Process method for recovering butanol-butyl acetate from antibiotic production wastewater
A technology for butyl acetate and waste water production, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylate, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient liquid heat recovery, low relative volatility between components, and low composition content. , to achieve the effect of reducing temperature, reducing mass fraction and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
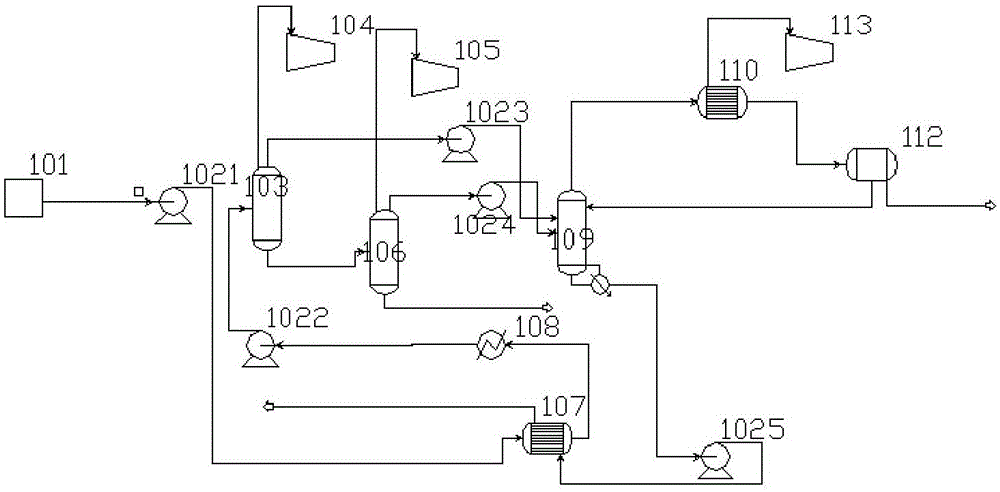
[0044] A kind of processing method of reclaiming butanol-butyl acetate from antibiotic production waste water, described processing method may further comprise the steps:
[0045] 1) The antibiotic production wastewater with a temperature of 20°C and containing 2% butanol-butyl acetate mass fraction first exchanges heat with the bottom liquid of the rectification tower in a tubular heat exchanger, and then flows into the heat exchanger to be heated to After 81°C, enter the first flash tower and the second flash tower successively for decompression flash; the first flash tower is maintained at an absolute pressure of 0.578atm through the first pressure reducer connected to the top of the first flash tower; The second flash tower is maintained at an absolute pressure of 8.5kPa by the second pressure reducer connected at its top;
[0046] 2) The steam at 82°C distilled from the top of the first flash tower and the second flash tower enters the rectification tower for rectificatio...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A kind of processing method of reclaiming butanol-butyl acetate from antibiotic production waste water, described processing method may further comprise the steps:
[0051] 1) The antibiotic production wastewater with a temperature of 40°C and containing 1% butanol-butyl acetate mass fraction first exchanges heat with the bottom liquid of the rectification tower in a tubular heat exchanger, and then flows into the heat exchanger to be heated to After 80°C, enter the first flash tower and the second flash tower successively for decompression flash; the first flash tower is maintained at an absolute pressure of 0.4 atm by the first decompressor connected to the top of the first flash tower; The second flash column is maintained at an absolute pressure of 12kPa by a second pressure reducer connected at its top;
[0052] 2) The steam at 85°C distilled from the top of the first flash tower and the second flash tower enters the rectification tower for rectification under redu...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A kind of processing method of reclaiming butanol-butyl acetate from antibiotic production waste water, described processing method may further comprise the steps:
[0057] 1) The antibiotic production wastewater with a temperature of 26°C and containing 5% butanol-butyl acetate mass fraction first exchanges heat with the bottom liquid of the rectification tower in a tubular heat exchanger, and then flows into the heat exchanger to be heated to After 85°C, enter the first flash tower and the second flash tower successively for decompression flash; the first flash tower is maintained at an absolute pressure of 0.7 atm by the first pressure reducer connected to its top; The second flash tower is maintained at absolute pressure 8kPa by the second pressure reducer that its top connects;
[0058] 2) The steam at 80°C distilled from the top of the first flash tower and the second flash tower enters the rectification tower for rectification under reduced pressure; the waste wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com