Implant prosthesis and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for implanting prostheses and prostheses, applied in the field of prostheses, can solve the problems of high processing costs and cumbersome operation steps, and achieve the effect of non-sensitization, simple operation steps, and obvious cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The invention also discloses a preparation method for the implanted prosthesis, comprising:
[0033] Coating a surface modifier on the surface of the inert implant material and drying it to obtain the implant prosthesis;
[0034] The surface modifiers include water, dispersants and bioceramic materials.
[0035] In the present invention, a surface modifier is first coated on the surface of the inert implant material, which refers to a biomedical material that can remain stable in a biological environment and does not or only weakly react, including but Not limited to silicone rubber, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, acrylic, PTFE, polyacrylamide or polyurethane. In the present invention, there is no special limitation on the source of the inert implant material, which can be purchased commercially. There is no special limitation on the shape of the inert implant material, and it can be trimmed into a desired shape according to the actual situation. In the present in...
Embodiment 1
[0045] 4 parts by mass of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was added to 94 parts by mass of pure water and stirred evenly, and then 2 parts by mass of nanoscale hydroxyapatite powder was added and stirred evenly to obtain a surface modifier.
[0046] Sterilize the obtained surface modifier, and put it into a hand-held pressure spray can after sterilization.
[0047] Trim the silicone rubber into a desired shape, then spray the surface modifier on the surface of the silicone rubber, and let it dry for 10 minutes to obtain an implanted prosthesis.
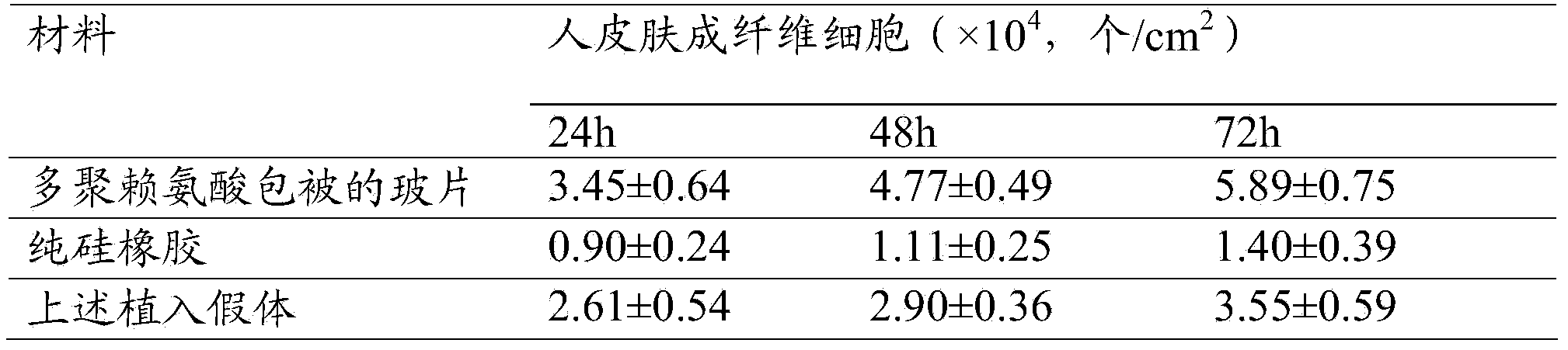
[0048] Biocompatibility testing of the above implanted prostheses
[0049] Sampling from the above implanted prosthesis, the sampling size is 0.2mm × 1cm × 1cm, the sampling sample is used as the experimental group, the polylysine-coated glass slide and pure silicone rubber are used as the control group, and the experimental group and the control group are used as the control group. After sterilization, the groups were placed in 24-we...
Embodiment 2
[0084] 1 part by mass of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was added to 94 parts by mass of pure water and stirred evenly, and then 5 parts by mass of nanoscale hydroxyapatite powder was added and stirred evenly to obtain a surface modifier.
[0085] Sterilize the obtained surface modifier, and put it into a hand-held pressure spray can after sterilization.
[0086] Trim the silicone rubber into a desired shape, then spray the surface modifier on the surface of the silicone rubber, and let it dry for 15 minutes to obtain an implanted prosthesis.
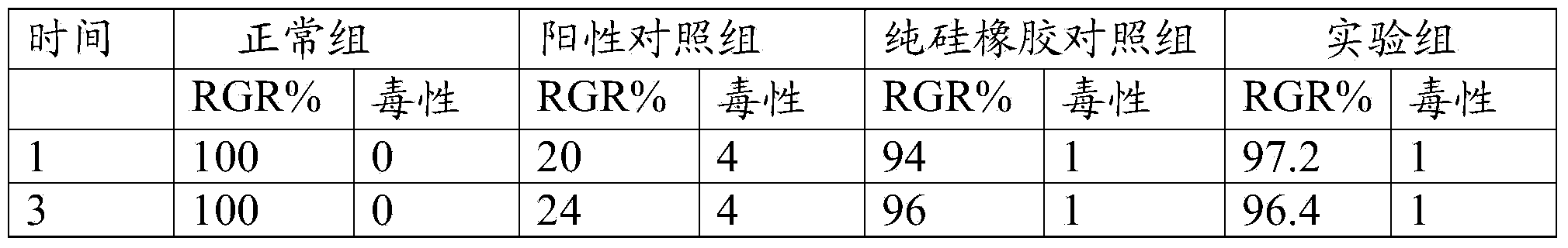
[0087] The biocompatibility test of the above implanted prosthesis shows that the above implanted prosthesis has good biocompatibility, and the growth and differentiation of cells on the surface of the above implanted prosthesis is obviously better than that of pure silicone rubber material.
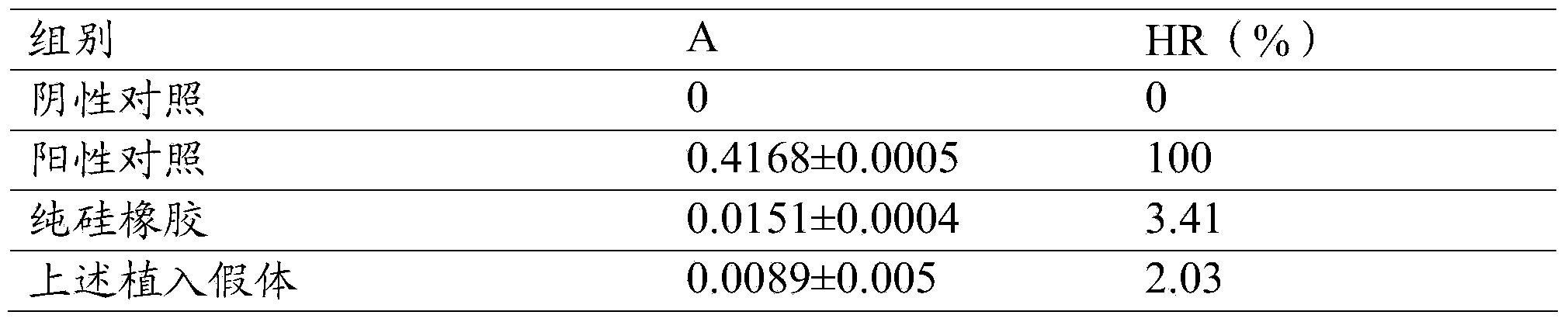
[0088] The biosafety test of the above implanted prosthesis shows that the hemolysis rate of the above implanted prosthesis is lower than 5%, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com