A method for measuring laccase activity in farmland soil
A technology for the determination of activity and enzyme activity, which is applied in the field of determination of laccase activity in farmland soil. Accelerate the reaction time node and other issues, to achieve the effect of high measurement accuracy and accuracy, high repeatability, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method for assaying laccase activity in farmland soil, the steps of which are as follows:
[0048] A. Extraction of soil laccase extract
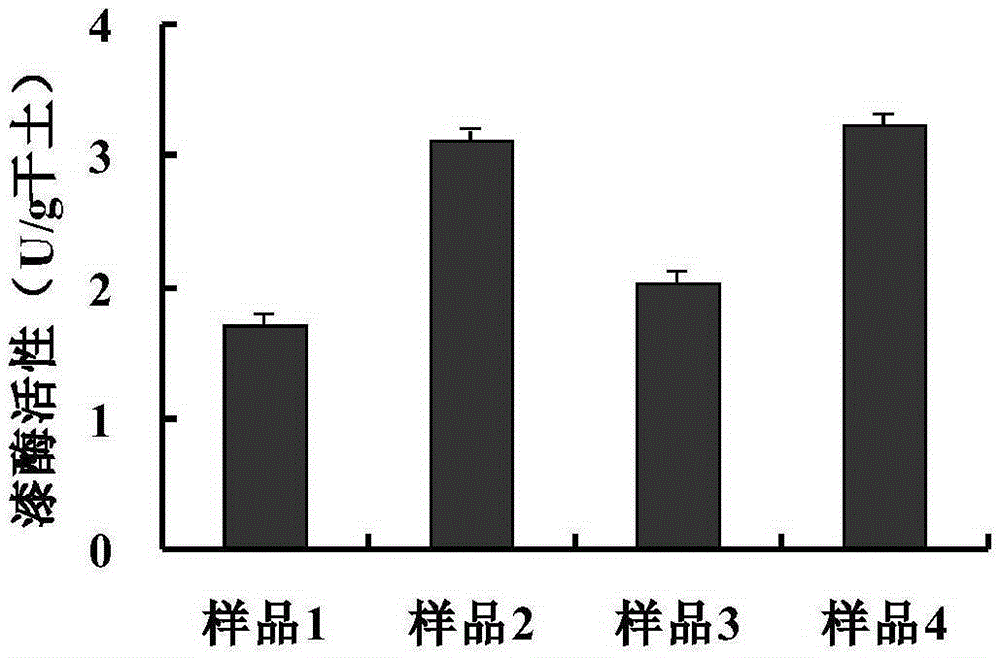
[0049] (1) Select four soil samples of red soil dry land (numbered as sample 1 and sample 2) and paddy and dry land (numbered as sample 3 and sample 4) to be tested in the subtropical red soil hilly area, and take 3g samples (passed through a 2mm sieve) soil samples respectively. Air-dried soil) into a 10ml sterile centrifuge tube, add 6ml of 50mM phosphate buffer (pH=7.1), vortex and mix well, and each sample is parallelized three times.
[0050] Described 50mM phosphate buffer preparation (pH=7.1) method is as follows:
[0051] 50mM sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH 2 PO 4 ·H 2 O) stock solution: weigh 8.907gNaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O is dissolved in sufficient water to make a final volume of 1 L;
[0052] 50mM disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na 2 HPO 4 ) stock solution: weigh 17.907gNa 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O is dissolved in sufficient ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Accuracy and repeatability of the determination method of laccase activity in farmland soil:
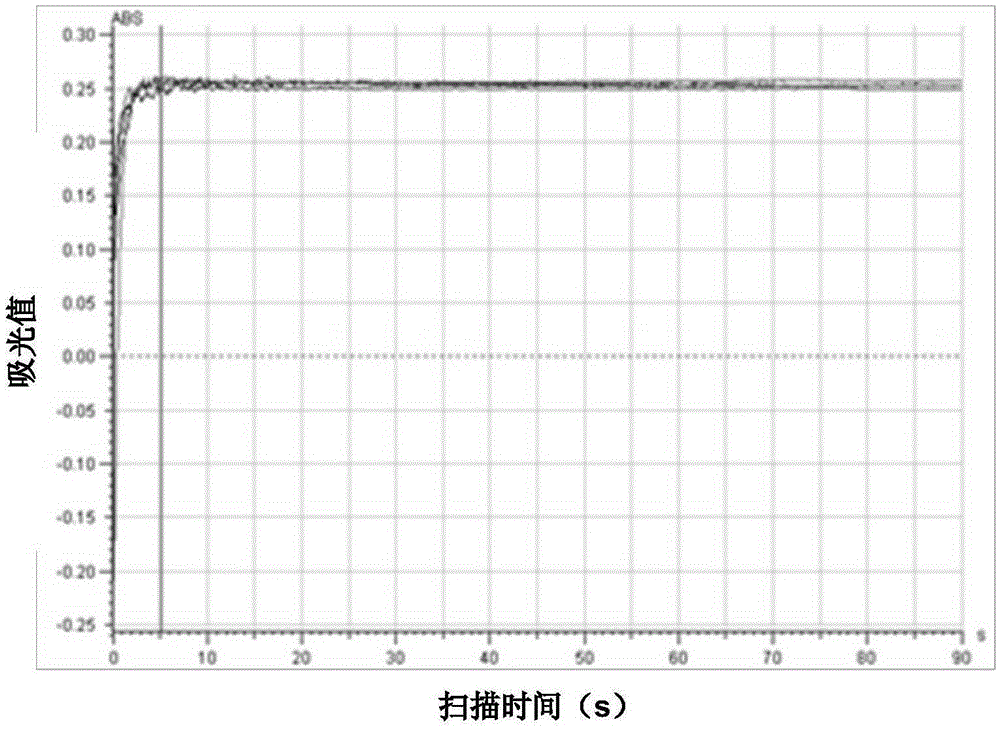
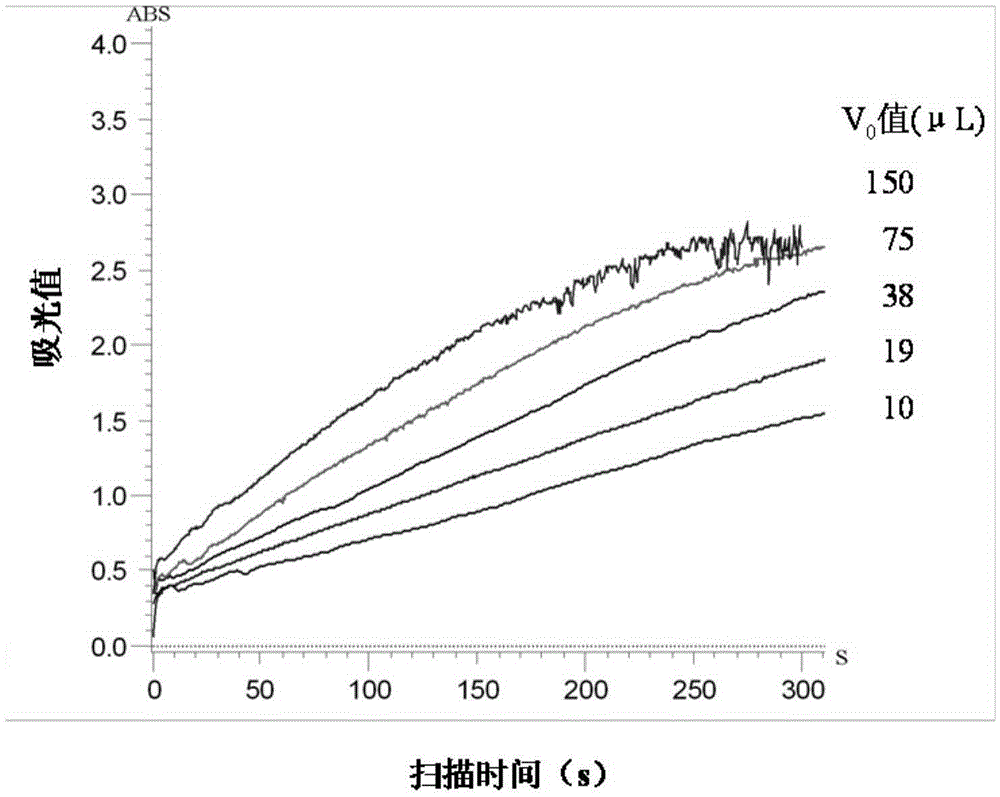
[0073] Weigh 0.0300 g of pure laccase (≥50 units / mg, sigma, product number L2157-10KU) into 1 ml of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH=7.1), vortex until fully dissolved. Pipette 150, 75, 38, 19, 10 μl of laccase solution into the soil (sample 2 of Example 1) laccase extract solution used to determine the optimum pH, and measure according to ③~④ in the above step B (1) Laccase activity, the original scanning curve is shown in image 3 . According to Mie equation: V=V max ×[S] / (K m +[S]), where V is the reaction speed (indicated by the difference ΔABS of the absorbance value in a certain period of time), K m The value is called the Michaelis constant, V max is the reaction velocity when the enzyme is saturated by the substrate, and [S] is the substrate concentration (by adding the volume V of the laccase solution 0 to indicate), after conversion, 1 / V=(K m / V max )×(1 / [S])+1 / V ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com