Storage control device, storage device, information processing system, and processing methods therefor
A storage control and storage unit technology, applied in memory systems, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of time deterioration of data retention characteristics, and achieve the effect of improving data retention characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0041] [Structure of information processing system]
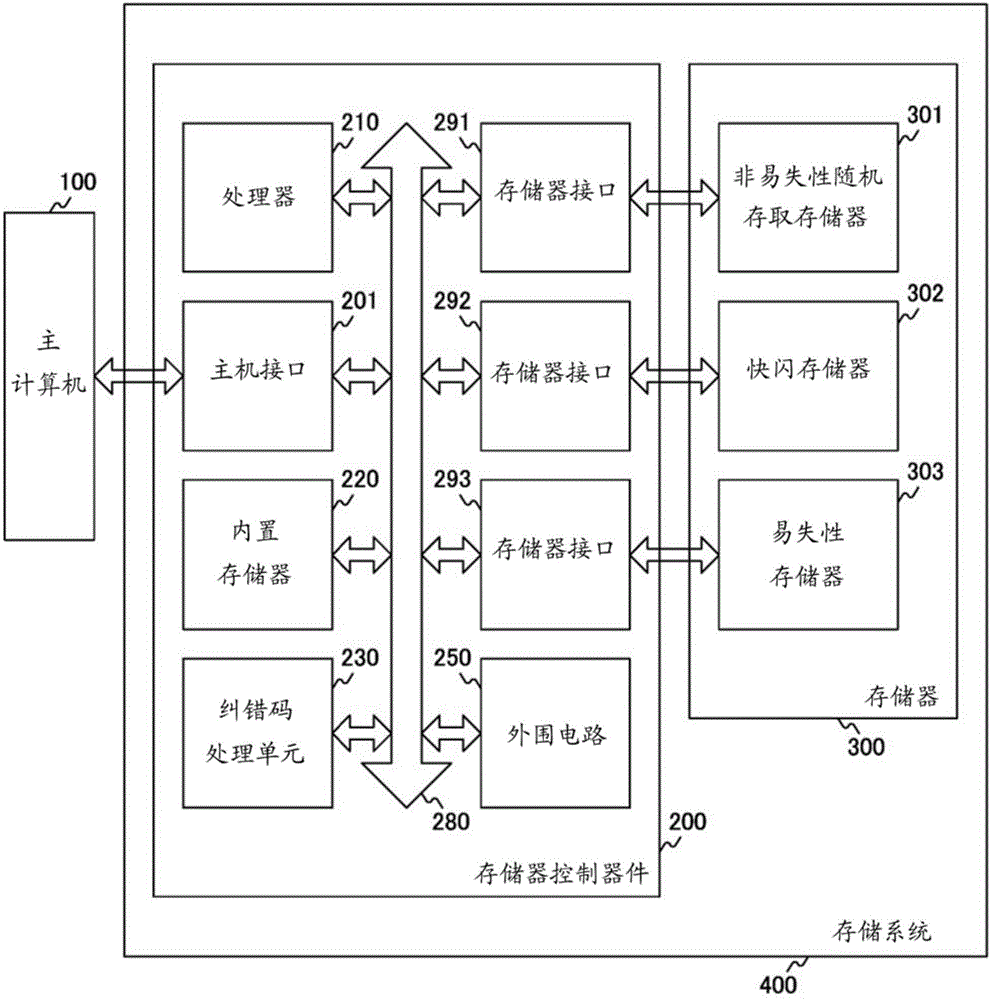
[0042] figure 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating an example structure of an information processing system according to an embodiment of the present technology. The information processing system includes a host computer 100 , a storage device 300 and a memory control device 200 . The memory control device 200 and the memory 300 constitute a memory system 400 . The host computer 100 issues instructions to request to read data from or write data to the storage system 400 .
[0043] Memory 300 includes non-volatile memory in addition to typical volatile memory 303 . The nonvolatile memory can be roughly classified into a flash memory 302 that allows data access to a large amount of data to be performed, and a nonvolatile random access memory (NVRAM) 301 that allows random access to a small amount of data to be performed at high speed. Here, a NAND type flash memory can be taken as a typical example of the flash memory 30...
no. 2 example
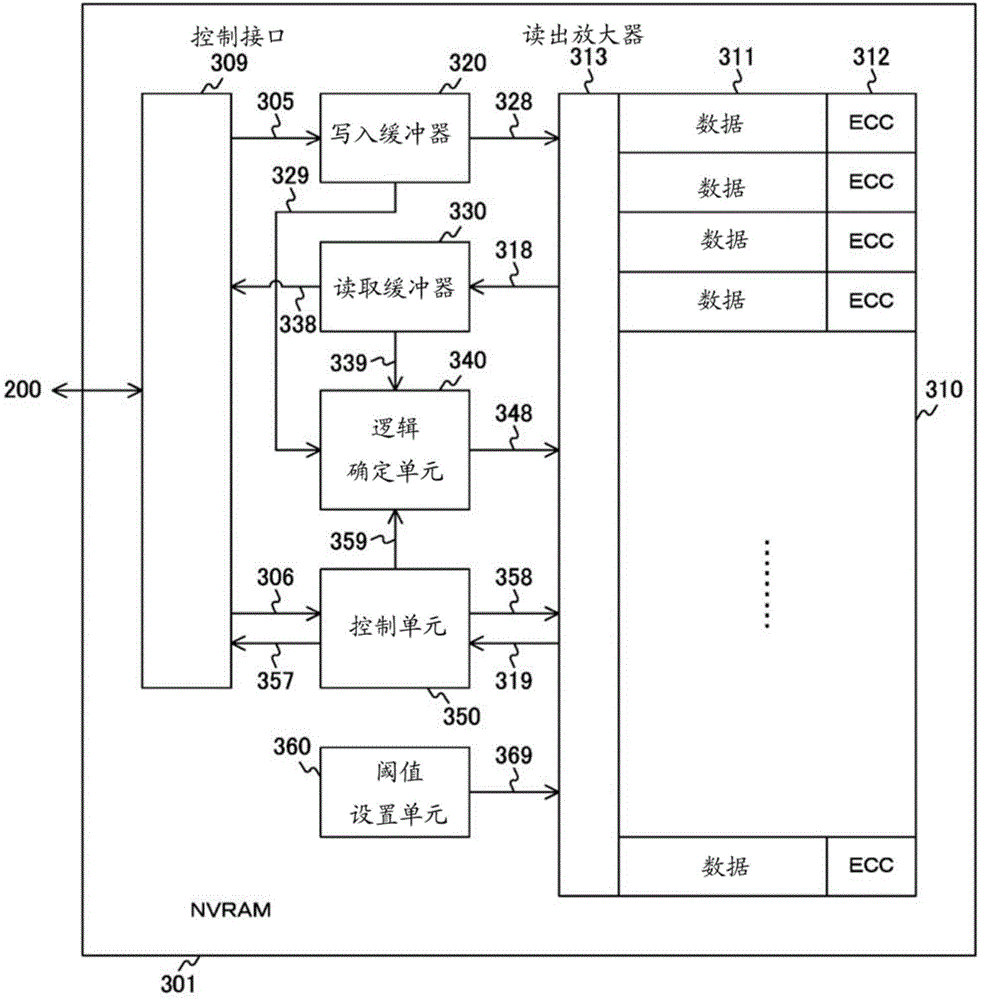
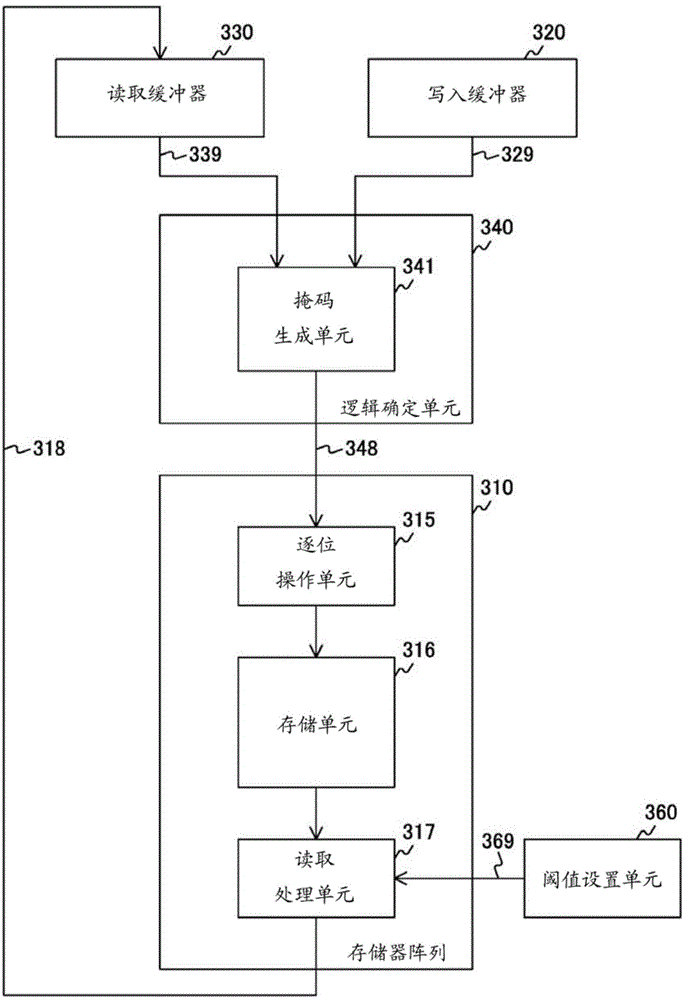
[0087] In the first embodiment described above, the rewriting of the bottom bit is always enforced by setting a high impedance threshold when establishing the erase mask and a low impedance threshold when establishing the programming mask. In this case, two read-aheads are performed per write, so there is an issue of operational latency. Therefore, the operation mode in the first embodiment is referred to as a protection mode, and a description will be given as the second embodiment in which operations are performed in the protection mode only when necessary. The main system structure is the same as that described in the first embodiment, so, for example, the control unit 350 performs the setting of the operation mode. That is, the control unit 350 is an example of an operation mode setting unit described in the claims.
[0088] [Operation of information processing system]
[0089] Figure 9 is a flowchart illustrating an example processing procedure of the information proc...
no. 3 example
[0097] In a ReRAM using a variable impedance element, data retention characteristics deteriorate with time elapsed since data is stored, and thus the number of errors to be detected and error corrected by an error correction code (ECC) increases. For example, when using an error correcting code with a bit correction capability capable of handling up to four bits, errors of up to four bits can be corrected, but errors of more than four bits cannot be corrected. For this reason, it is effective to use a method of rewriting error-corrected data (data refresh) before error correction becomes impossible. However, when the control is performed as in the standard mode of the second embodiment described above, if the pre-read data and the write data are the same, the programs in all bits are not erased either. On the other hand, when the control is always performed as in the protection mode, the number of times of pre-reading increases, so there is a risk of delaying the operation.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com