Method for recycling heavy-metal-accumulated plants
A heavy metal and recycling technology, applied in the field of resource utilization of plants, can solve the problems of occupying landfill space, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing quality, easy operation, and high-efficiency catalytic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] A method for resource utilization of plants accumulating heavy metals, comprising the steps of: the selected plants are castor-oil plant tissue samples (containing Cu: 6.42 ± 1.17 mg kg) grown in polluted soil -1 , Zn: 86.19±2.28 mg kg -1 ) to break up and mix well, and record it as sample A. Put the dried plant tissue sample A into a corundum boat, put the corundum boat into a tube-type resistance furnace, blow nitrogen for 15 min, and control the flow rate at 0.5 L min -1 , and then adjust the flow to stabilize at 0.2-0.3 L min -1 , turn on the resistance furnace, set the required temperature to 500°C, and start timing after heating until the set temperature is stable, so that the plant tissue sample is heat-treated at the set temperature for 8 hours, and then continue to pass nitrogen gas until the temperature is cooled to room temperature, take out the sample, and grind.
[0017] After heat treatment of sample A, its mass residual rate is 38.01%. After the heat t...
Embodiment 2
[0021] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the selected plant sample is a castor plant tissue sample grown in clean soil, which is recorded as sample B after crushing and mixing.
[0022] The mass residual rate of sample B after heat treatment is 38.63%, which reduces the mass of hazardous waste by 62%, which facilitates subsequent transportation and landfill.
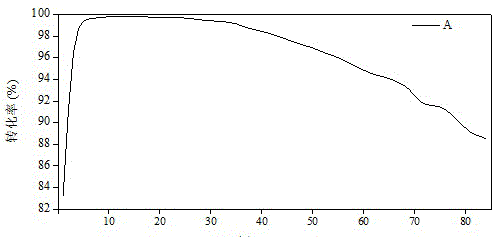
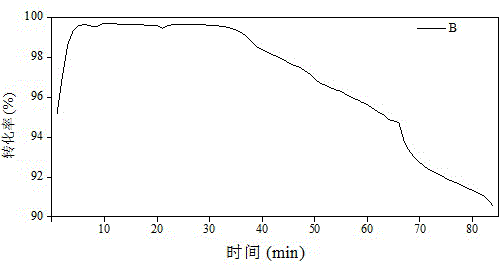
[0023] Such as image 3 It was shown that the catalytic efficiency (99.71%) of the carbon-based catalyst B burned with clean plant tissue reached the best when the catalytic time was 10 min, and the catalytic effect was stable in the next 20 min. The catalytic effect of carbon-based catalyst B decreased after 40 min of catalytic time, but the catalytic effect could still be maintained above 80%, showing a good catalytic reduction effect on NO. The catalytic effect of the carbon-based catalyst A in the presence of heavy metals is not significantly different from that of the control carbon-based...
Embodiment 3
[0025] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the required temperature is set to 700°C, and the time is started after heating until the set temperature is stable, so that the plant tissue sample (denoted as C) accumulating heavy metals is heat-treated at the set temperature 6 h. After heat treatment, the mass residual rate of sample C is 32.76%. The two heat treatment temperatures (700 ℃, 6 h; 500 ℃, 8 h) have little difference in mass residual rate. The specific implementation can be based on the actual situation and comprehensive consideration Thermal input and catalytic effect to choose.
[0026] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the catalytic efficiency (99.80-99.92%) of the carbon-based catalyst C fired from plant tissues accumulating heavy metals remained stable and efficient within the measured catalytic time, showing green and efficient resource utilization value.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com