Lithium iron manganese phosphate composite positive electrode material and preparation method, positive electrode and lithium battery
A composite cathode material, lithium iron manganese phosphate technology, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, phosphorus compounds, secondary batteries, etc. It can improve the conductivity, improve the electrochemical performance, and reduce the volume resistivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
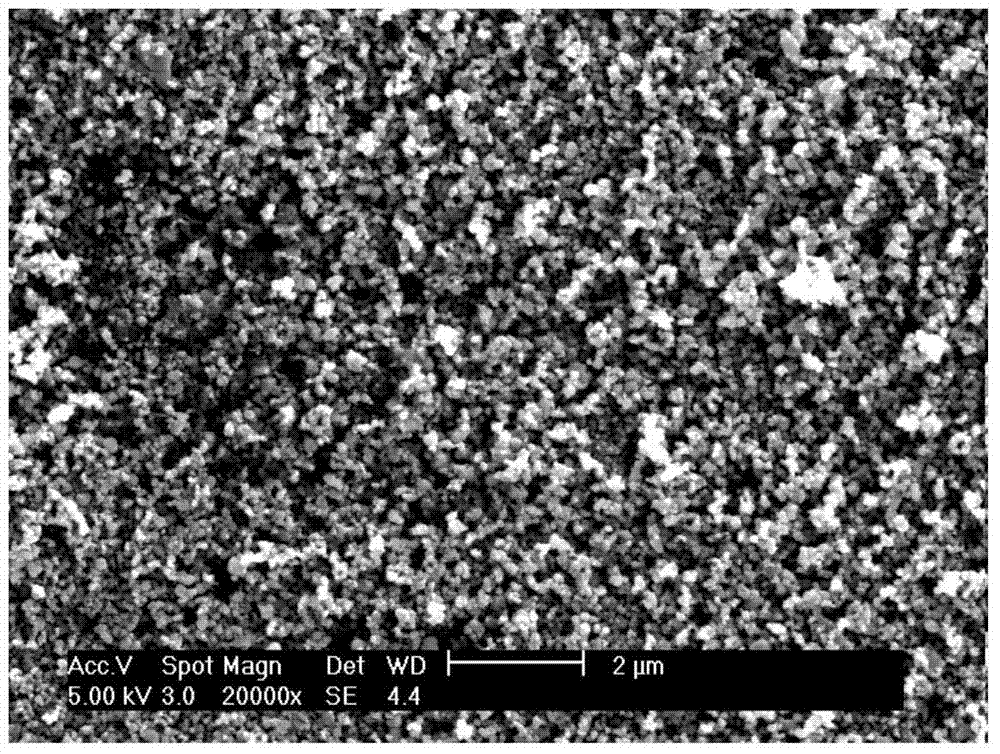
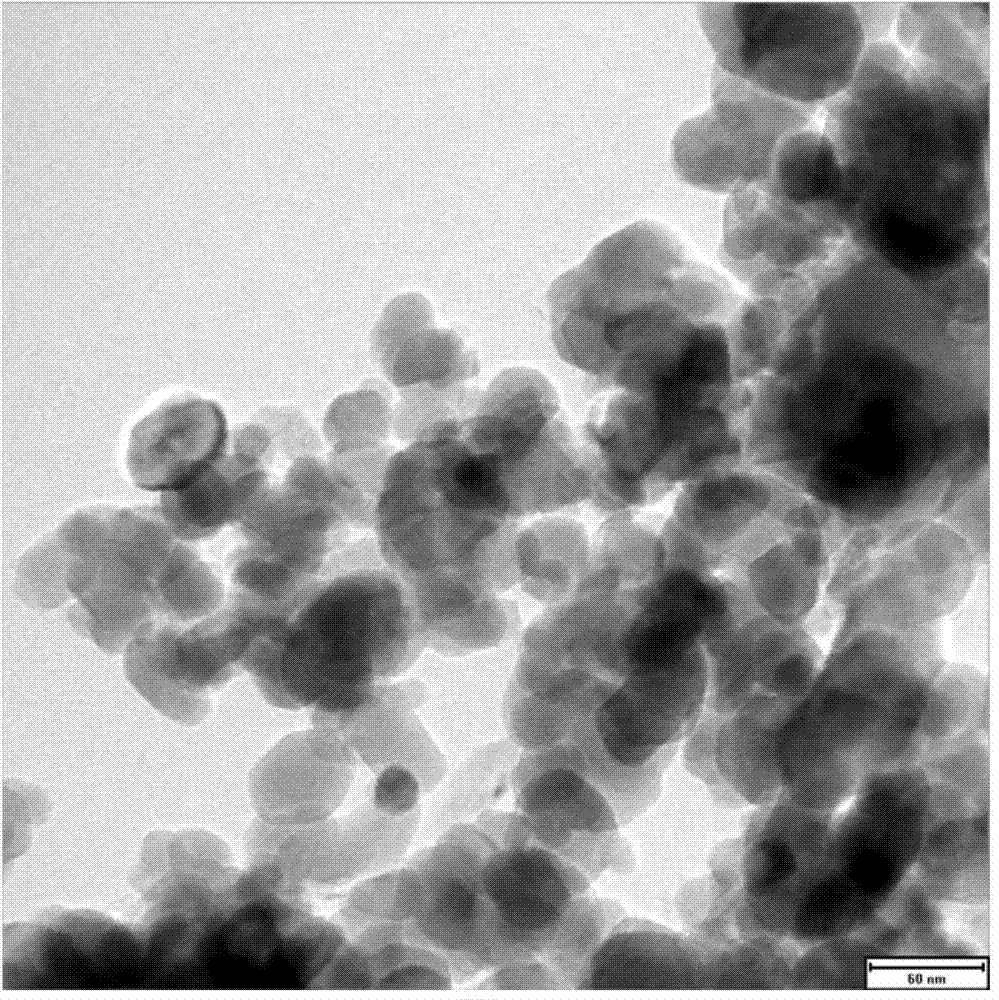
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
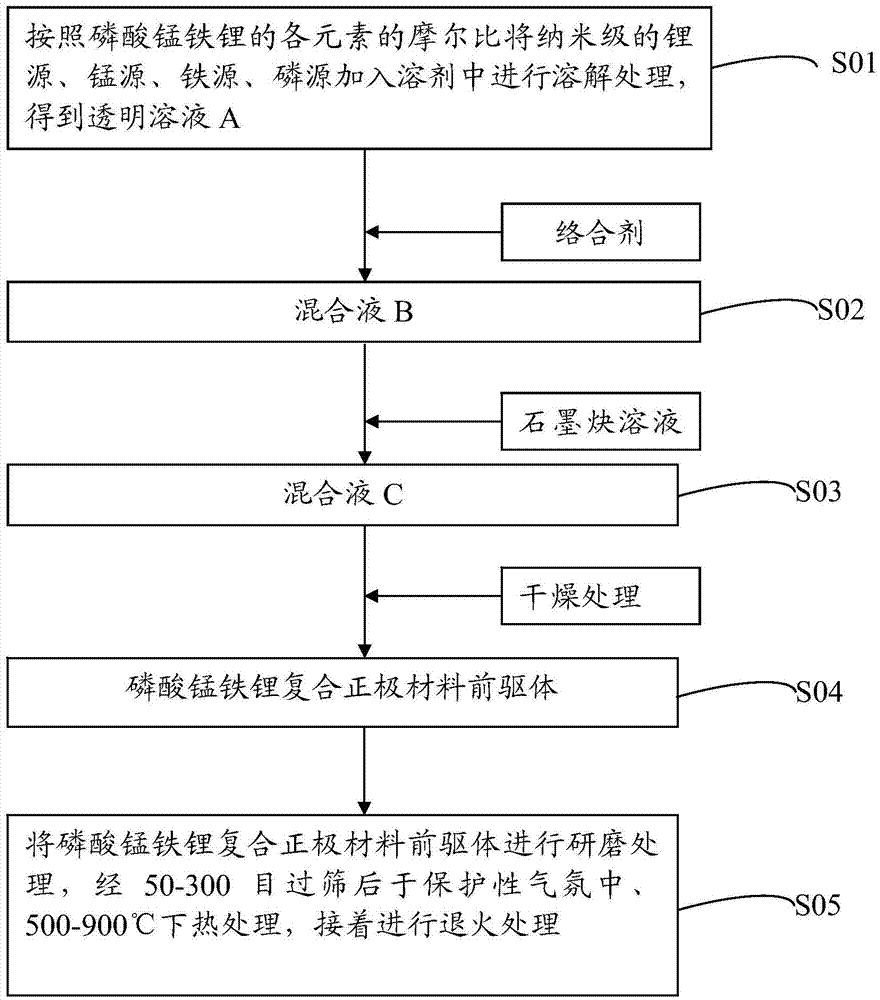
[0031] Correspondingly, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of the above-mentioned lithium manganese iron phosphate composite positive electrode material. For the process flow of this method, please refer to figure 1 . The preparation method of lithium manganese iron phosphate composite cathode material comprises the following steps:
[0032] Step S01: According to the molar ratio of each element of lithium manganese iron phosphate, adding nano-scale lithium source, manganese source, iron source, and phosphorus source into the solvent for dissolving treatment, to obtain a transparent solution A;
[0033] Step S02: adding a complexing agent to the transparent solution A prepared in step S01, and performing mixing treatment to obtain a mixed solution B;
[0034] Step S03: adding a graphyne solution to the mixed solution B prepared in step S02, and performing mixing treatment to obtain a mixed solution C;
[0035] Step S04: drying the mixe...
Embodiment 1
[0056] A lithium manganese iron phosphate composite positive electrode material and a preparation method thereof, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0057] Step S11: After the battery-grade raw materials lithium carbonate, manganese nitrate, iron nitrate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and ethyl acetate were treated by a sand mill for 30 minutes, the molar ratio was Li:Mn:Fe:P= 1.1:0.8:0.2:1 for weighing (theoretical product is 1 mole), and sequentially dissolved in deionized water and oxalic acid, magnetically stirred until a transparent solution A is formed;
[0058] Step S12: Weigh 10 g of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and add it to solution A, and stir magnetically. When the color of the solution turns dark brown, add 4 g of ethyl acetate, and stir magnetically for 1 hour to form mixed solution B;
[0059] Step S13: ultrasonically disperse 0.5 g of graphdiyne in ethanol solvent for 1 h to form solution C;
[0060] S...
Embodiment 2
[0065] A lithium manganese iron phosphate composite positive electrode material and a preparation method thereof, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0066] Step S21: After the battery-grade raw materials lithium carbonate, manganese nitrate, iron nitrate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and ethyl acetate were treated by a sand mill for 30 minutes, the molar ratio was Li:Mn:Fe:P= 1.1:0.8:0.2:1 for weighing (theoretical product is 1 mole), and sequentially dissolved in deionized water and oxalic acid, magnetically stirred until a transparent solution A is formed;
[0067] Step S22: Weigh 12 g of organic carbonate and add it to solution A, and stir magnetically. When the color of the solution turns dark brown, add 5 g of ethyl acetate, and stir magnetically for 1 hour to form mixed solution B;
[0068] Step S23: ultrasonically disperse 0.5 g of graphdiyne in ethanol solvent for 1 h to form solution C;
[0069] Step S24: addin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com