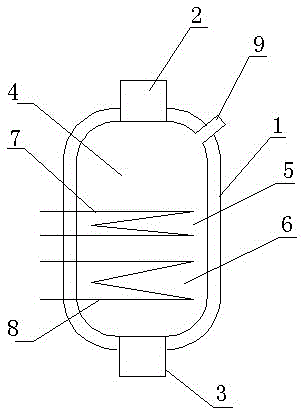
A technology of iron ore shaft furnace-rotary kiln direct reduction to produce iron powder
A rotary kiln, iron ore technology, applied in furnaces, rotary drum furnaces, furnace components, etc., can solve the problems of low pellet strength and metal recovery rate, shorten the reduction time, increase production, and reduce pulverization. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] An iron ore shaft furnace-rotary kiln direct reduction process for producing iron powder, comprising the following process steps:
[0031] (1) Dry grinding and pelletizing of iron ore: After the ore is ground to a particle size of -200 mesh and accounts for more than 80%, it is enriched by magnetic separation to obtain a coarse concentrate powder with an iron grade of 36.1%. The obtained coarse concentrate powder is mixed with The bentonite is mixed according to the mass ratio of 100:1, then moistened, ground and pelletized to obtain pellets with a particle size of 8-16mm;
[0032] (2) Drying pre-consolidation and oxidative roasting of pellets: Pellets are added from the top of the shaft furnace, and in the drying zone of the shaft furnace, the pellets are dried at a temperature of 200-300°C for 15 minutes and then flow down to the Shaft furnace preheating roasting zone and soaking zone. In the preheating roasting zone and soaking zone, the pellets are fully heated, oxi...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0041] In step (1), the iron grade of the coarse concentrate powder obtained after magnetic separation and enrichment is 37.8%, and the obtained coarse concentrate powder and bentonite are mixed in a mass ratio of 100:2 and then moistened and pelletized;
[0042] In step (2), in the drying zone of the shaft furnace, the pellets are dried at a temperature of 250-350°C for 12 minutes and then flow down to the preheating roasting zone and soaking zone of the shaft furnace by their own gravity. In the preheating roasting zone and soaking zone, The time for controlling the oxidation and roasting of the pellets is 50 minutes;
[0043] In step (3), the oxidized pellets and the dried granulated coal are mixed in a mass ratio of 100:40 and then added to the rotary kiln for reduction. The reduction temperature of the pellets is controlled at 1080-1120°C and the time is 90 minutes;
[0044] In step (5), after weak magneti...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is:
[0047] In step (1), the iron grade of the coarse concentrate powder obtained after magnetic separation and enrichment is 42.3%, and the obtained coarse concentrate powder and bentonite are mixed in a mass ratio of 100:3 and then moistened and pelletized;
[0048] In step (2), in the drying zone of the shaft furnace, the pellets are dried at a temperature of 300-400°C for 10 minutes and then flow down to the preheating roasting zone and soaking zone of the shaft furnace by their own gravity. In the preheating roasting zone and soaking zone, The time for controlling the oxidation and roasting of the pellets is 45 minutes;
[0049] In step (3), the oxidized pellets and the dried granulated coal are mixed in a mass ratio of 100:50 and then added to the rotary kiln for reduction. The reduction temperature of the pellets is controlled at 1110-1150°C and the time is 60 minutes;
[0050] In step (5), after weak magneti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com