Pasteurella multocida cell-free antigen, preparation method and application thereof
A Pasteurella, multi-kill technology, applied in the field of veterinary biological products, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation steps, difficult to achieve large-scale production, etc., to reduce side reactions, easy to scale production, good specificity and sensitivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Preparation of Pasteurella multocida cell-free antigen
[0034] Pasteurella multocida C51-2 and C51-17 strains from rabbits (both purchased from the China Veterinary Drug Administration, and the strain preservation numbers are CVCC499 and CVCC1753 respectively) and Pasteurella multocida C48-2 and 1502 strains from chickens were taken. strains (both purchased from the China Veterinary Drug Control Institute, and the strain preservation numbers are CVCC44802 and CVCC2082) freeze-dried strains were dissolved in 1-2ml sterile saline and inoculated in 2-20% (V / V) serum-modified Martin After recovery of the agar plate, take the colonies and inoculate them in 2-20% (V / V) serum-modified Martin broth, place at 37°C, shake at 200 rpm for 12 hours, add 0.15% formaldehyde solution to the bacterial solution, and inactivate at 37°C for 24 hours. Centrifuge at 10000rpm for 20min, and the supernatant is the cell-free antigen of Pasteurella multocida.
[0035] Among them: th...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Detection of the main components of the cell-free antigen of Pasteurella multocida
[0038] 1 Determination of cell-free antigen protein content
[0039] The protein content of each cell-free antigen was directly measured using a nucleic acid protein analyzer (BioPhotometer plus, Eppendorf, Germany), and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0040] Table 1: Determination results of protein content in cell-free antigen of Pasteurella multocida
[0041] Strain number Protein content in cell-free antigen (mg / ml) C51-2 10.2 C51-17 10.6 C48-2 8.8 1502 9.5
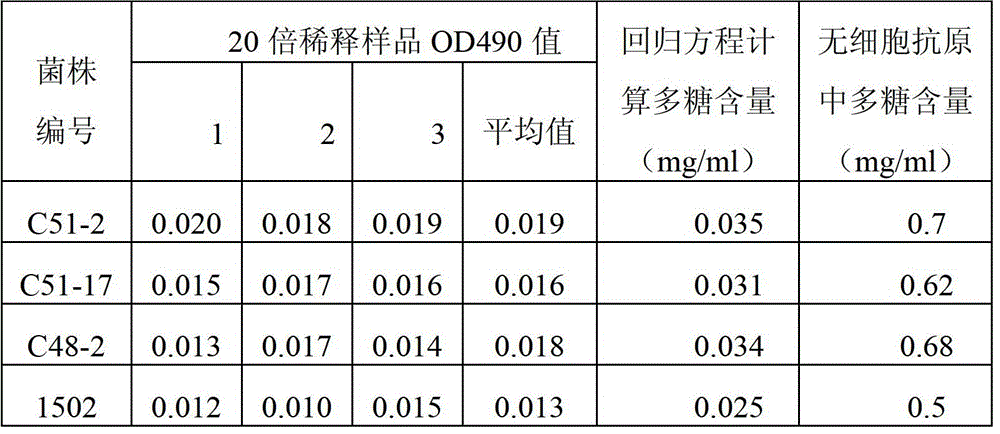
[0042] 2 Determination of polysaccharide content of cell-free antigen (using phenol-sulfuric acid colorimetric method)
[0043] Using anhydrous glucose (sigma) as a reference substance, the regression equation y=1.3914x+0.0086 (R 2 =0.997), each cell-free antigen sample was diluted 20 times with sterile normal saline, and its absorbance at 490nm wavelength was measured by ph...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: Establishment and application of Pasteurella multocida indirect hemagglutination test method
[0047] 1 Preparation of sensitized sheep red blood cells
[0048] 1.1 Collection and washing of sheep red blood cells
[0049] Fresh anticoagulated sheep blood was stored at 4°C and centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10min, and the supernatant and white blood cells were discarded. Wash with PBS (0.15mol / L, pH7.2) for 3-5 times, make 5% erythrocyte suspension by volume, and store at 4°C for later use.
[0050] 1.2 Formylation and tanninization of red blood cells
[0051] Mix glutaraldehyde with water to make a 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution by volume, and store it at 4°C for later use.
[0052] Place the 5% erythrocyte suspension pre-cooled at 4°C in a magnetic stirrer, stir at a low speed, and add the glutaraldehyde solution pre-cooled at 4°C dropwise at a volume ratio of 5:1. Then the erythrocyte suspension was hydroformylated in a constant temperature shaker at 30°C and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com