High-fluidity powder material for selective laser sintering
A laser sintering and high fluidity technology, applied in the field of 3D printing consumables, can solve the problems of high process control requirements, difficult application, complicated process, etc., and achieve the effects of wide application range, reduced shrinkage rate, and improved dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In this embodiment, the method for preparing a high fluidity powder material for selective laser sintering includes the following steps:
[0029] 1) Select 97 parts of polyether ether ketone powder with an average diameter of 70 μm, and 3 parts of nano-SiO 2 ;
[0030] 2) Step 1) selected nano-SiO 2 Disperse in ethanol solution, stir for 30 minutes until uniform, add 0.15 parts of silane coupling agent, continue stirring for 30 minutes, filter with suction, and dry to constant weight;
[0031] 3) The polyether ether ketone powder selected in step 1) and the nano-SiO modified in step 2) 2 The desired composite powder is obtained by mechanical stirring and mixing.
Embodiment 2
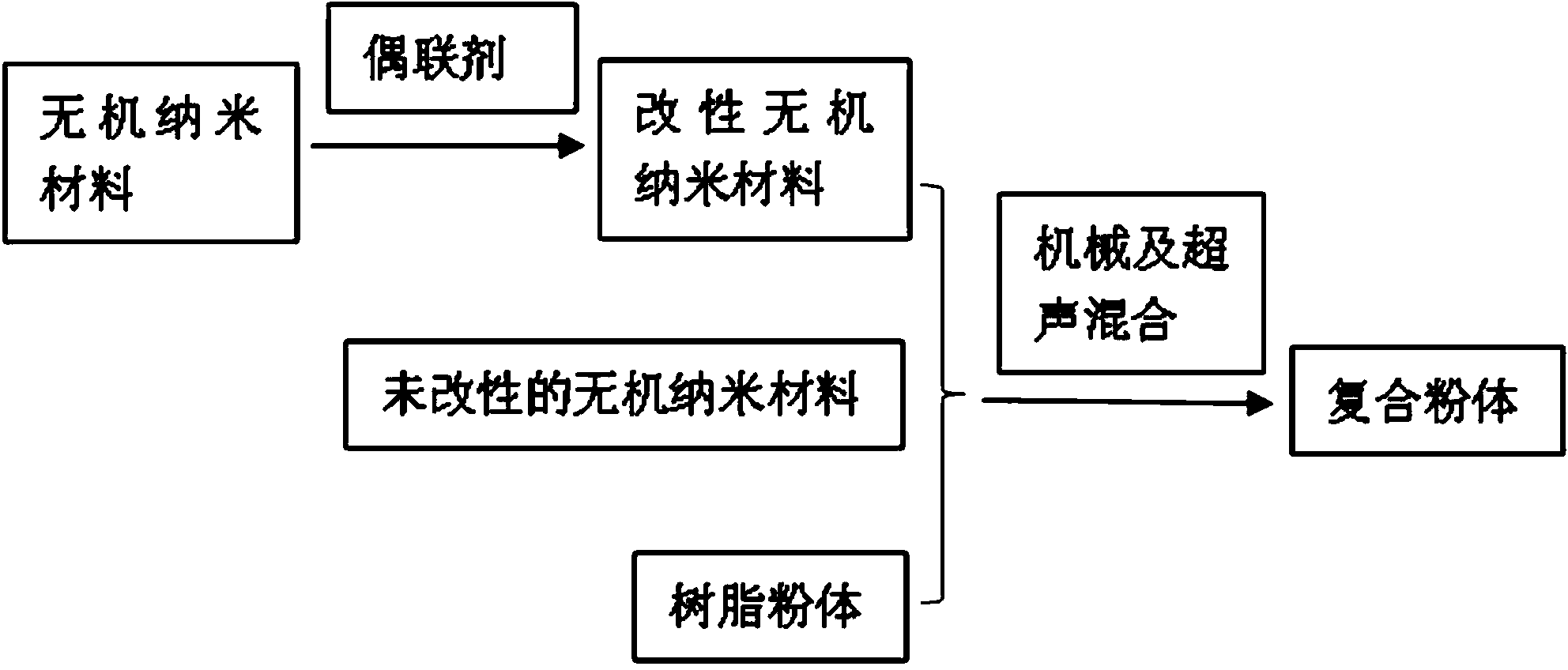
[0033] The method for preparing high fluidity powder material for selective laser sintering in this embodiment is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0034] 1) Select 95 parts of polyamide powder with an average diameter of 120 μm, 5 parts of nano-SiO 2 and nano Al 2 o 3 mixture;
[0035] 2) 3 parts of step 1) selected nano-SiO 2 Add 0.05 parts of silane coupling agent to the ethanol solution, then use high-energy ultrasonic (20kHz, 4000W) to treat for 3h, filter out the ethanol, wash 3-5 times, and dry to obtain modified nano-SiO 2 ;
[0036] 3) Step 1) selected polyamide powder, step 2) modified nano-SiO 2 and step 1) unmodified nano-SiO 2 Mix to obtain the desired composite powder.
Embodiment 3
[0038] In this embodiment, the method for preparing a high fluidity powder material for selective laser sintering includes the following steps:
[0039] 1) Select 96 parts of polyethersulfone powder with an average diameter of 40 μm, 4 parts of nano-nano TiO 2 and carbon nanotube mixtures;
[0040] 2) the step 1) selected polyethersulfone powder and nano-SiO 2 The desired composite powder is obtained by mechanical stirring and mixing.
[0041] The performance of the composite powder obtained in Example 1 was tested and compared with the polyether ether ketone powder without adding nanomaterials, the results are shown in Table 1:
[0042] Table 1 Example 1 Composite powder and pure PEEK powder performance comparison
[0043] Performance
Pure PEEK powder
Add 3% SiO 2 PEEK powder
pressure drop, PD 15.2 (mbar)
3.87
2.23
Basic kinetic energy, BFE(mJ)
39.5
25.6
Activation energy, AE(mJ)
<5mJ
<5mJ
Flow funct...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com