafnium target with surface polished and cleaned into a target position in a vacuum chamber as a target, closing a target baffle, utilizing high vacuum multifunctional radio frequency sputtering coating equipment to vacuumize the vacuum chamber, carrying out backwash cleaning on the substrate, switching on a radio frequency power supply and adjusting the power of the radio frequency power supply after backwash cleaning, carrying out pre-sputtering, finally adjusting the argon flux, filling oxygen and opening the target baffle to formally sputter a hafnium dioxide film, thus forming the hafnium dioxide amorphous film. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that crystallization of the hafnium dioxide film can not be caused, and the preparation method is suitable for preparation of the hafnium dioxide amorphous film.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Pyrometallurgical separation method for zirconia/hafnium dioxide mixture
ActiveCN103725901AEasy to separateInvestment economyRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementHafnium tetrabromideZirconium(IV) bromide
The invention relates to a pyrometallurgical separation method for a zirconia / hafnium dioxide mixture. The zirconia / hafnium dioxide mixture, carbon and pure bromine react at 650 DEG C for 1 hour to obtain bromides of zirconium and hafnium, the bromides of the zirconium and the hafnium are added into a fused salt mixture to perform rectification separation, the temperature of the tower bottom of a rectifying tower is kept below 357 DEG C for 2 hours, and a non-target is obtained; the non-target is kept at 357 DEG C for 5 hours, and a target, namely high-purity zirconia tetrabromide is collected; residue in a kettle is stored; rectification separation is performed in the same equipment, the temperature is increased to 400 DEG C and kept for over 5 hours, hafnium tetrabromide is obtained, and the zirconia tetrabromide and the hafnium tetrabromide are respectively subjected to metathesis to obtain pure zirconium and pure hafnium. The separation effect is good, and the equipment investment is economical, so that industrialization is facilitated. The pyrometallurgical separation method can fill a blank in China, and greatly contributes the localization of zirconia / hafnium nuclear materials.
Owner:ЧЖУ, СИНФЭН
Multilayer structure used especially as a material of high relative permittivity
InactiveUS20030207097A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNatural mineral layered productsLanthanideHafnium
Multilayer structure, used especially as a material of high relative permittivity, characterized in that it comprises a plurality of separate layers, each having a thickness of less than 500 Å. Some of those layers are based on aluminium, hafnium and oxygen and especially based on hafnium dioxide (HfO2) and on alumina (Al2O3). In practice, the hafnium dioxide and alumina layers form alloys of formula HfxAlyOz. Advantageously, the stoichiometry of the HfxAlyOz varies from one layer to another. Some of the layers containing HfxAlyOz alloys, or some of the layers between those containing HfxAlyOz alloys, also include a lanthanide element.
Owner:SAKURATECH
Low-dimensional nano photodetector based on in-plane asymmetric local field control and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108400198AReduce dark currentEasy to separateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIn planeNon symmetric
The invention discloses a low-dimensional nano photodetector based on in-plane asymmetric local field control and a preparation method thereof. The device structure sequentially includes a substrate,an oxide layer, a nano semiconductor, source and drain electrodes and a dielectric layer from bottom to top. The preparation steps of the device are as follows: transferring ultra-thin zinc oxide (ZnO) nanosheets grown by using a CVD method onto a silicon substrate with the oxide layer, preparing the source and drain electrodes by using electron beam exposure, thermal evaporation and other processes, and then preparing a hafnium dioxide (HfO2) dielectric layer by using electron beam exposure, atomic layer deposition and other processes, and finally preparing a low-dimensional nano photodetector. By introducing asymmetric HfO2, the partial adsorption of charged gas molecules on the nanosheets is formed to control the concentration of carriers on both sides of the zinc oxide nanosheets, andthus an in-plane asymmetric local field is formed, the response speed of the device can be finally increased, and the device can also show an ultra-high detection rate. The scheme of the invention hasthe advantages of simple preparation, fast response speed, low dark current, high detection rate and low power consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for atomic energy level hafnium dioxide
InactiveCN111020230AIncrease concentrationQuality improvementProcess efficiency improvementPhysical chemistryWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of wet-process zirconium and hafnium metallurgy, and particularly relates to a preparation method for atomic energy level hafnium dioxide. According to themethod, P204 is adopted as an extraction agent to extract and enrich hafnium in raffinate, the concentration of the hafnium in the enriched hafnium solution can be improved by 20-30 times, the consumption of caustic soda for precipitation is obviously reduced, and a precipitation mother solution can return to prepare a stripping agent; hafnium-extracted raffinate water can return to a zirconium and hafnium separation system for recycling or for producing a sodium nitrate product; the color of the produced hafnium dioxide is white, and the total impurity content conforms to the atomic energy level hafnium dioxide quality standard; and compared with direct precipitation of the raffinate, the preparation method has the advantages that the waste water amount is reduced by 60% or above, the raffinate can be recycled, the consumption of the caustic soda is reduced by 85% or above, the production cost is low, the product quality of the hafnium dioxide is stable, and obvious social benefits and obvious economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:中核二七二铀业有限责任公司
Three-dimensional tapered nano-layer film structure, preparation method thereof and application thereof
PendingCN109943810AEnhanced infrared absorptionSolve the technical defect of low net radiative cooling powerMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingCooling powerSilicon dioxide
The invention belongs to the field of novel energy technical development, in particular to a three-dimensional tapered nano-layer film structure, a preparation method thereof and application thereof.The three-dimensional tapered nano-layer film structure provided by the invention comprises silicon dioxide layer-hafnium dioxide composite layers and sliver layers, wherein silicon dioxide layers arearranged above hafnium dioxide layers; number of the silicon dioxide layer-hafnium dioxide composite layers is greater than 10; and the silicon dioxide layer-hafnium dioxide composite layers are arranged above the sliver layers. The invention further provides a preparation method for the three-dimensional tapered nano-layer film structure, and further provides application of the three-dimensionaltapered nano-layer film structure or a product prepared by the preparation method in a radiation cooling device. The three-dimensional tapered nano-layer film structure is introduced, so that high-performance dual-window atmospheric radiation can be realized, and high-efficiency passive radiation cooling ability can be finally realized. The technical defect that a daytime cooling method has low net radiation cooling power in the prior art is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Refractory ceramic material having a high solidus temperature, its manufacturing process and structural part incorporating said material
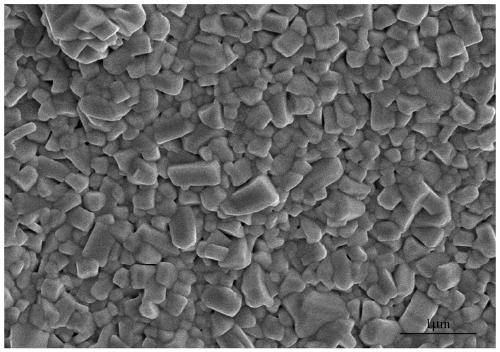
ActiveUS8236414B2Preserving a solidus temperatureUseful working temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyNatural mineral layered productsYttriumMicrostructure
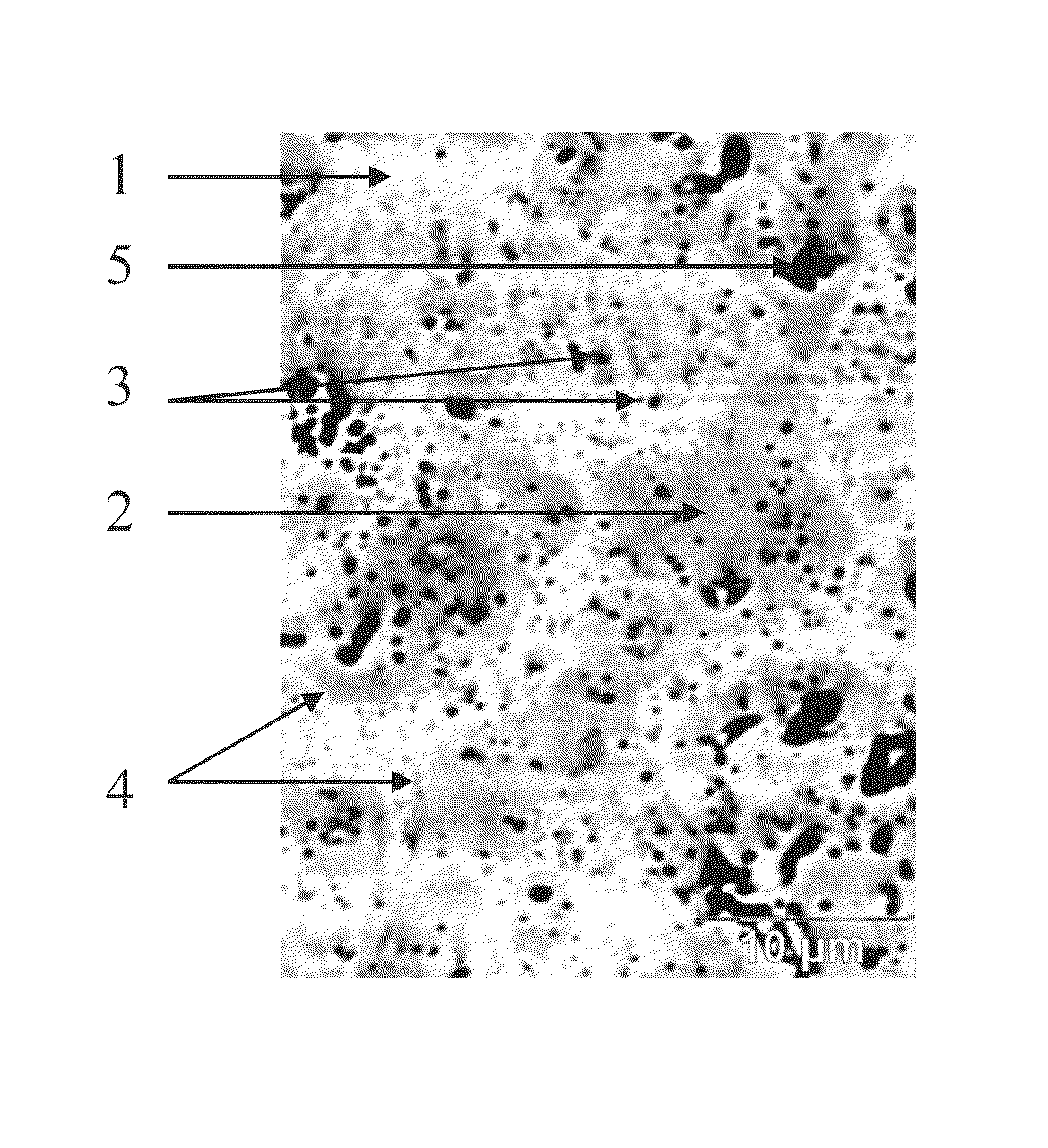
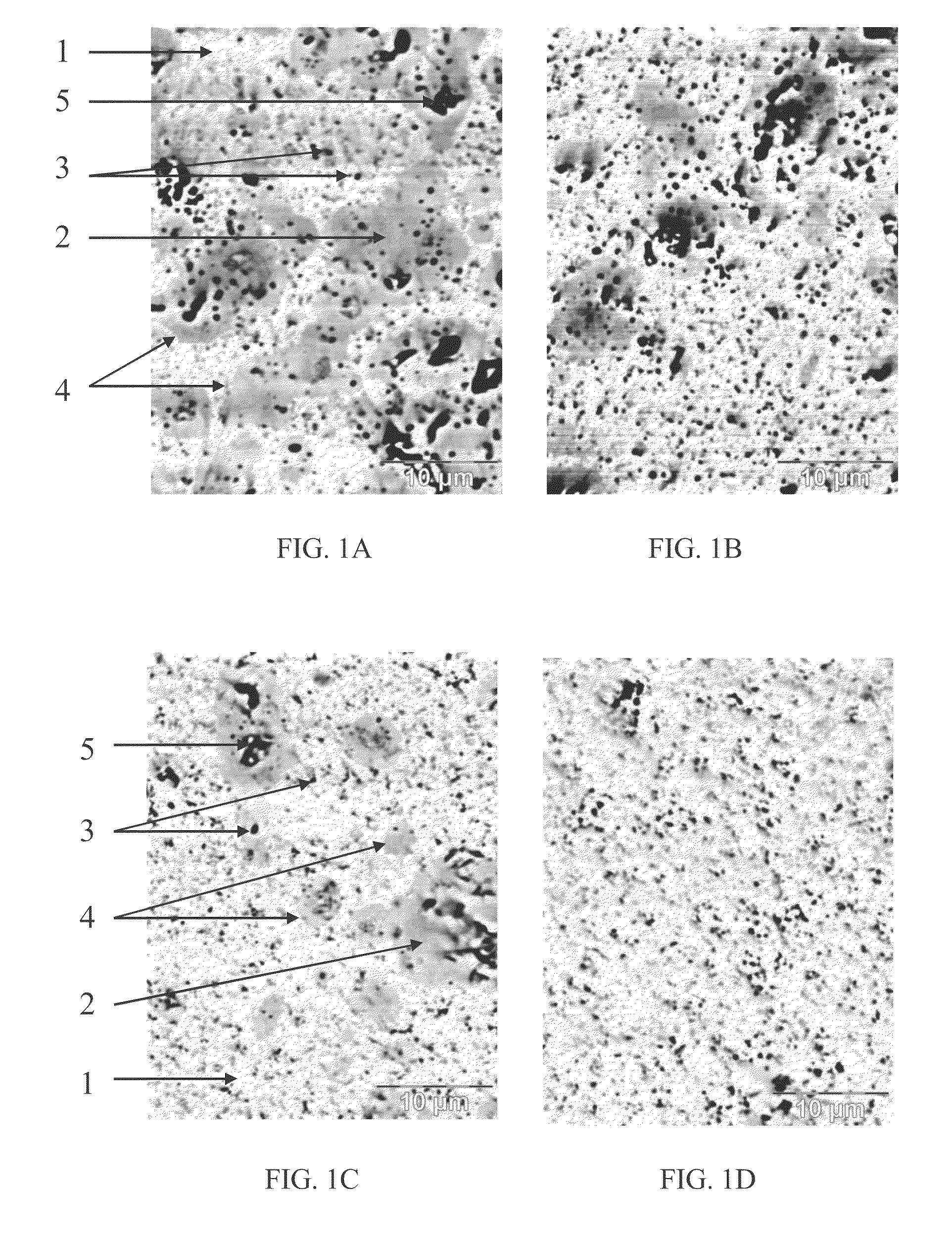
A refractory ceramic material possessing a solidus temperature between 2500° C. and 2800° C., having a compactness greater than 85%, and a microstructure such that the material is composite of: (a) hafnium dioxide HfO2 grains having a monoclinic structure (1); (b) hafnium dioxide HfO2 grains having a cubic structure (2) which is stabilized by yttrium oxide Y2O3, the yttrium oxide Y2O3 representing 0.5 mol % to 8 mol % relative to the total number of moles of hafnium dioxide HfO2; (c) closed pores (3); (d) non-interconnected open pores. The process of manufacturing the material and a structural part incorporating the material are also set forth.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Method for preparing hafnium-oxide-based thin ferroelectric film by using all-inorganic precursor solution and application
InactiveCN108493102ALow costSimple equipment requirementsSemiconductor devicesMaterials preparationElectricity
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of material preparation, discloses a method for preparing a hafnium-oxide-based thin ferroelectric film by using an all-inorganic precursor solutionand application of the film. A hafnium-oxide-based precursor solution doped with different elements is prepared by using inorganic hafnium salt and an inorganic high-symmetry phase stabilizer as rawmaterials; a substrate is cleaned based on a standard RCA process to remove impurity contamination on the surface of the substrate and then the substrate is preprocessed to enhance wettability of thesurface of the substrate; a hafnium-oxide-based thin film is deposited on the surface of the substrate; and then pre-heat treatment and annealing crystallization are carried out on the thin film to realize stability of the high-symmetry quadrature phase, tetragonal phase, cubic phase or other mixed phase at a room temperature, so that the thin film having the initially intrinsic property may generate a ferroelectric property under the field induction. According to the method, the prices of the raw materials are low and thus the cost is lowered; the equipment and operation environment requirements are simple; the types of the doped elements are diversified and thus selection becomes flexible; the ferroelectric property is easy to control; and the industrialized production is realized easily.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of low leakage current HfO2 film suitable for gate dielectric layer
InactiveCN103451611AReduce leakage currentVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGate dielectricHafnium
The invention relates to a semiconductor technology, and provides a preparation method of a low leakage current HfO2 film suitable for a gate dielectric layer, which solves the problem that preparation processes of existing HfO2 gate dielectric film materials are unfavourable for large-scale preparation of films. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly putting a silicon substrate into a vacuum chamber base after the surface of the silicon substrate is cleaned and a natural oxidation layer on the surface is removed, secondly putting a metal hafnium target with surface polished and cleaned into a target position in a vacuum chamber as a target, closing a target baffle, utilizing high vacuum multifunctional radio frequency sputtering coating equipment to vacuumize the vacuum chamber, carrying out backwash cleaning on the substrate, switching on a radio frequency power supply and adjusting the power of the radio frequency power supply after backwash cleaning, carrying out pre-sputtering, finally adjusting the argon flux, opening the target baffle, pre-depositing an ultra-thin hafnium film and filling oxygen to formally sputter a hafnium dioxide film, thus forming the hafnium dioxide film. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the preparation method is convenient for large-scale preparation and is suitable for MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) capacitors.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
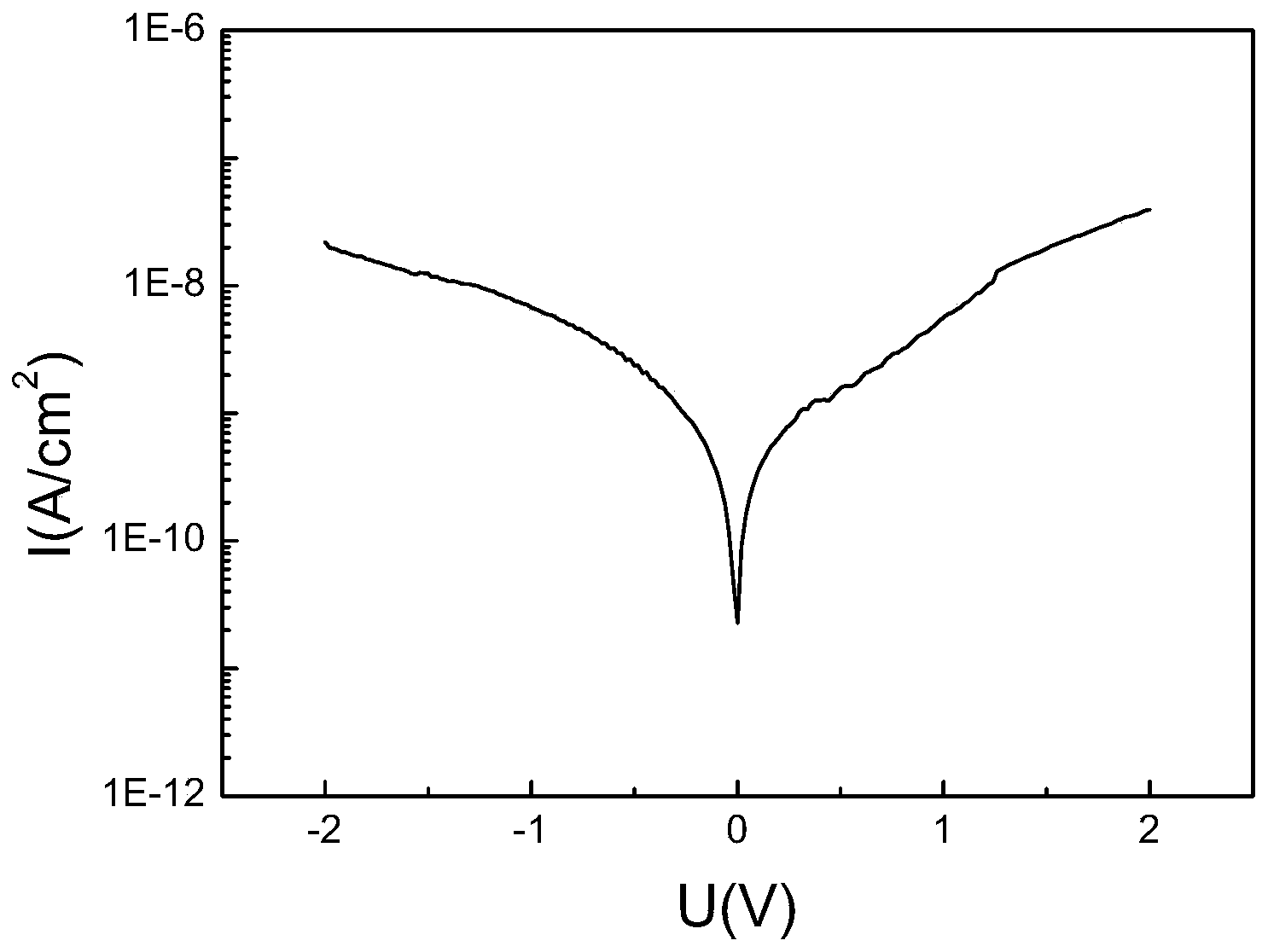
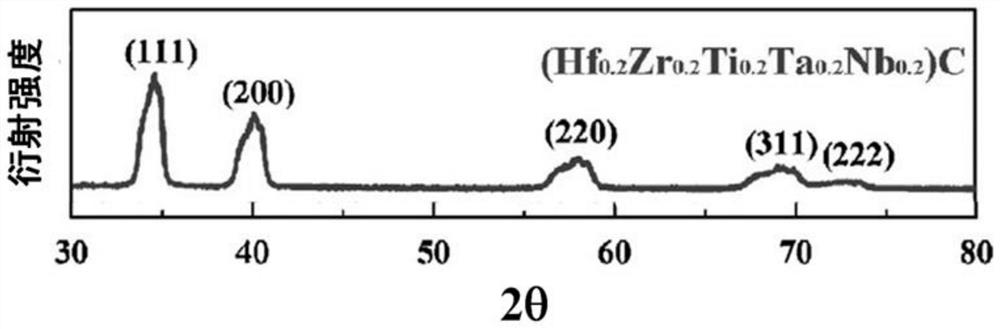
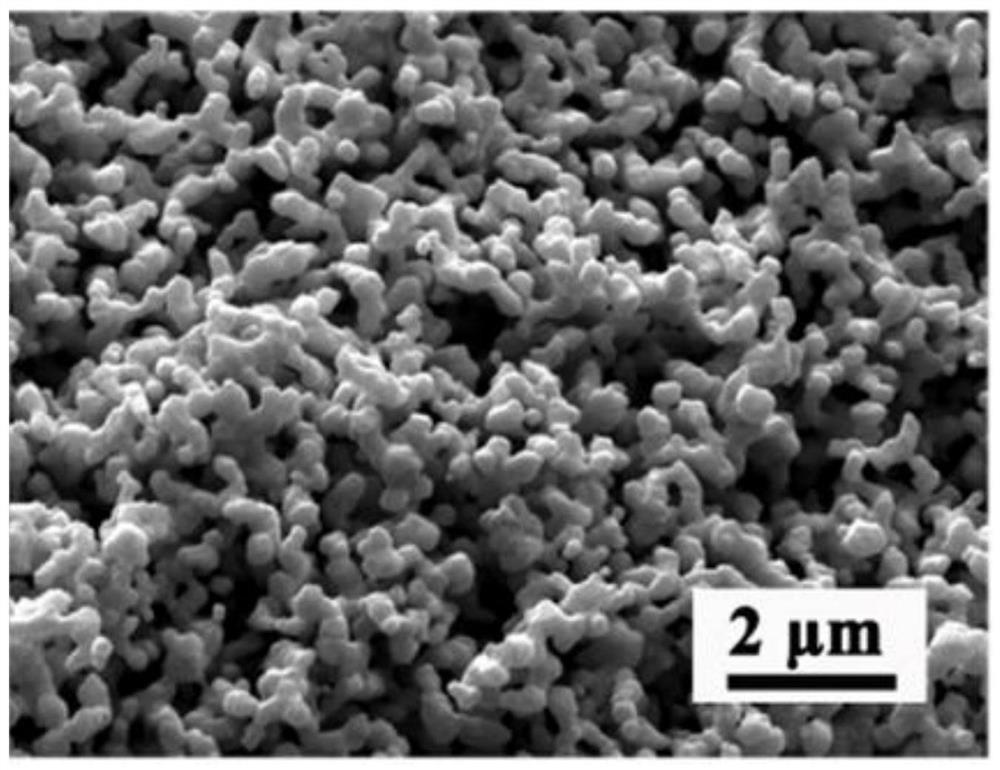
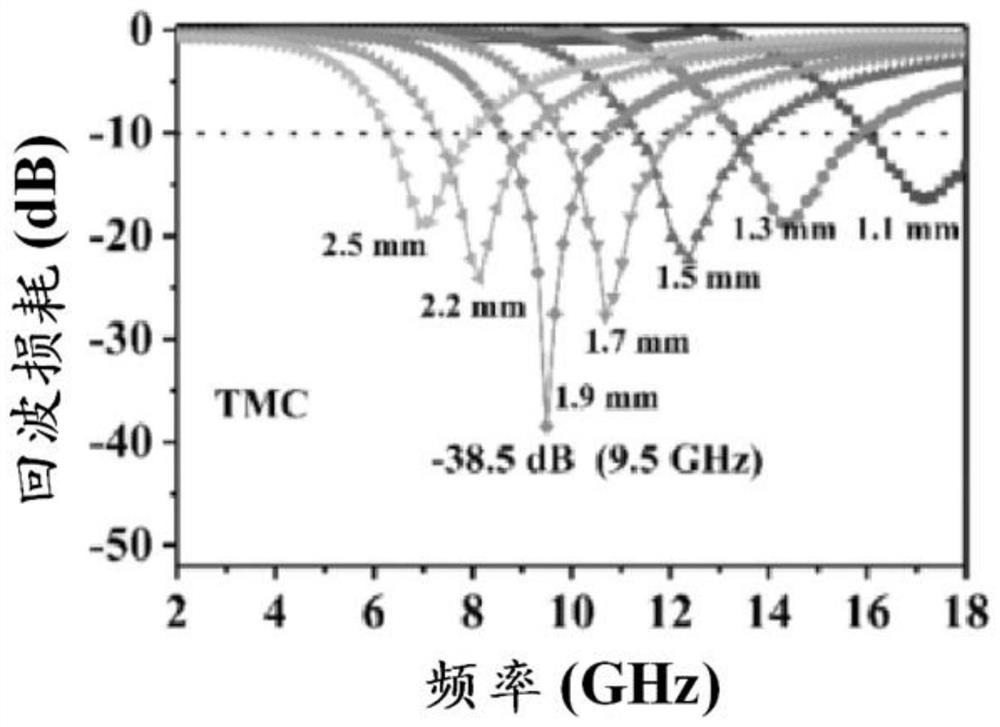
High-entropy wave-absorbing carbide ceramic powder material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112341199AHigh purityImprove absorbing performanceRadiation-absorbing paintsSlurryZirconium dioxide
The invention provides a high-entropy wave-absorbing carbide ceramic powder material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The ceramic powder material is prepared from the followingraw materials in mole ratio: 0-5mol% of titanium dioxide, 0-5mol% of zirconium dioxide, 0-5mol% of hafnium dioxide, 0-2.5 mol% of niobium pentoxide, 0-2.5 mol% of tantalum pentoxide, 0-2.5 mol% of vanadium pentoxide and the balance of carbon black, the dosage of any more than five transition metal oxides is not 0. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting five or more ofthe transition metal oxides; mixing the transition metal oxides with carbon black in the presence of a mixed medium to obtain uniformly mixed slurry; drying the slurry, sieving the slurry to obtain mixed powder, and calcining the powder to obtain the carbide ceramic powder material. The high-entropy ceramic powder material disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high purity, good wave-absorbing performance and wide absorption frequency band, and has an excellent application prospect in the field of wave-absorbing materials.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
Preparation method of silicon nitride ceramic balls
The invention discloses a preparation method of silicon nitride ceramic balls, and relates to the technical field of ceramic preparation. According to the technical key points, the preparation methodof the silicon nitride ceramic balls comprises the steps of ceramic ball raw material preparation, compression molding, sintering, grinding and polishing. Ceramic ball raw materials comprise the following components by the mass percentage: 85-95% of silicon nitride powder, 1-5% of yttrium oxide, 1-10% of erbium oxide, 0.5-2% of hafnium dioxide, 1-5% of titanium dioxide, and 0.5-2% of magnesium oxide. The silicon nitride ceramic balls prepared by the preparation method have the advantages of low density, high hardness, low friction coefficient, self-lubrication and good rigidity.
Owner:上海步进精密陶瓷有限公司
Thin layer of hafnium oxide and deposit process
InactiveUS20040091612A1Increase resistanceSubstantial gain in timePretreated surfacesSpecial surfacesThin layerOptoelectronics
A thin layer of hafnium oxide or stacking of thin layers comprising hafnium oxide layers for producing surface treatments of optical components, or optical components, characterised in that at least one layer of hafnium oxide is in amorphous form with a density less than 8 gm / cm<3>. The invention also relates to a process for producing a layer of amorphous hafnium oxide on a substrate, characterised in that the deposit is carried out without energy input to the substrate.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Infrared waveband diaphragm composite membrane and preparation method as well as composite material
ActiveCN104354365AAvoid cracking and falling offImprove bindingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInfraredBi layer
The invention discloses an infrared waveband diaphragm composite membrane and a preparation method as well as a composite material, belonging to the technical field of manufacturing of optical thin films. The infrared waveband diaphragm composite membrane has a double-layer membrane structure; the first layer is a hafnium oxide membrane layer and the second layer is a chromium membrane layer; the first layer and the second layer have strong bonding force with a calcium fluoride base; and the inner stress is small and the manufacturability of an infrared diaphragm prepared by a photographing copying method is good. According to the preparation method of the infrared waveband diaphragm layer, the hafnium oxide membrane layer and the chromium membrane layer are plated by adopting an evaporation manner and the chromium membrane layer is plated by two times so that the diaphragm prepared by adopting the photographing copying method has flat and smooth lines and have no light-transmitting point; and the preparation method has a simple technological process, is easy to operate and is suitable for industrial popularization and application. A base material of the infrared waveband diaphragm composite material is calcium fluoride, the inner layer membrane is the hafnium oxide membrane layer and the outer layer is the chromium membrane layer; and the bonding capability of the chromium membrane layer and calcium fluoride is strong and the process performance is good.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com