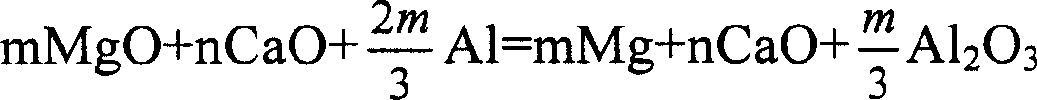Patents
Literature
197results about How to "Reduce restore time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
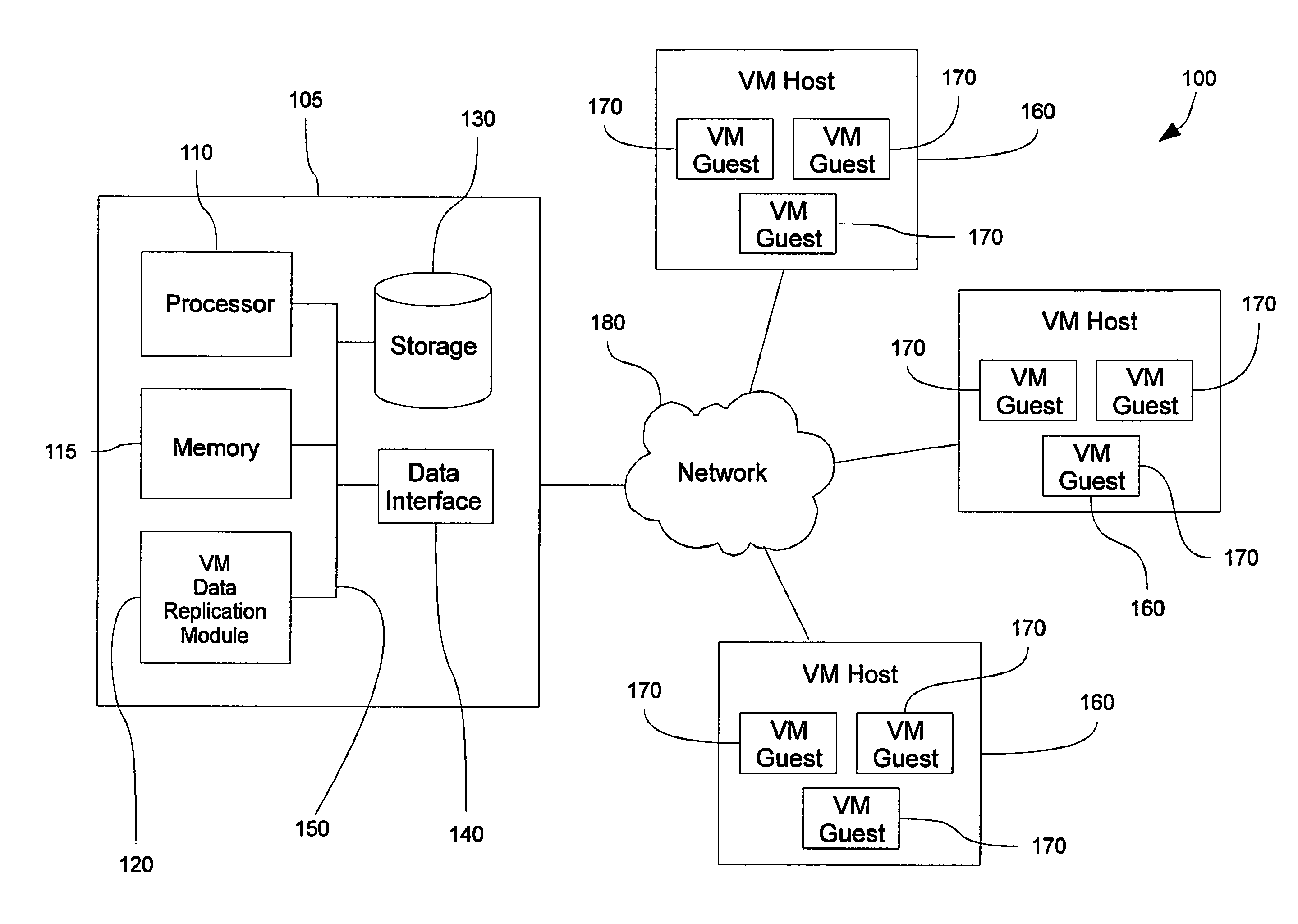
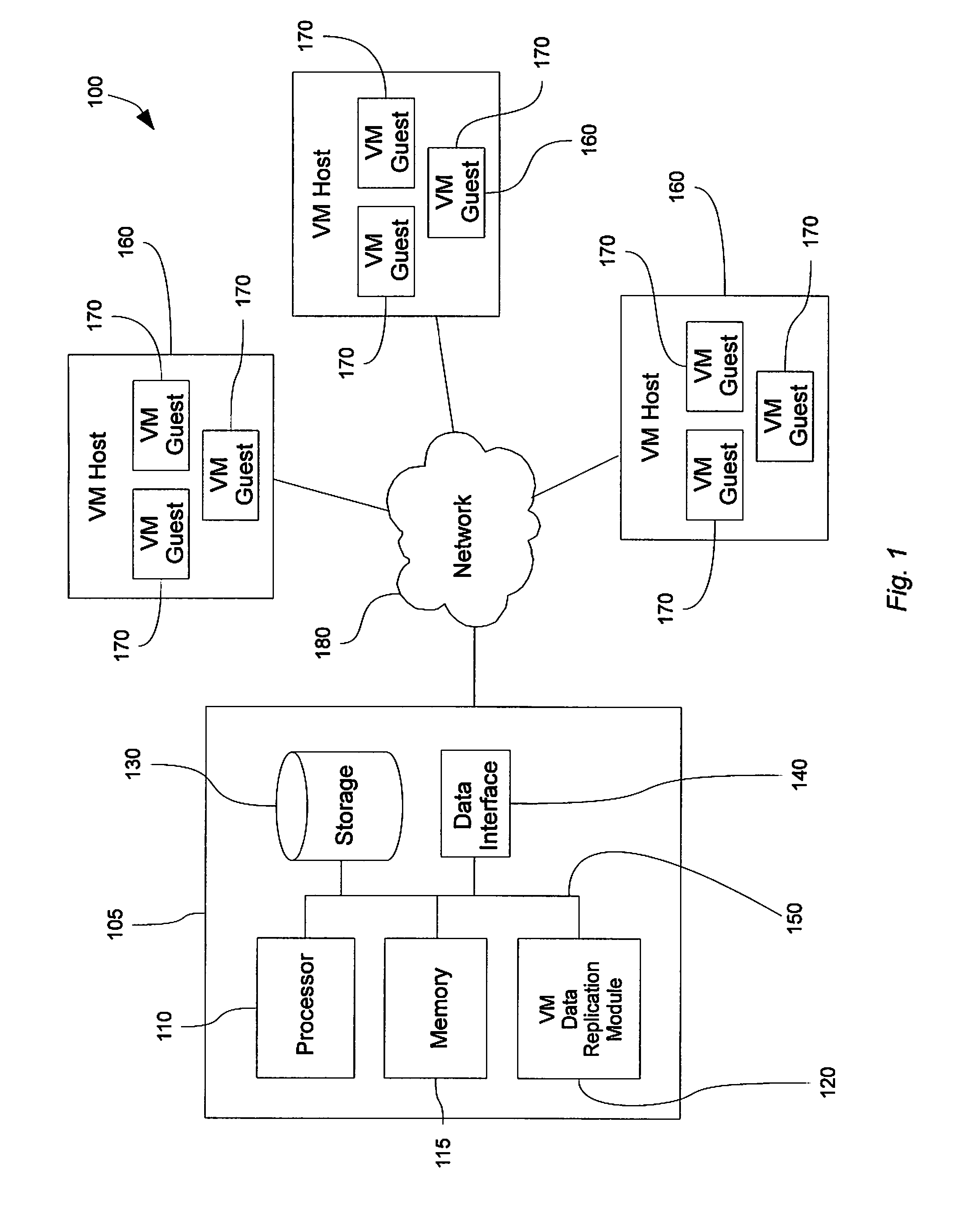
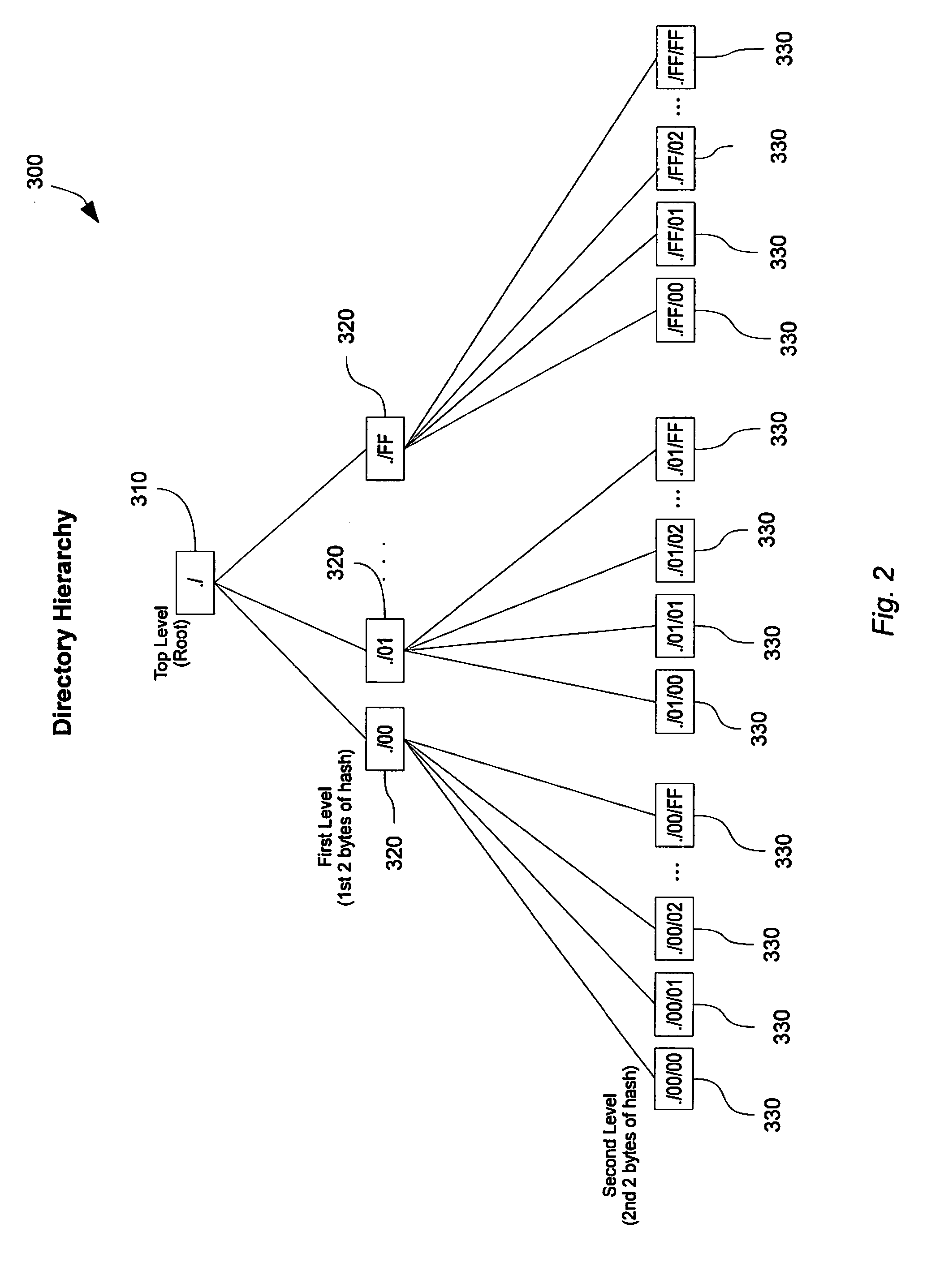
Virtual machine data replication
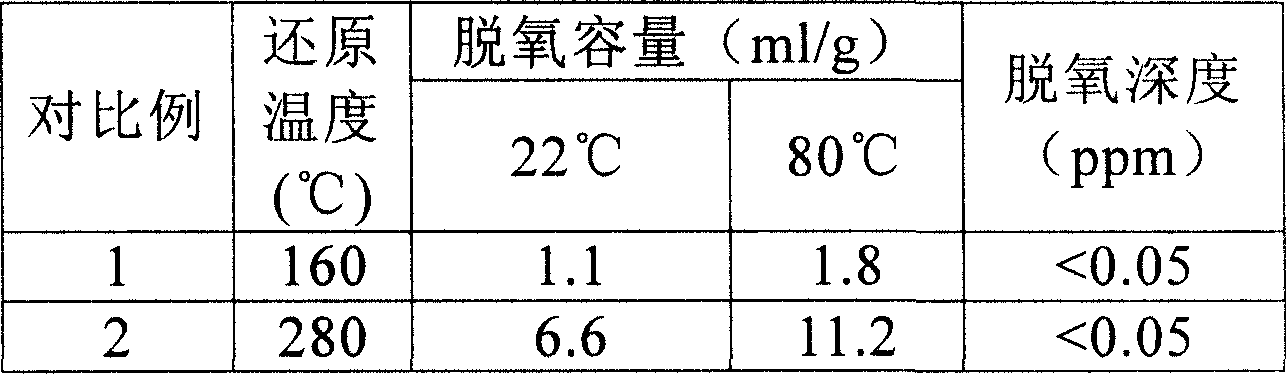
ActiveUS20100262586A1Efficiently restoring backup setShorten recovery timeError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsHard disc driveData set
Disclosed is a method and system for selectively restoring file-level data from a disk image backup. In embodiments, a virtual machine backup may be performed by dividing a virtual machine virtual disk file into a plurality of discrete fixed-sized data blocks sharing a common index file that is stored on a backup medium, such as a hard drive, to form a backup set. Upon restoration of data from the backup set, individual blocks of the data set are compared to corresponding blocks of the target virtual machine file. Redundant data and unchanged blocks are skipped, and only those block which have changed are restored to the target file. In this manner network bandwidth and processor resources are conserved, and replication times decreased.
Owner:UNITRENDS
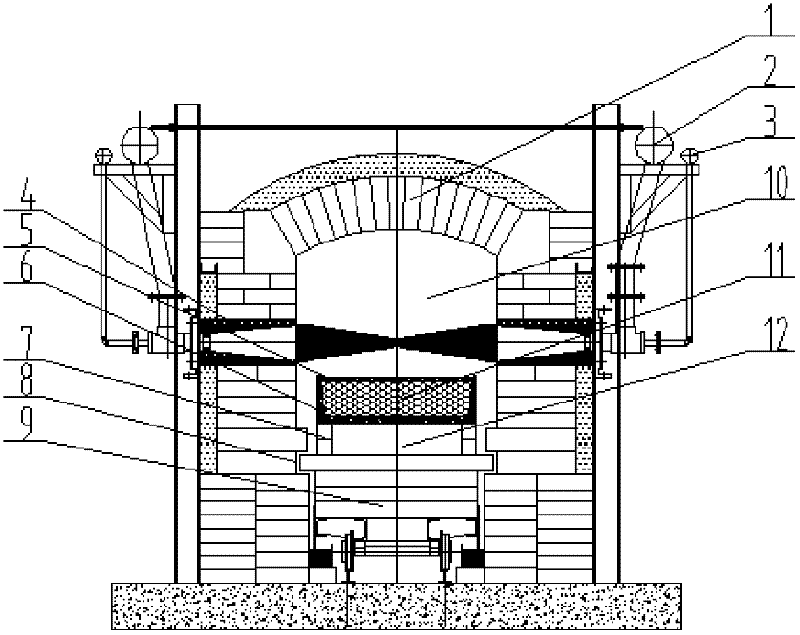
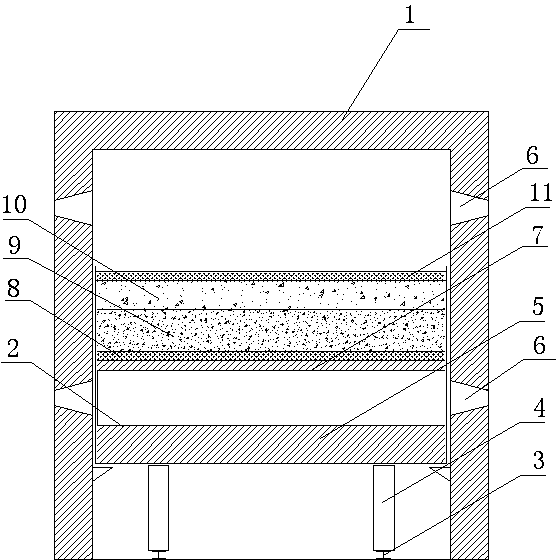
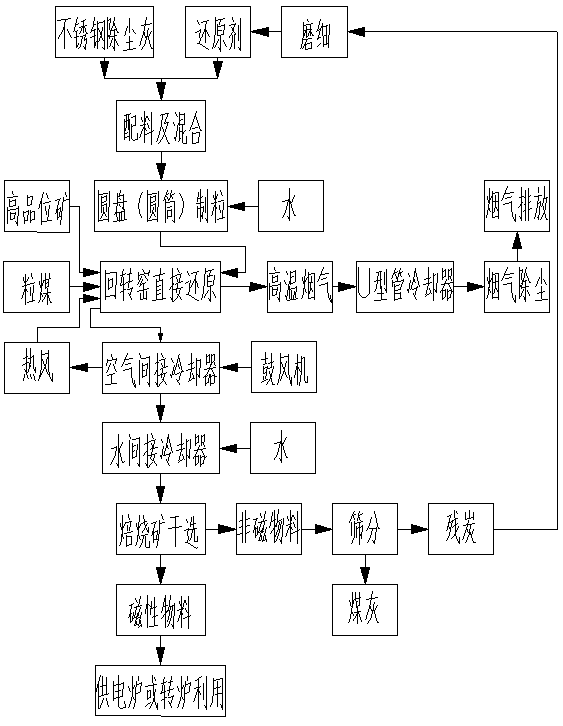
Direction reduction and electric furnace smelting-separation preparation process of vanadium-titanium magnetite cold bound pellet
The cooled agglomerated carbon-contained pellet prepared with vanadium titano magnetite concentrate and opposite direct reduction with former pellet comprises: mixing the concentrate, reducer and bonding agent, drying, grinding, and pelletizing to obtain the cooled agglomerated carbon-contained pellet drying and sieving into the reduction furnace with reducer for reduction atmosphere; loading the reduced pellet into electric furnace to melt and separate the iron liquid, V, Ti and Cr. This invention is fit to the pellet on wide application temperature and low energy consumption, has well efficiency and low running cost, and can also extract V, Ti Fe and Cr from electric furnace with high yield and obvious environmental protection.
Owner:鲜帆 +2
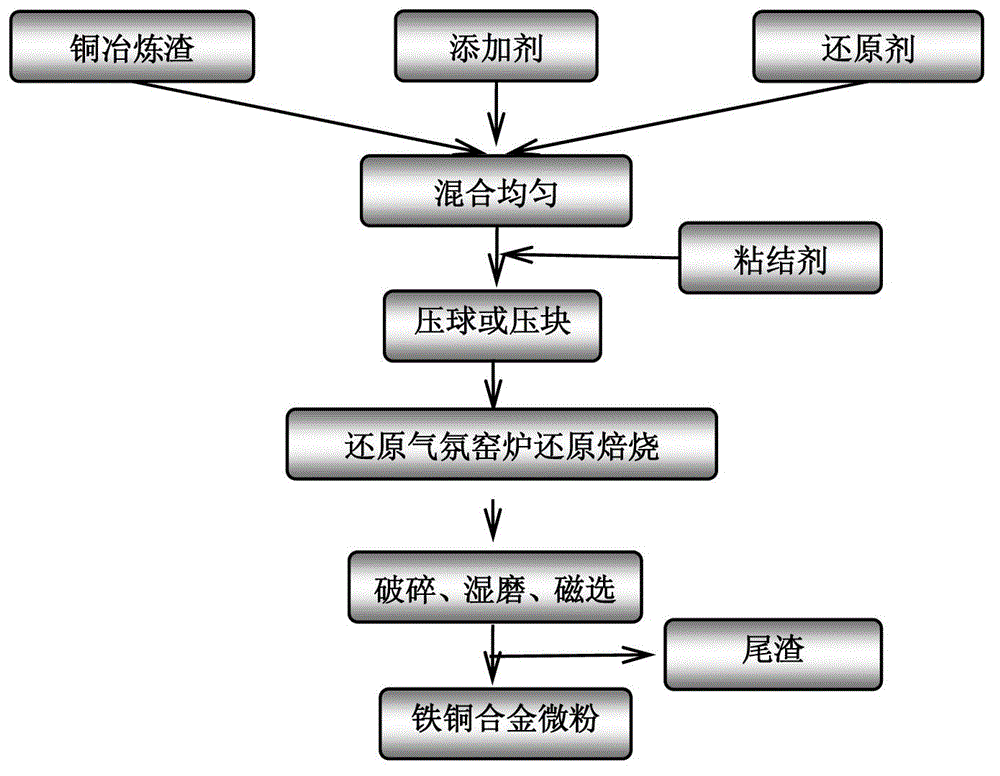
Method for rapidly reducing copper slags to produce iron-copper alloys in kiln in reducing atmosphere
ActiveCN102719676AIncrease added valueAchieve restorationProcess efficiency improvementSilicic acidReducing atmosphere
A method for rapidly reducing copper slags to produce iron-copper alloys in a kiln in a reducing atmosphere is characterized by including the steps: proportionally mixing the copper slags, reducing agents and additives, crushing or levigating the mixture to 200 meshes to obtain 20%-40% of residues on sieve; doping agglomerants and water occupying 5-20% of all materials on a dry mass basis, uniformly mixing, producing the uniformly mixed mixture to pellets with the diameters ranging from 15mm to 30mm and small cylindrical briquettes with all the heights ranging from 15mm to 30mm by a pellet press or a briquetting machine, and drying the pellets or small cylindrical briquettes; flatly laying the dried pellets or small cylindrical briquettes at the bottom of the kiln, wherein the material layer thickness ranges from 20mm to 45mm, the material layer reducing temperature ranges from 1250 DEG C to 1450 DEG C, and the reducing time is 10-40min; and subjecting the reduced pellets or the briquettes to cooling, crushing, wet grinding and wet separation so that iron-copper alloy powder with the iron recovery rate of 85%-99% is obtained. According to the method, iron in a great quantity of silicate iron in the copper slags, which cannot be separated out by the traditional technology, is extracted and turns into the iron-copper alloy micro powder with high added value so that iron and copper in the copper slags are extracted and used simultaneously, and physical and chemical heat energy in strong reducing waste gas can be completely recovered during rapid depth reduction.
Owner:TONGLING NON FERROUS METAL GROUP CORP +1
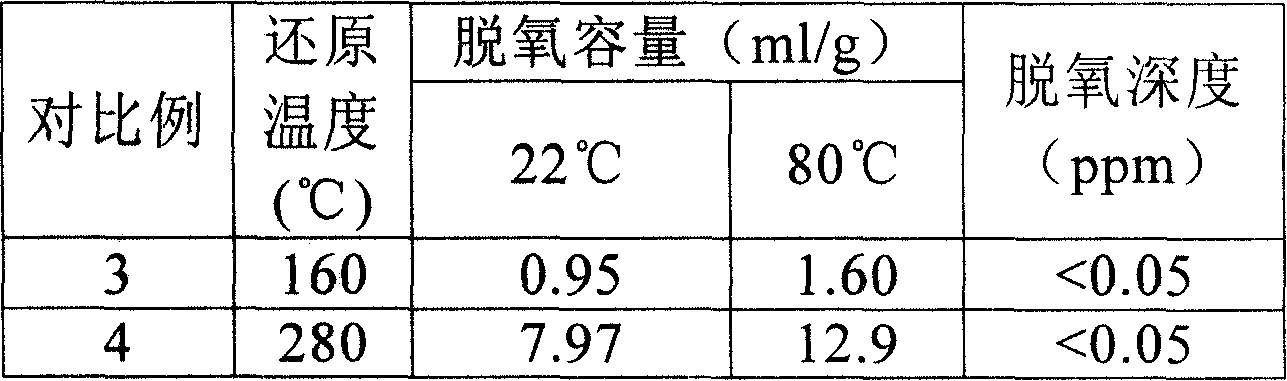
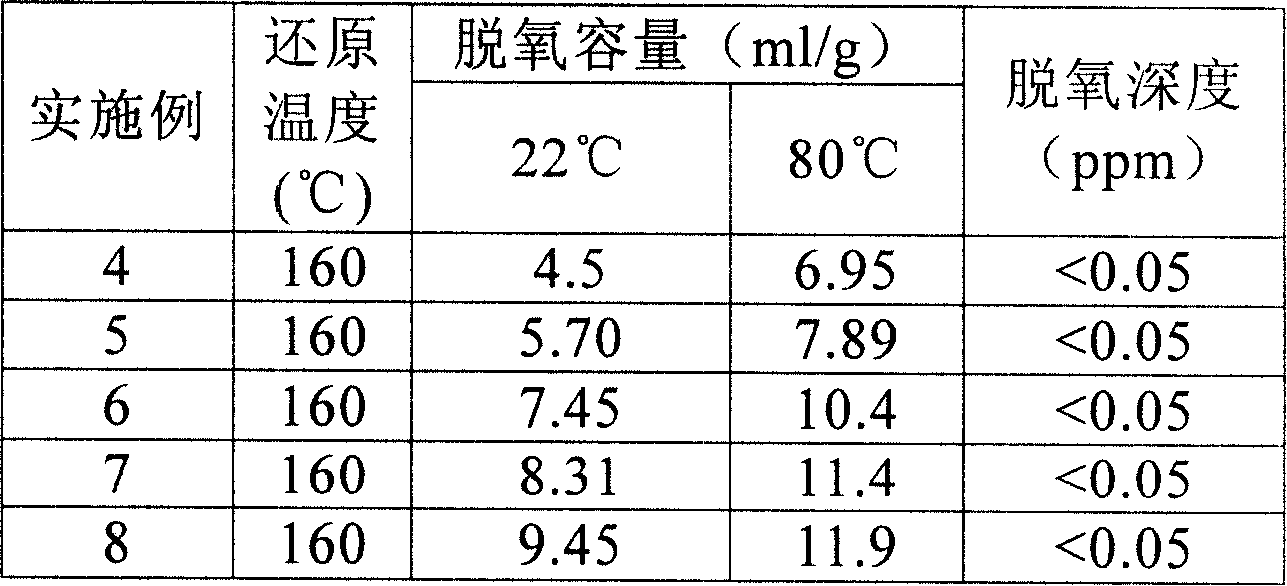
Mn-Ag double active components desoxidant, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101165030AImprove deoxygenation capacityExtended regeneration cycleManganese oxides/hydroxidesSilve compoundsCalcium aluminatesPolyolefin
The present invention relates to olefin processing technology, and is especially double active component Mn-Ag deoxidizer for deoxidizing olefin and its preparation process and application. The Mn-Ag deoxidizer has Mn3O4 as main active component and small amount of Ag2O catalyst capable of lowering the temperature and decreasing the time for reducing Mn3O4 into MnO possessing deoxidizing activity. The Mn-Ag deoxidizer has calcium aluminate carrier and no other adhesive, high active component content and high deoxidizing capacity, and possesses very high compression strength. The Mn-Ag deoxidizer may be regenerated through reduction at 80-160 deg.c, and can reduce oxygen content in ethylene, propylene, etc at room temperature to below 0.05 ppm. The Mn-Ag deoxidizer is applied in industrial polyolefin production, and has long regeneration period, capacity of preventing poisoning of polymerizing catalyst and low production cost.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
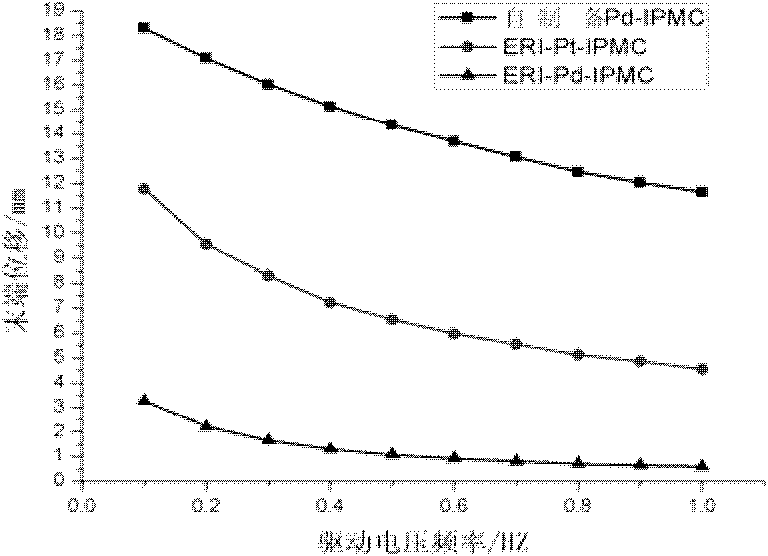
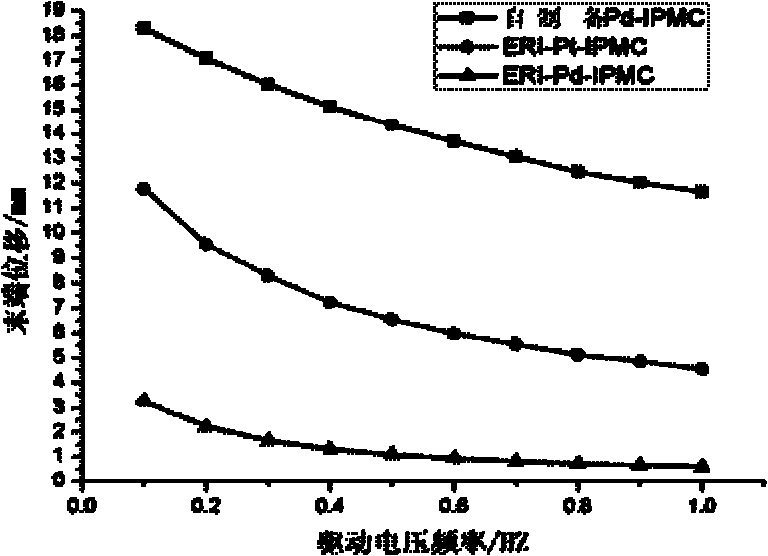
Preparation process of palladium electrode ion polymer and metal composite
InactiveCN102168260AIncrease profitImprove electrical actuation performanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingIonic polymer–metal compositesChemical plating
The invention discloses a preparation process of a palladium electrode ion polymer and metal composite, which is used for preparing a palladium metal electrode IPMC (Ion Polymer Metal Composite) by using immersion reduction plating and chemical plating methods in which an ion exchange membrane is used as a matrix material and [Pd (NH3)4] C12 is used as a main salt. The preparation process comprises the following four main steps of: (1) pretreatment of the matrix membrane: carrying out roughening, surface cleaning, foreign ion removal and full swelling on the matrix membrane; (2) immersion reduction plating including two processes, i.e., ion exchange and ion reduction: subjecting a pretreated Nafion membrane to repeated palladium ion immersion and exchange, and reducing the pretreated Nafion membrane with NaBH4 by adopting ultrasonic waves to form palladium metals on the surface and the internal surface of the ion exchange membrane; (3) chemical plating: wherein the thickening electrodes on the outer surface of a core material to compact internal surface electrodes by using an improved chemical plating method; and (4) postprocessing of the composite. The preparation process has a higher popularization value due to relatively improved efficiency, relatively lower cost and excellent actuation response.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for synthetically reclaiming iron, vanadium and titanium from vanadium titanium magnet concentrate
InactiveCN101168802ATake advantage ofCannot be efficiently recycledRotary drum furnacesTitanium dioxideRecovery methodMagnetite
The invention relates to a comprehensive recovery method of iron, vanadium and titanium for vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ores, in particular to the comprehensive recovery and utilization of the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore of which the vanadium content is higher. In particular, the invention is vanadium extraction through water immersion after the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore is performed with sodium activation and sintered, the vanadium product is made from leach solution, the remaining slag is performed with reduction quickly through a rotary furnace after carbon is added, the reduction product is melted through the electric furnace, to segregate the melted iron and the titanium slag, the melted iron is used to make steel, and the titanium slag is used to produce white titanium pigment through a sulfuric acid method titanium white technology. The method of the invention is applied to the refining technology of the vanadium and titanium magnetite concentrated ore, to ensure that the recovery rate of the vanadium and titanium is greatly enhanced, the recovery rate of the total vanadium in the iron concentrated ore can reach more than 80 percent, titanium is fully recovered, and the production of massive blast furnace slag is avoided.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
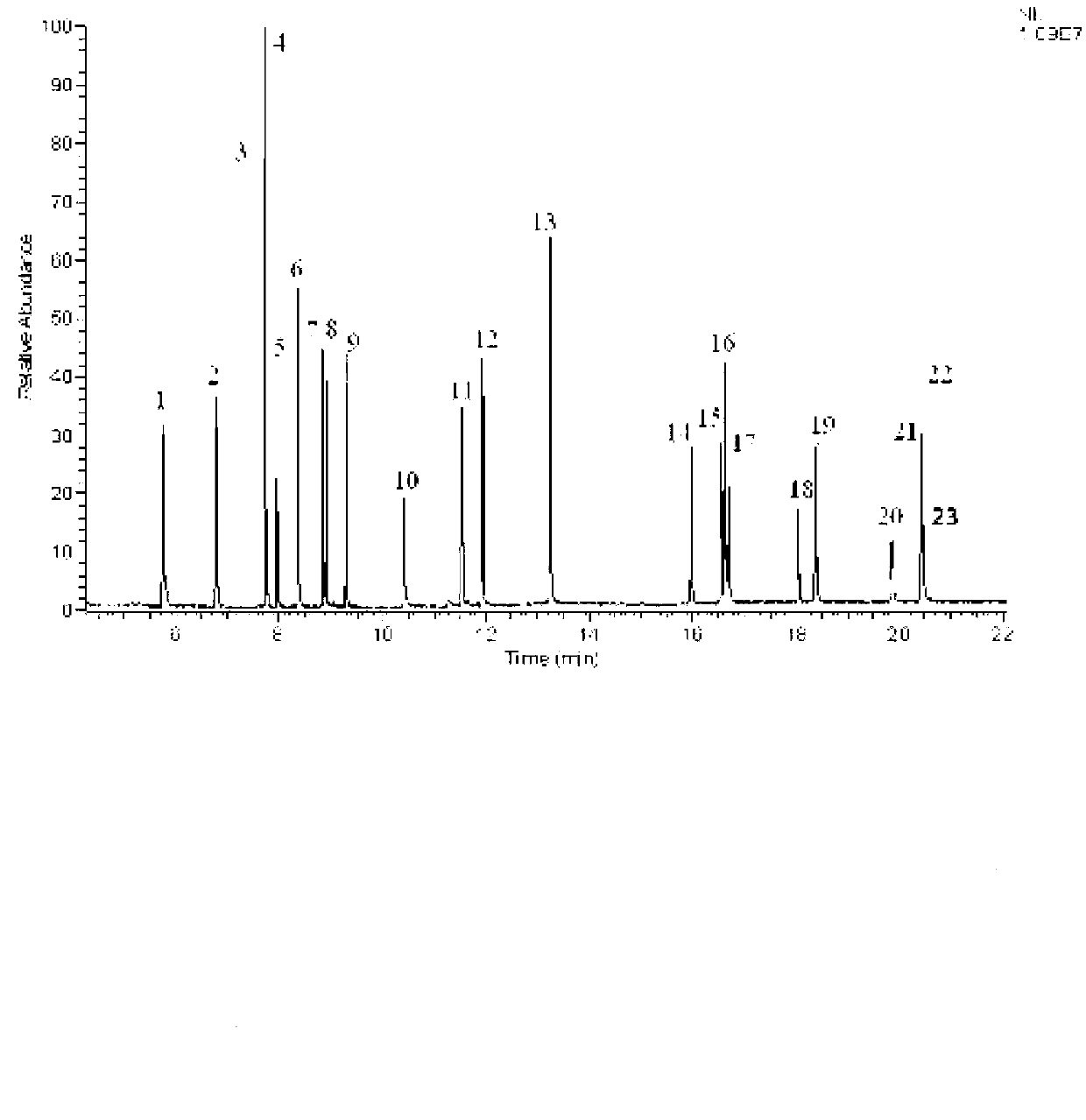
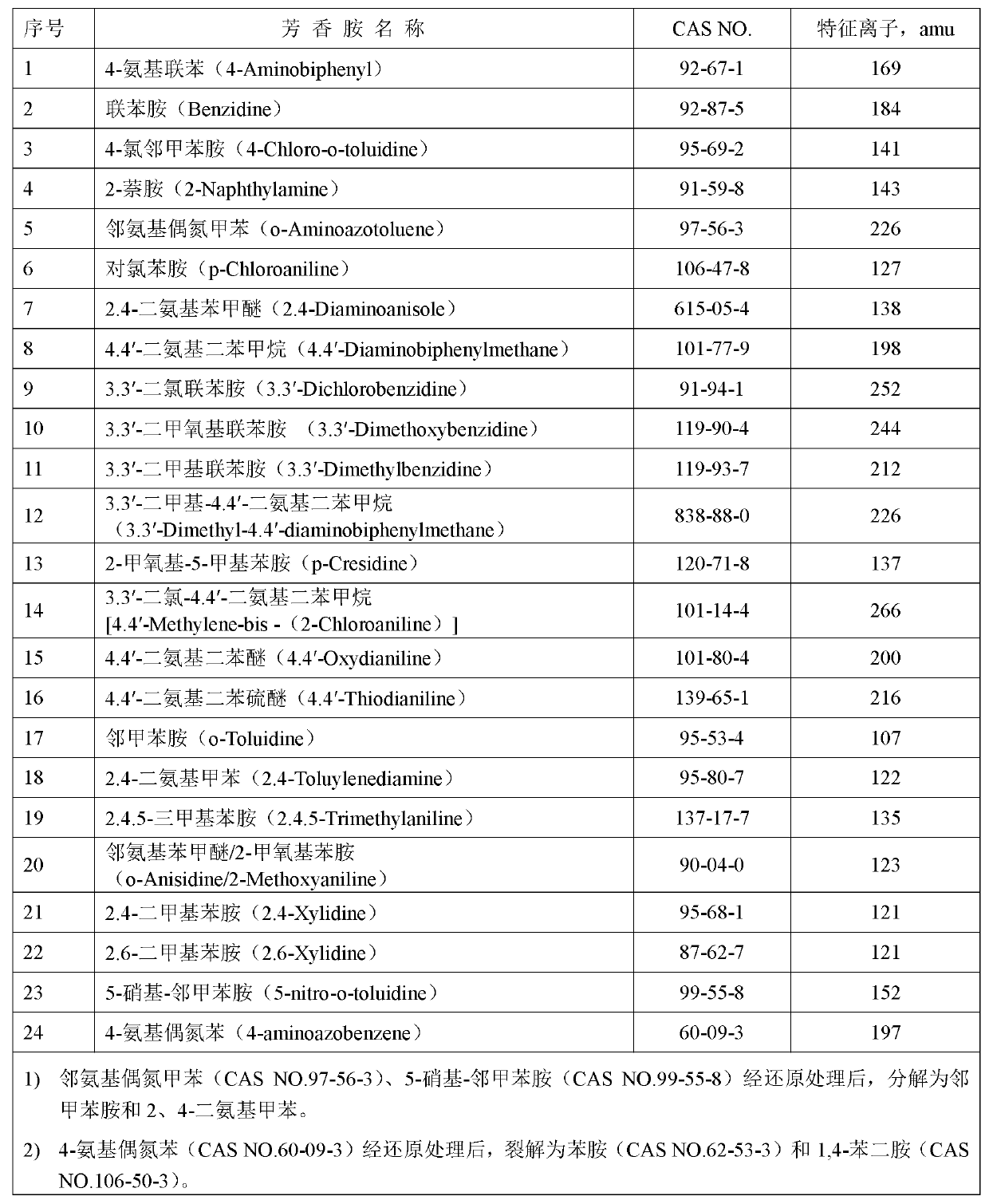
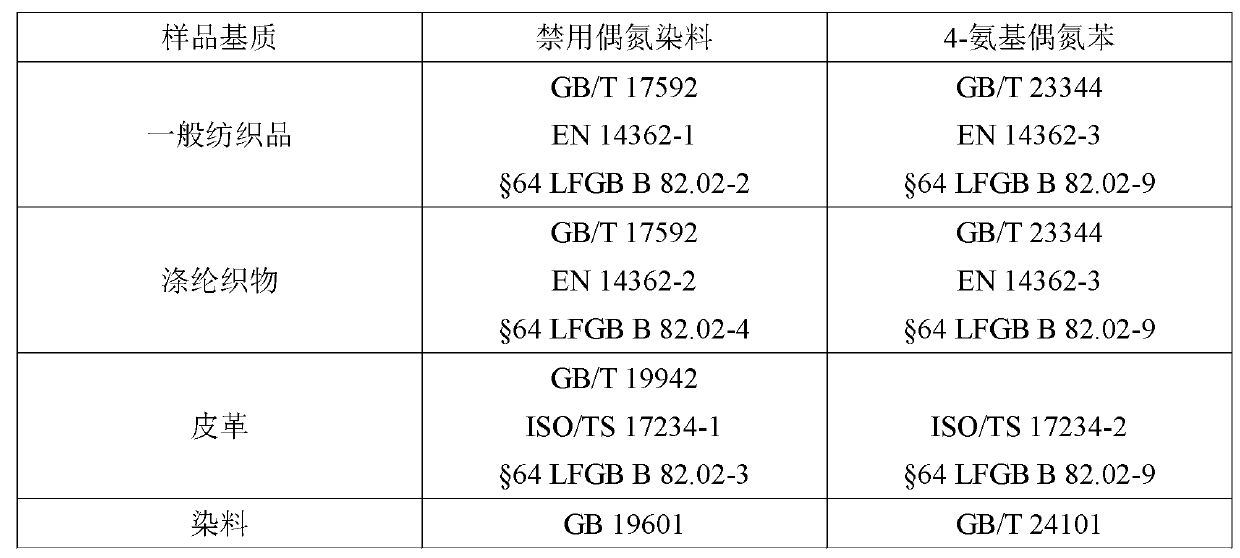
Method for quickly screening and detecting azo dyes forbidden in textile materials, leathers and dyes using gas chromatography mass spectrometry
ActiveCN102798677AReduce processing timeHigh consumption of reagents and materialsComponent separationChemistryMass spectrum analysis
The invention discloses a method for quickly screening and detecting azo dyes forbidden in textile materials, leathers and dyes using gas chromatography mass spectrometry, which comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a sample, 2) subjecting the sample to reduction reaction, 3) extracting the sample, 4) performing the gas chromatography mass spectrometry on the sample, 5) screening decision: compared with the GC-MS analysis result of a standard solution, if the retention time and the mass spectrum of the aromatic amine in the sample keep with standards, the sample is judged as a suspicious positive sample, otherwise it is a negative sample and directly judged as a qualified sample. The sample pre-treatment time is shortened, the cost is reduced, the detection time is shortened, the operation step is simple, the operation is convenient, the operation time is short, the operation cost is low, the detection efficiency is improved; the aromatic amine in the sample is detected by a gas chromatography mass spectrometer, color interference problem is not existed, the sample matrix is effectively prevented from being infected, and the judgment accuracy is high, thus the method is not only suitable for textile materials, but also suitable for other products such as leathers and dyes.
Owner:南京海关工业产品检测中心
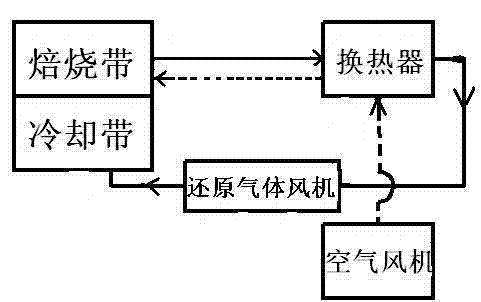
Single-dip pipe silicon iron bath vacuum circulated magnesium-smelting device and method
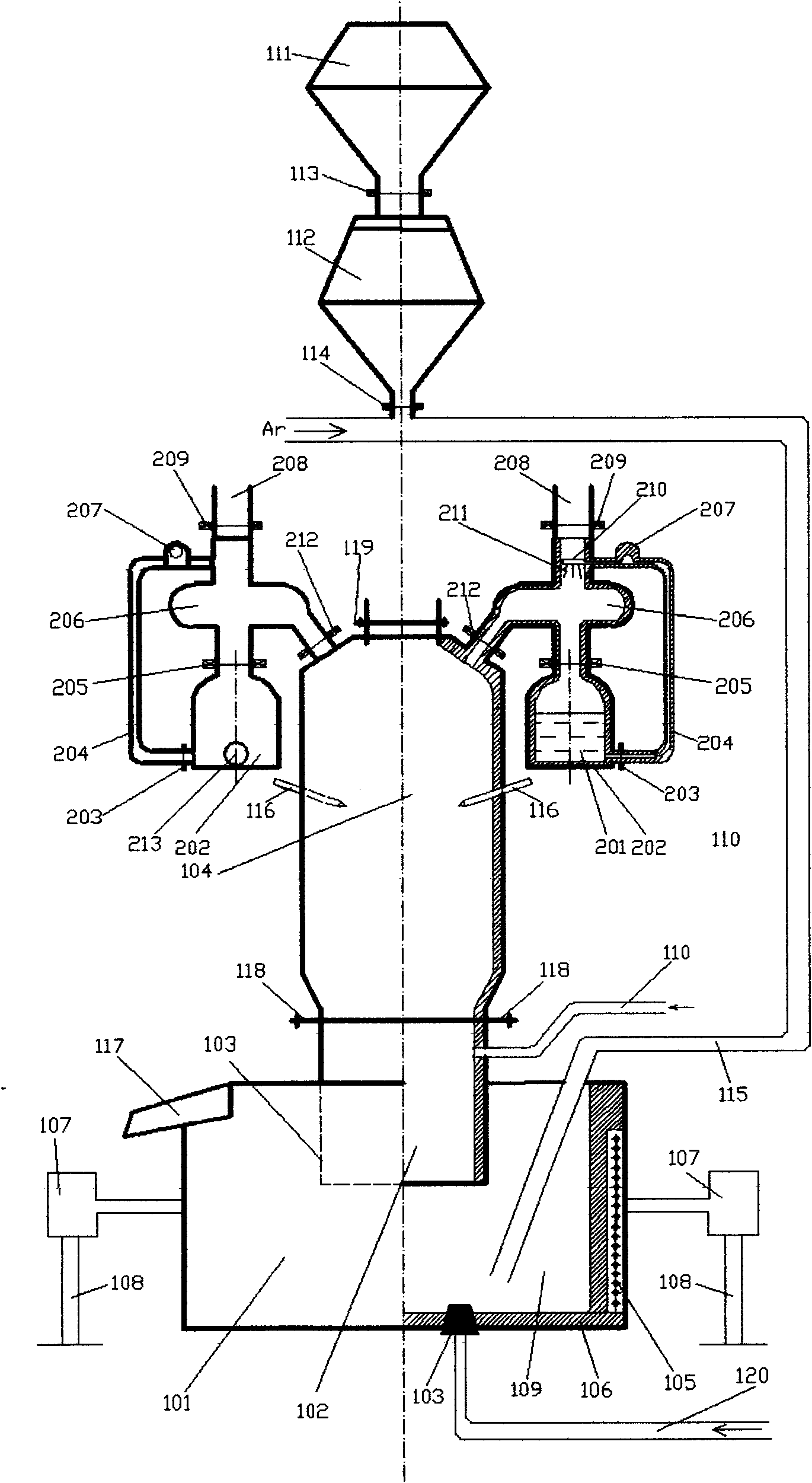
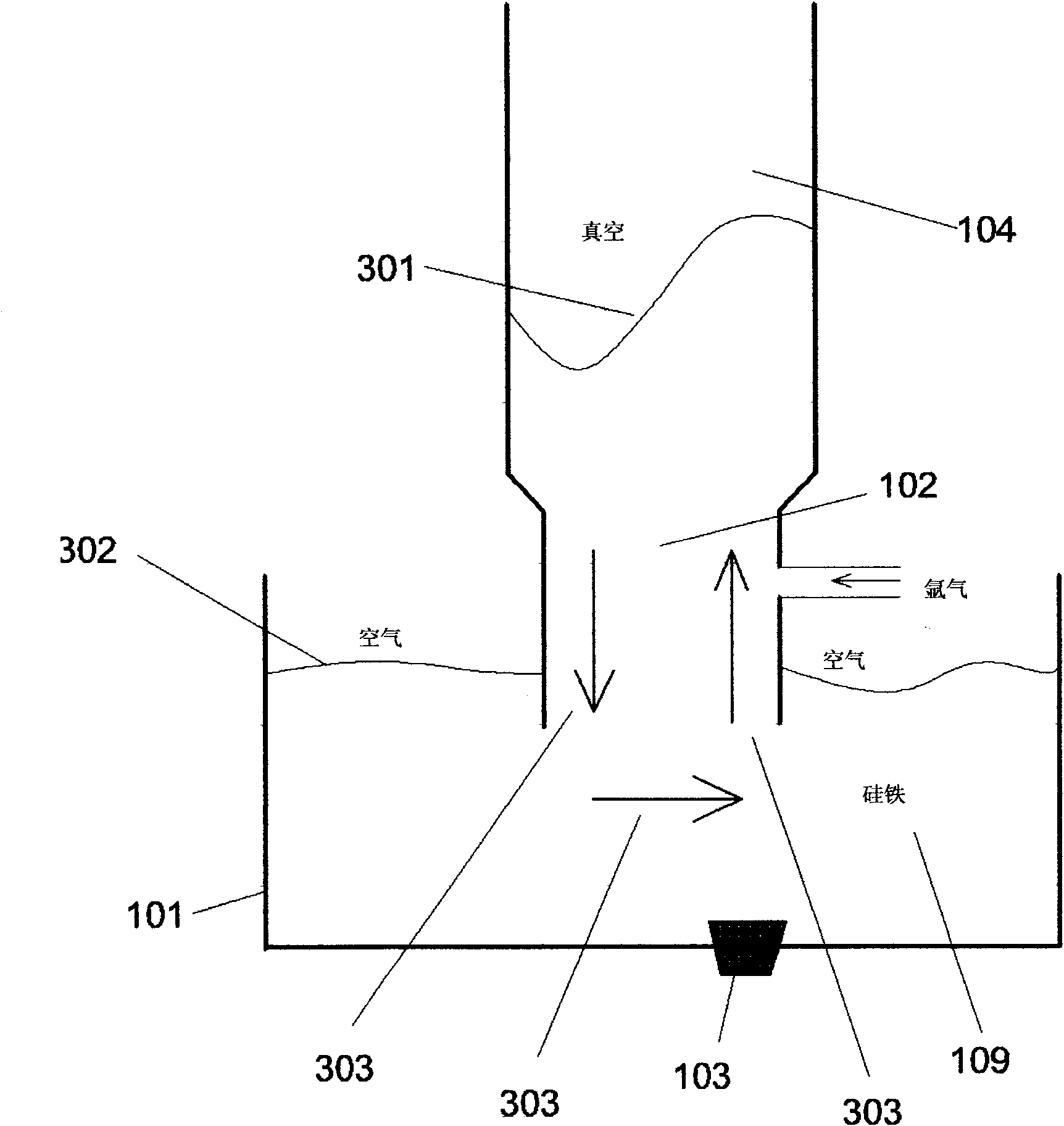
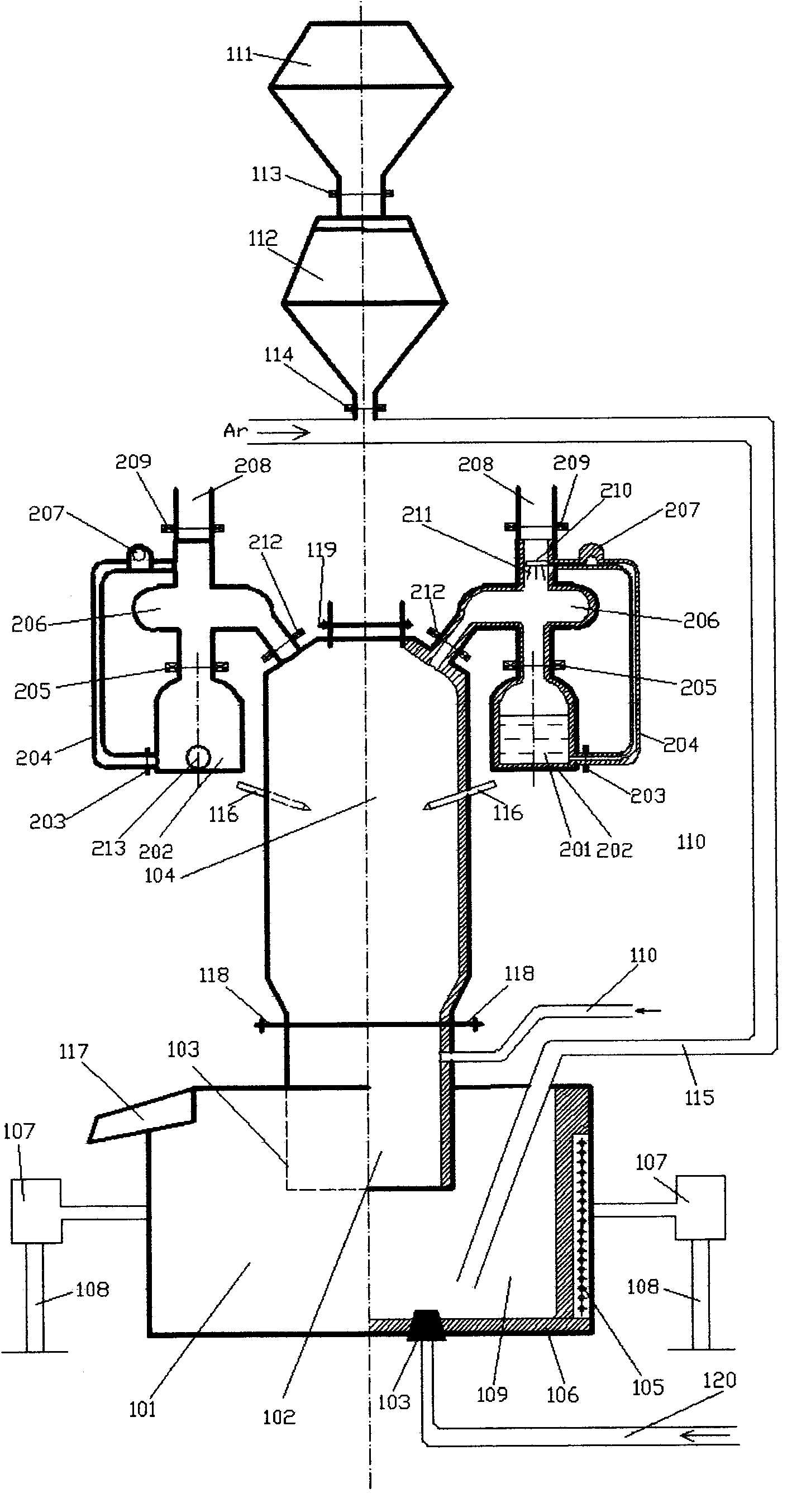
The invention discloses single-dip pipe silicon iron bath vacuum circulated magnesium-smelting device and method. The device comprises an induction furnace (101), a vacuum reaction chamber (104), a single dip pipe (102) and an argon blowing pipe (110) with a side wall communicated with guided flows; and besides, the device also comprises a magnesium steam condenser (206), a magnesium liquid spray thrower (210), a magnesium liquid storer (202) and magnesium mining powder conveying and spraying devices (111)-(115), wherein the magnesium steam condenser (206), the magnesium liquid spray thrower (210) and the magnesium liquid storer (202) are communicated. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing silicon iron liquid with the silicon content of 30%-65% and the temperature of 1,350-1,600 DEG C, making the mixtures of the silicon iron liquid and magnesium mining powder blown into the silicon iron liquid annularly flow between a vacuum reaction device and the induction furnace at the vacuum degree of 350 Pa-10,000 Pa for reaction to generate magnesium steam, carrying out condensation and magnesium liquid spraying to the magnesium steam to generate magnesium liquid, making the magnesium liquid flow into a storing device, and then pouring magnesium ingots. The device has the advantages of energy saving, low consumption, high productivity and the like.
Owner:杭州吉幔铁氢能科技有限公司
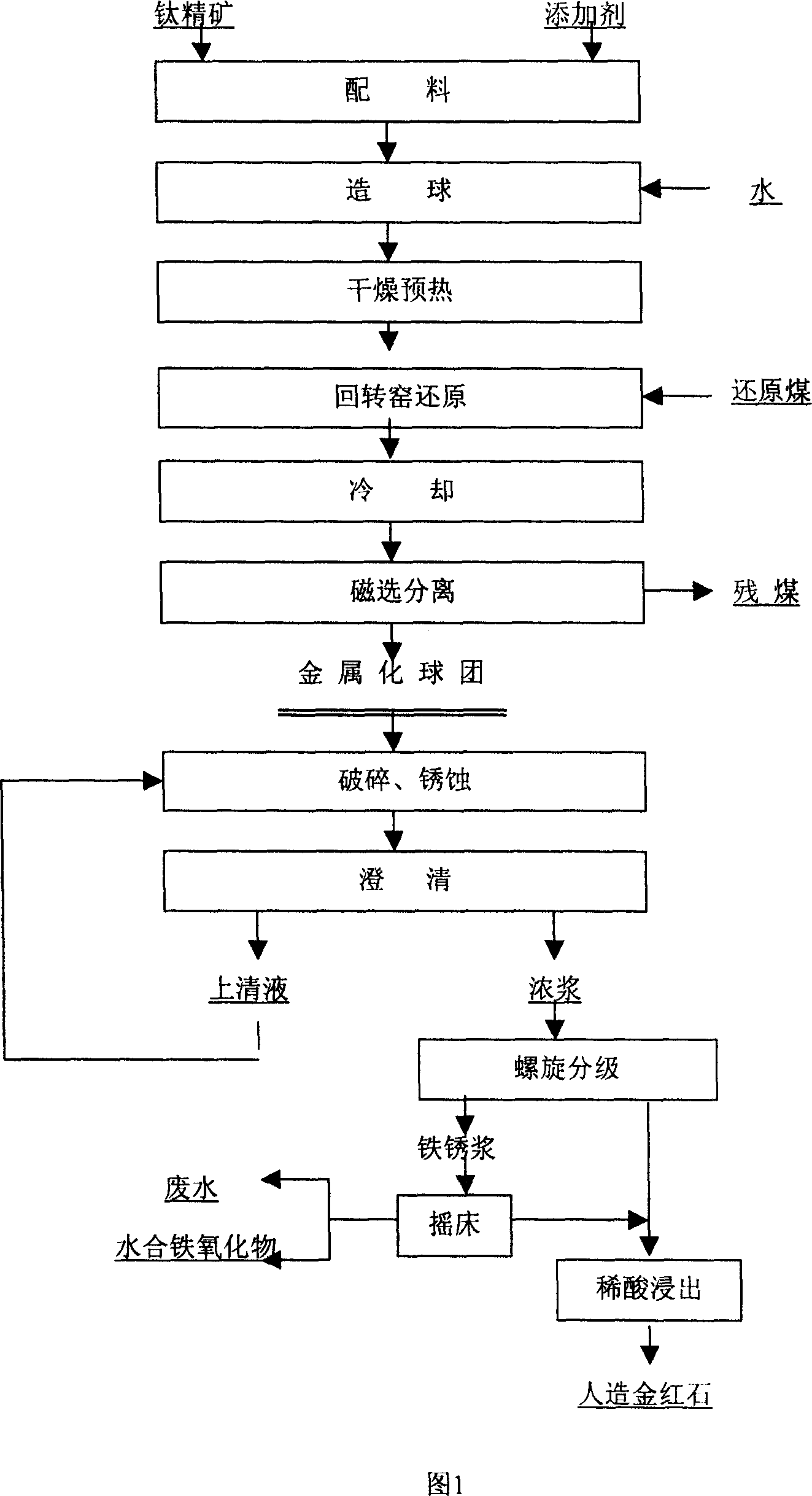
Method of preparing synthetic rutile from ore type ilmenite concentrate
InactiveCN1923703AEliminate the hidden danger of loopingImprove reducibilityTitanium dioxideIlmeniteTitanium
The invention discloses an artificial rutile preparing method through rock ilmenite concentrate, which comprises the following steps: preheating rock ilmenite concentrate in the rotary kiln to reduce directly; separating the corrosion of reduced ilmenite; immersing material with titanium in the diluted acid to remove impurity to prepare the artificial rutile.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for rapidly and directly reducing haematite or limonite into ferrous powder
The invention relates to a method in which hematite or limonite are quickly reduced and made into iron powder, which aims to use iron ore difficult to be magnetically separated as a raw material to reduce the cost. The method is characterized in that hematite ore or limonite ore are crushed and then washed and magnetically separated; iron ore powder, coal powder and lime powder are mixed according to the proportion, and calcium fluoride and adhesive are added to be pressed into flans with pores, and the flans are dried; the structure of a kiln car surface is improved, and a sagger is made; the pressed and dried flans are hoisted to the kiln car surface after being put orderly, and the sagger is covered outside the flans; a tunnel kiln is used for calcinating the flans, and two ends of the tunnel kiln are covered with air sealing machines; after the kiln car travels out of the tunnel kiln, a motor hoist is used to hoist the sagger, calcinating blocks are pushed into a water pool to be quickly cooled and automatically ground, and the iron powder and dregs are fished out to directly enter a ball mill to be wetly milled and be pressed into blocks or bagged after the separation of a magnetic separator and the drying.
Owner:王号德
Method for producing ferronickel alloy grain by directly reducing lateritic nickel ore by rotary kiln
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgical chemical industry and particularly relates to a method for producing ferronickel alloy grain by directly reducing lateritic nickel ore by a rotary kiln, comprising the following steps of: breaking and grinding the raw lateritic nickel ore free from drying; adding carbonaceous reducing agent and complex additive; removing natural moisture by a ball-pressing preheater; directly reducing in the rotary kiln; carrying out quenching and ore grinding to produced material; carrying out high-intensity magnetic separation to obtain the ferronickel alloy grain; and desulphurizing by using shell powder of which the activity is 40 times of that of the common lime stone. The ferronickel alloy grain contains less than 0.03% of sulphur, coal consumption of the method is 20% of that of the traditional process, The nickel recovery rate is more than 95%, the ferrum recovery rate is 70%, the tailing contains less than 0.08% of nickel, the reduction time is shortened, and the cost of the method is 1 / 3 of that of the traditional process. The tail gas of the rotary kiln can be used for generating electricity, the operation is simple and is easy to control, and the product is smelted by an electric furnace to directly smelt the ferronickel alloy grain; the quality of the product is good; a new path is provided for producing the ferronickel alloy grain; and the problems of high ore smelting grade, complex process, long flow, high energy consumption and environmental pollution can be solved.
Owner:徐伟
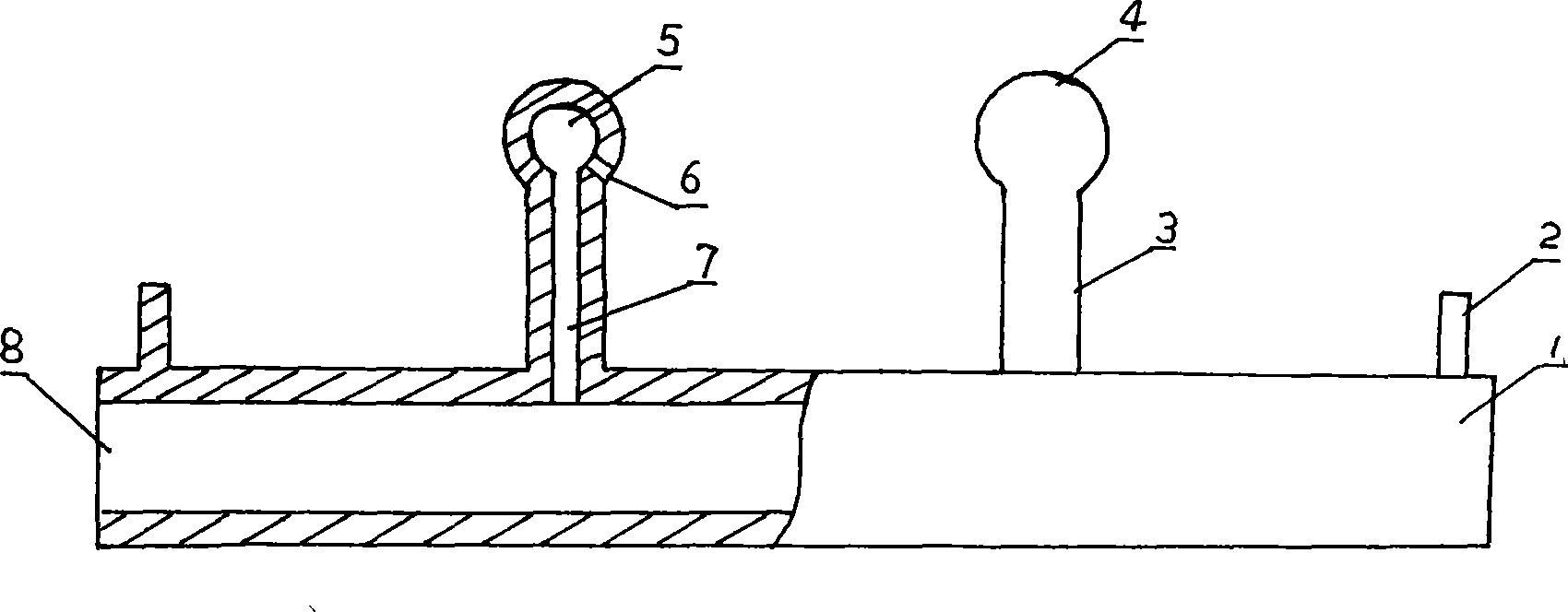
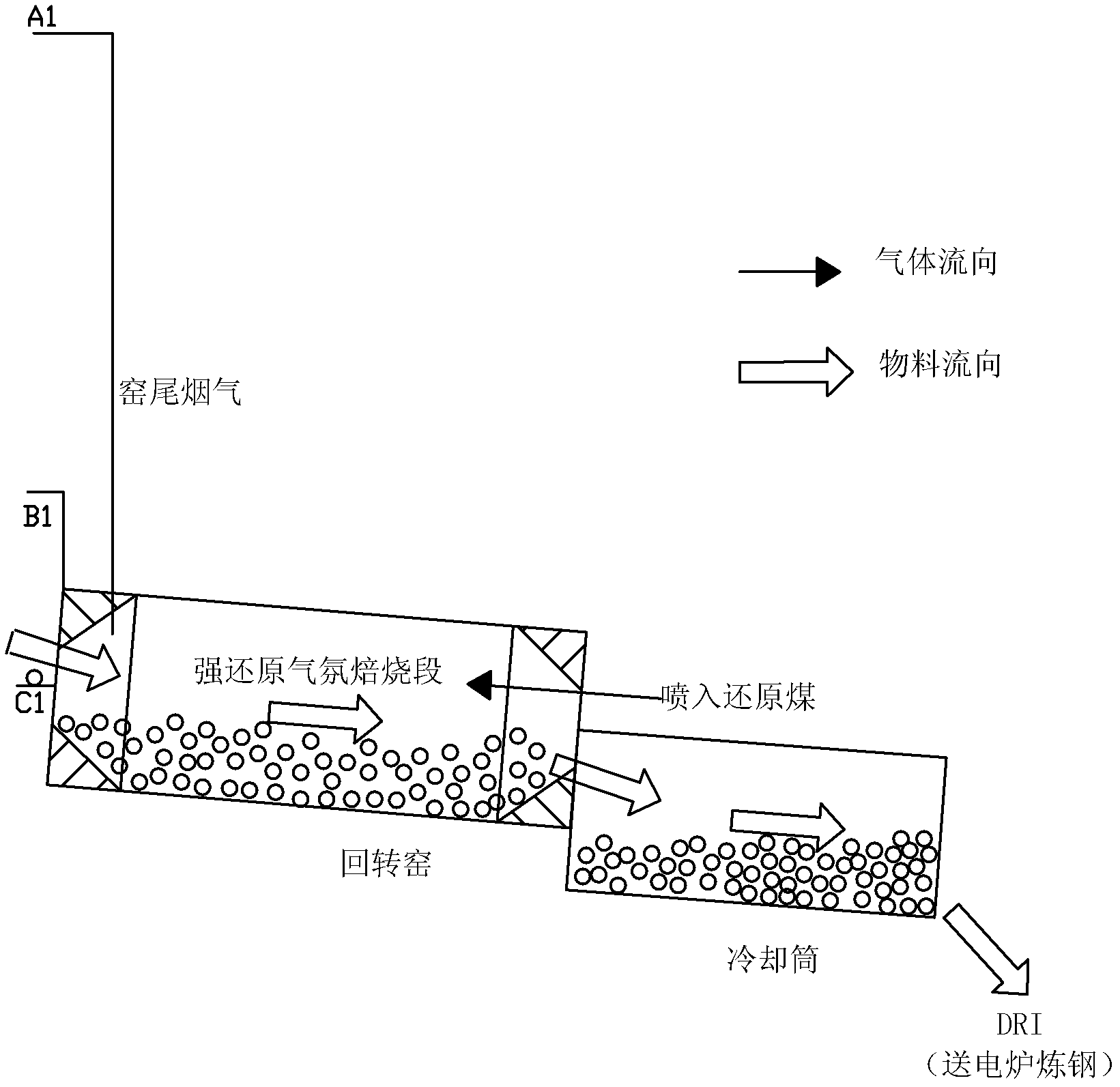
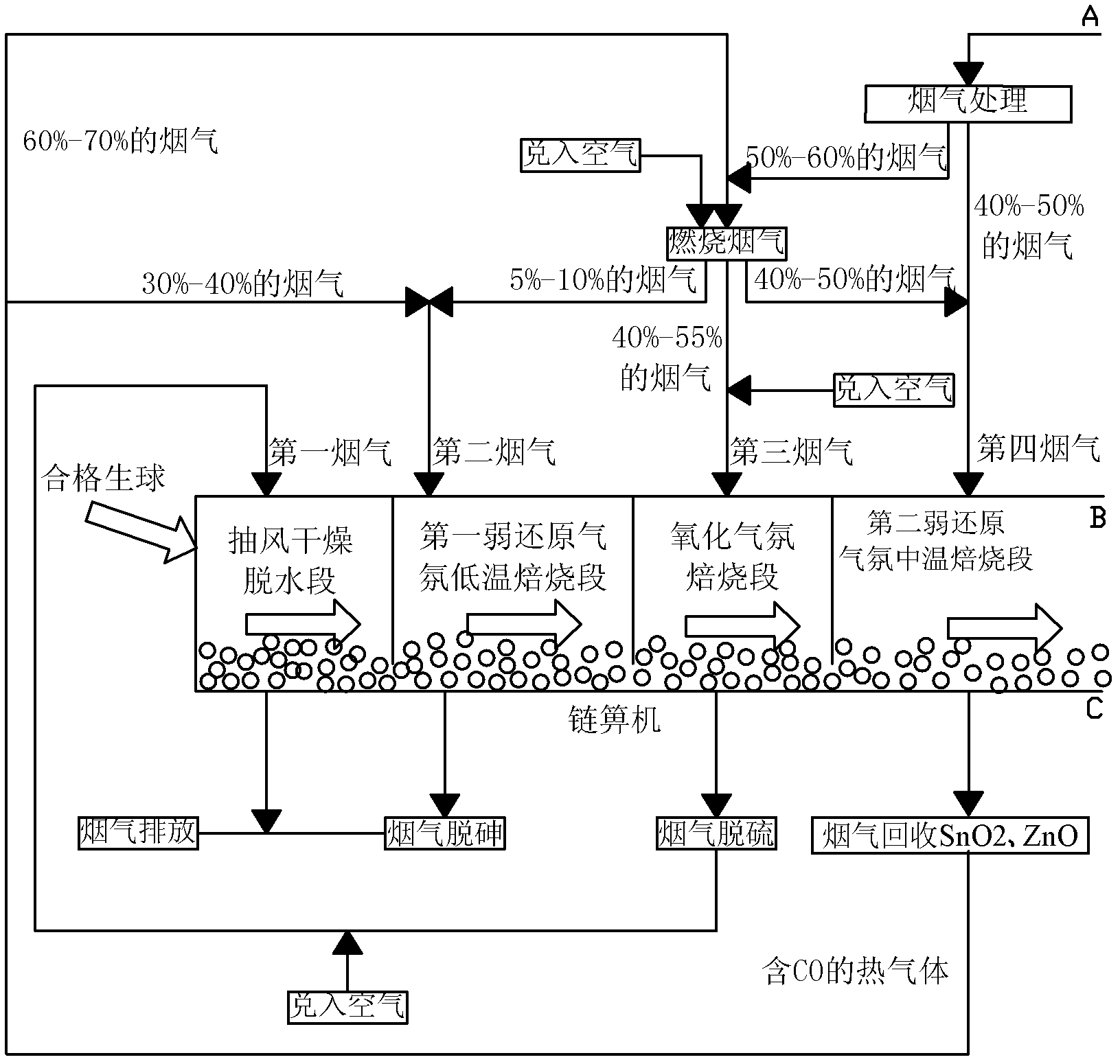
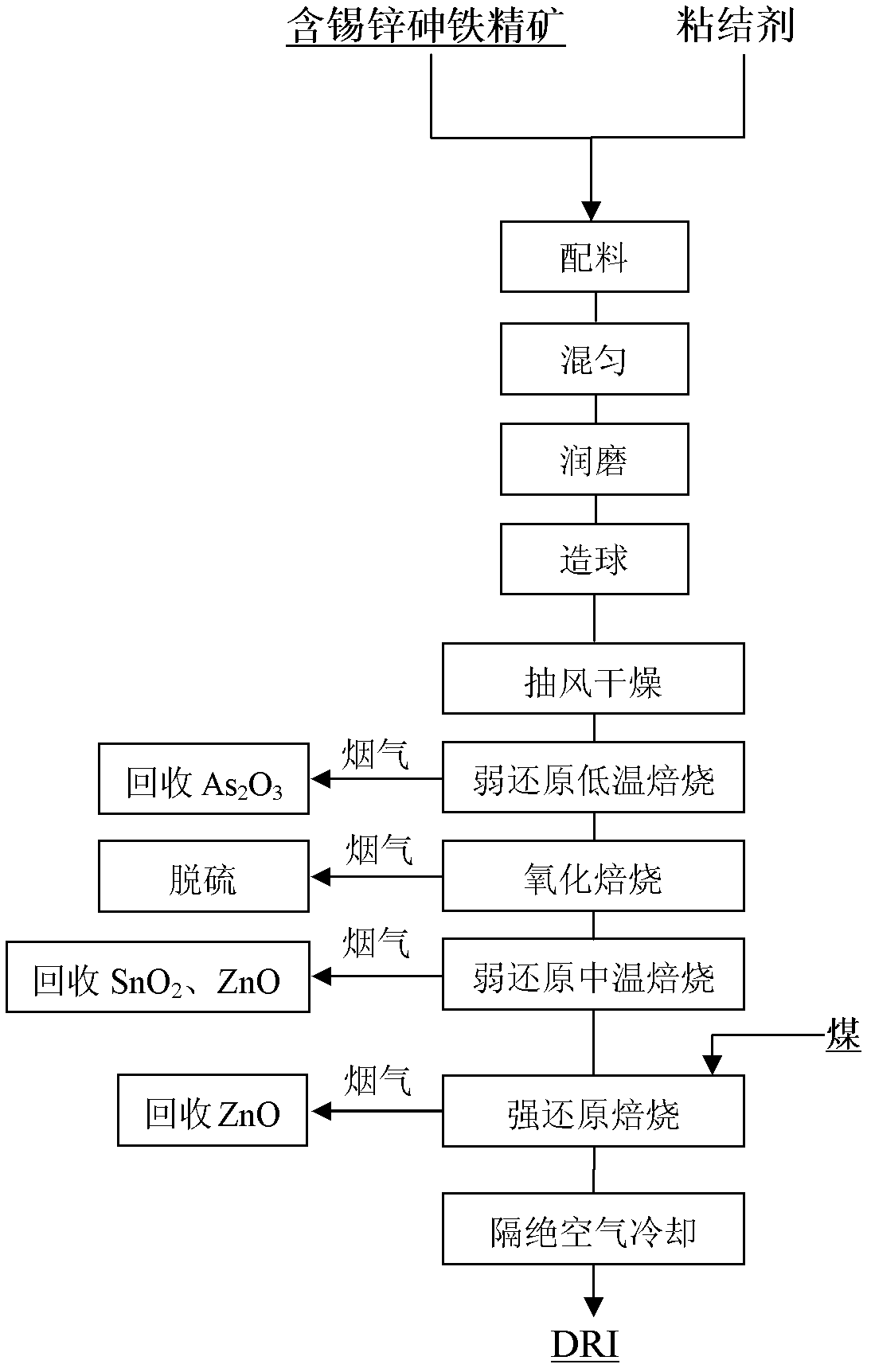
Method for preparing metallized pellets by utilizing stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained complex iron ore
InactiveCN102534087ARealize Deep RestorationResolve area processingRotary drum furnacesReducing atmosphereZinc
The invention relates to a method for preparing metallized pellets by utilizing stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained complex iron ore, which comprises the following steps: proportioning stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained iron ore concentrate with a binder, evenly mixing and damp milling and then pelletizing; drying and dehydrating fresh pellets on a chain grating machine through air draft; roasting in a weak reducing atmosphere at low temperature to remove arsenic; roasting in an oxidizing atmosphere to remove sulphur; roasting in the weak reducing atmosphere at high temperature to remove stannum and zinc to obtain pre-reduced pellets; and filling the pre-reduced pellets into a rotary kiln to perform coal-based direct reduction roasting to obtain the metallized pellets (DRI- direct reduced iron). According to the method for preparing the metallized pellets by utilizing the stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained complex iron ore, the technology of thermally filling the pre-reduced pellets into the kiln is adopted, thereby, the reduction speed of the pellets in the rotary kiln is obviously accelerated, and the production rate is increased. Simultaneously, the stannum, the zinc and the arsenic in the stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained complex iron ore are selectively separated, thereby, large-scale processing and utilization on the stannum-zinc-arsenic-contained iron ore concentrate can be realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Stainless steel smelting method
ActiveCN101476016AShorten heating timeReduce restore timeElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceIntermediate frequency
The invention belonging to the field of smelting relates to a stainless steel smelting method.The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1) electric furnace smelting; 2) a intermediate frequency furnace melting alloy; 3) LF furnace heating; 4) VOD vacuum decarburizing; 5) VOD vacuum reducing and adding aluminum as the reductive in the vacuum state; 6) argon protecting and teeming.According to the invention, by adopting an electric furnace added with a intermediate frequency furnace and adopting a method of adding reductive under a vacuum state, the LF heating and reducing time is shortened, stay time of molten steel in ladle is reduced, steel-making cost is reduced and the manufacture security is improved. The technology has a remarkable economic benefit by producing stainless steel with a high alloy content. The reducing time is shortened from 7 hours primarily to 3-4 hours currently, therefore, the production efficiency is improved greatly, the forgeable pieces producing capability is extended and the economic benefit is remarkable.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA NORTH HEAVY INDS GROUP
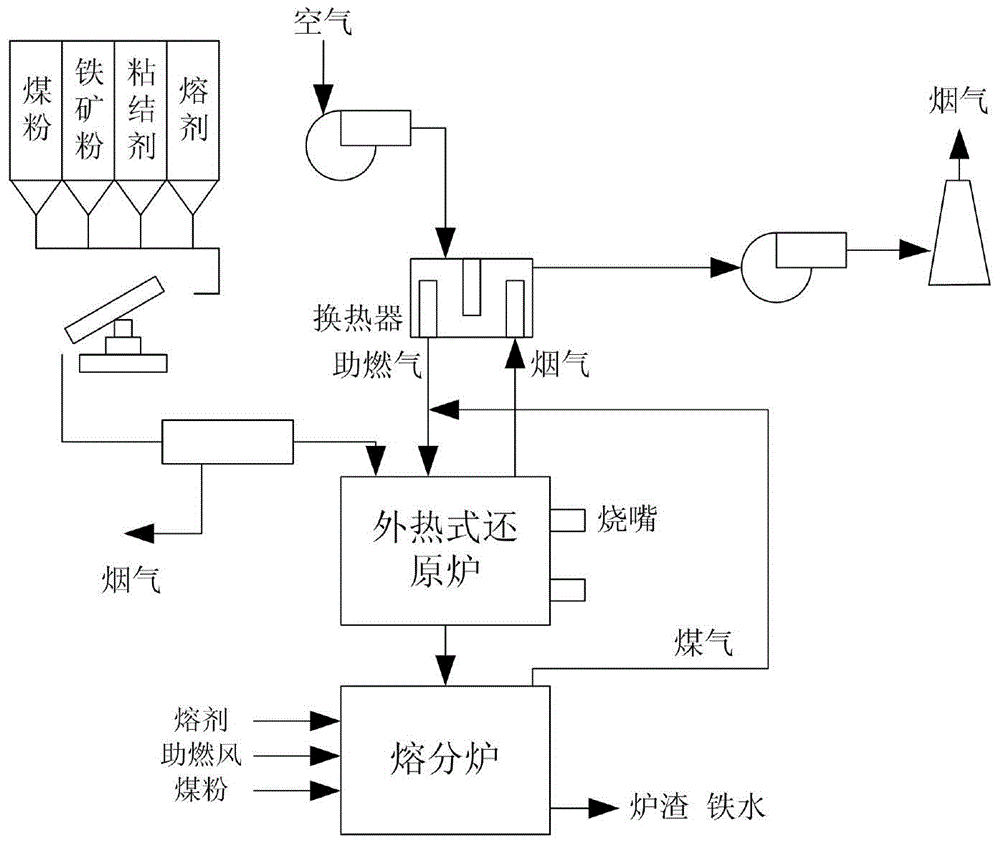
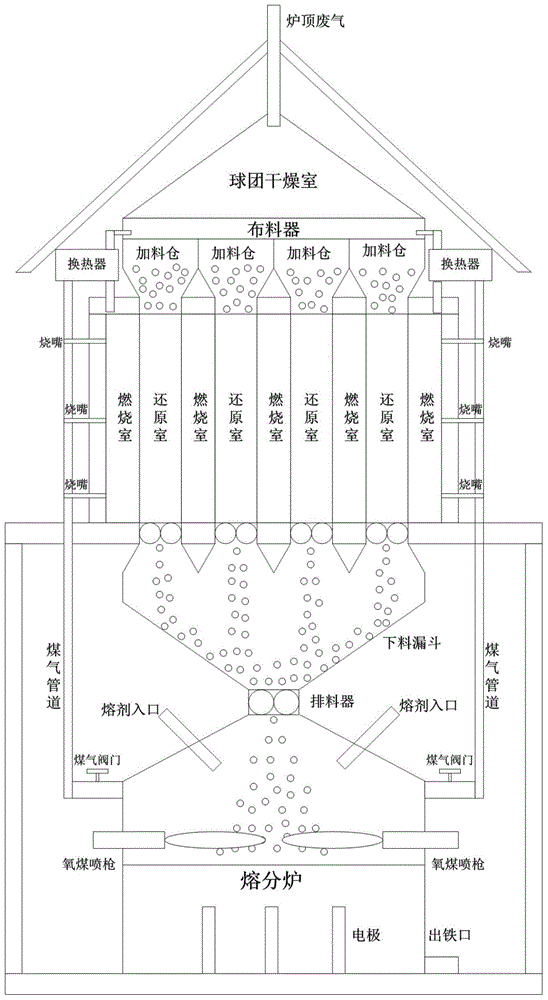
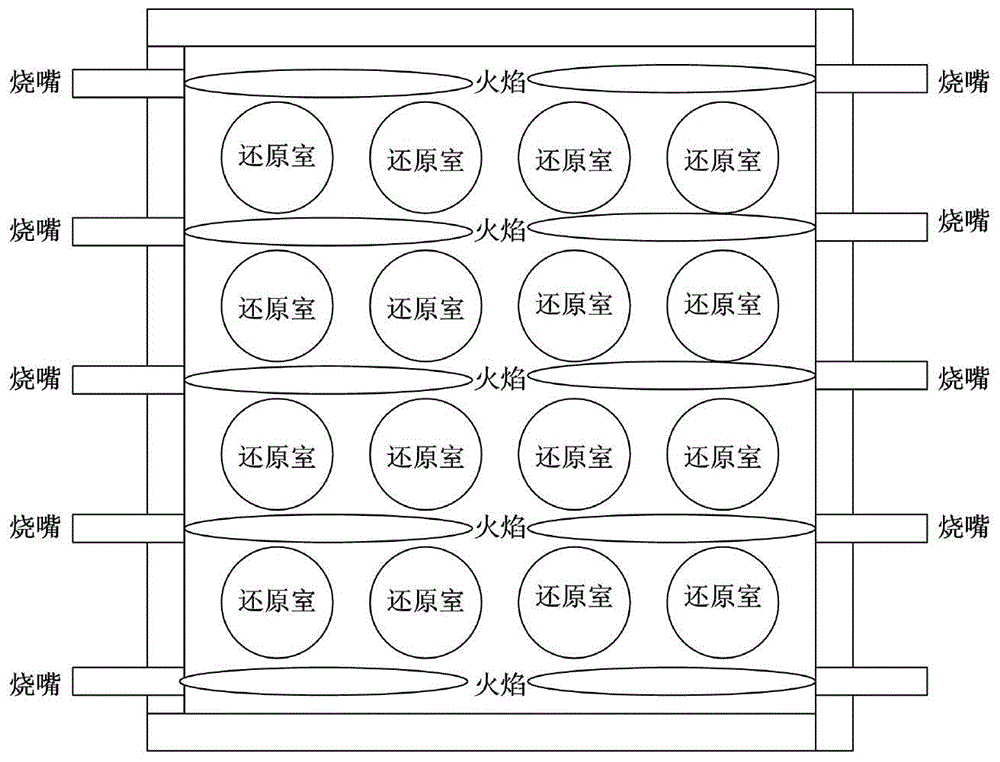
Coal-based direct reduction-melt separation furnace smelting reduction iron-making process using external heating mode
The invention relates to a coal-based direct reduction-melt separation furnace smelting reduction iron-making process using an external heating mode. Equipment used in the process comprises a pellet drying chamber, a distributing device, an external heating type reduction furnace and a melt separation furnace which are arranged from top to bottom. The process includes the steps that S1, carbon-bearing pellets are preheated and dried in the pellet drying chamber; S2, the carbon-bearing pellets in a reduction chamber are continuously and evenly heated, and the carbon-bearing pellets are quickly reduced in the reduction chamber; S3, high-temperature metallized pellets are obtained after the carbon-bearing pellets in the reduction chamber are reduced, and the high-temperature metallized pellets are charged into the melt separation furnace in a hot-delivery and hot-charging mode to be subjected to reduction smelting; S4, after the metallized pellets enter the melt separation furnace, the melting point, the viscosity and the separating effect of slag iron are controlled through the content of added flux and pulverized coal, reduction smelting of the metallized pellets is completed, and accordingly high-quality molten iron and high-temperature furnace slag are obtained. By the adoption of the process, iron ore which is low in grade and difficult to reduce is utilized comprehensively, the technological process is shortened, production cost is lowered, product quality is improved, and production efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
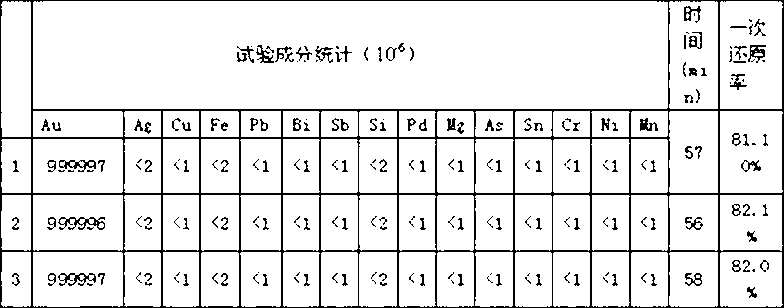
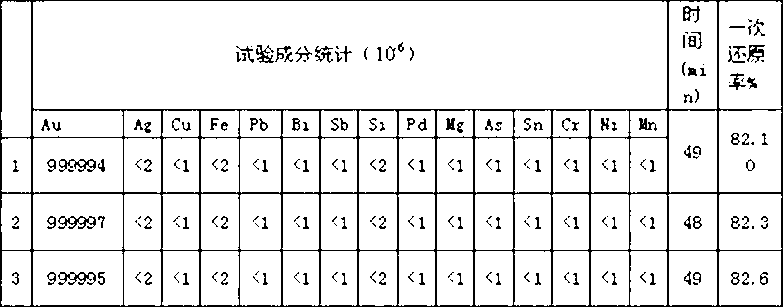
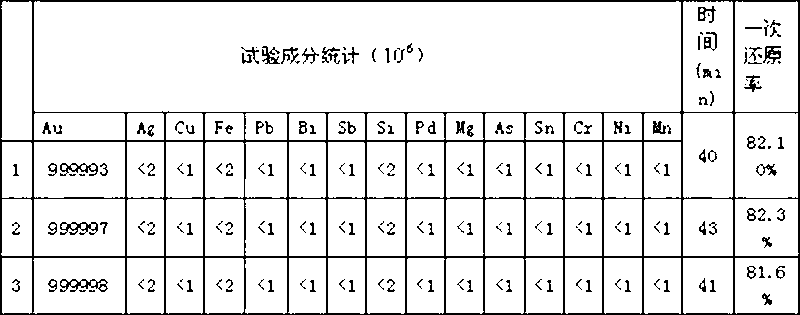
New technology for extracting high-purity gold by adopting wet process
InactiveCN102703691AProduct quality is stableReduce restore timeProcess efficiency improvementIngot castingAqua regia
The invention relates to a new technology for extracting high-purity gold by adopting a wet process, which comprises the following steps: melting gold in aqua regia; concentrating and removing nitrate; diluting and filtering; reducing and depositing; filtering and cleaning; and fusing ingot casting. In the step of reducing and depositing, SO2 is taken as a reducing agent; when the electric potential of the solution is 680-730mv, especially when the electric potential of the solution is 700mv, the introduction of reducing gas is stopped, so that the purity of the end product is kept above 99.999% and the once percent reduction of the product is higher. According to the new technology, the optimal reduction temperature is confirmed; when the reduction temperature is at 40-60 DEG C, optimal temperature is at 50 DEG C; and the reduction time is effectively shortened.
Owner:SICHUAN TIANZE PRECIOUS METALS
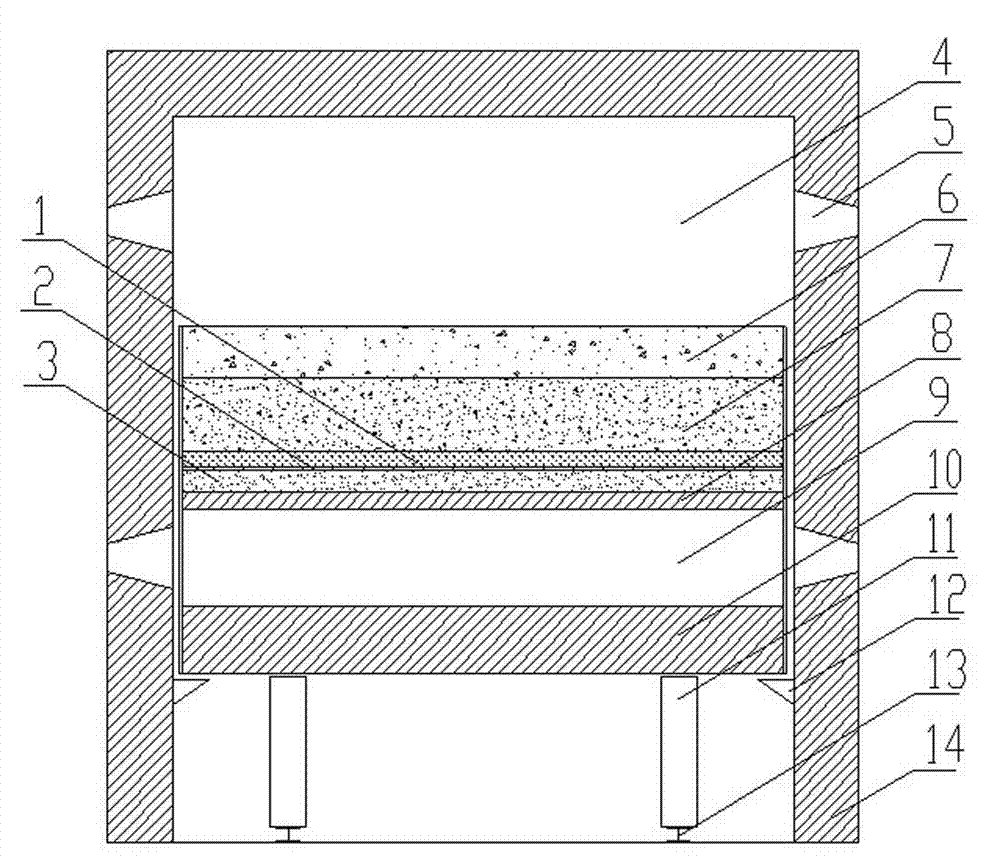
Hierarchical material distribution reduction method for sponge iron tunnel kiln and tunnel kiln applying same
ActiveCN103937921ARestore evenlySolve the problem of using external gas fuel for normal productionFurnace typesTunnel kilnCarbon layer
The invention discloses a hierarchical material distribution reduction method for a sponge iron tunnel kiln and the tunnel kiln applying the hierarchical material distribution reduction method. Materials to be reduced are divided into different grades according to the particle size range, the materials, in different grades, to be reduced are respectively mixed with reducers to form mixed materials, the mixed materials are tiled on a table board of a tunnel kiln car in layers, the particle size range of the materials to be reduced in each layer is gradually increased from the bottom layer to the top layer, and the kiln car carries out reduction by passing through a preheating zone, a roasting zone and a cooling zone in the tunnel kiln after the materials are tiled. By adopting the hierarchical material distribution reduction method, iron ores in different particle sizes can be uniformly reduced during reduction from the upper layer to the bottom layer and in a process of oxygenating for the upper layer by the lower layer in the tunnel kiln; ash of a reduced carbon layer can leak into the lower part from an isolation pore plate, and magnetic separation quantity of a magnetic separation step for the reduced materials after drawing is reduced; and a heat exchanger specially used for the tunnel kiln and a fan are arranged, so that a reducing gas is fully utilized, burning gas does not need to be additionally supplemented, and cost is reduced.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
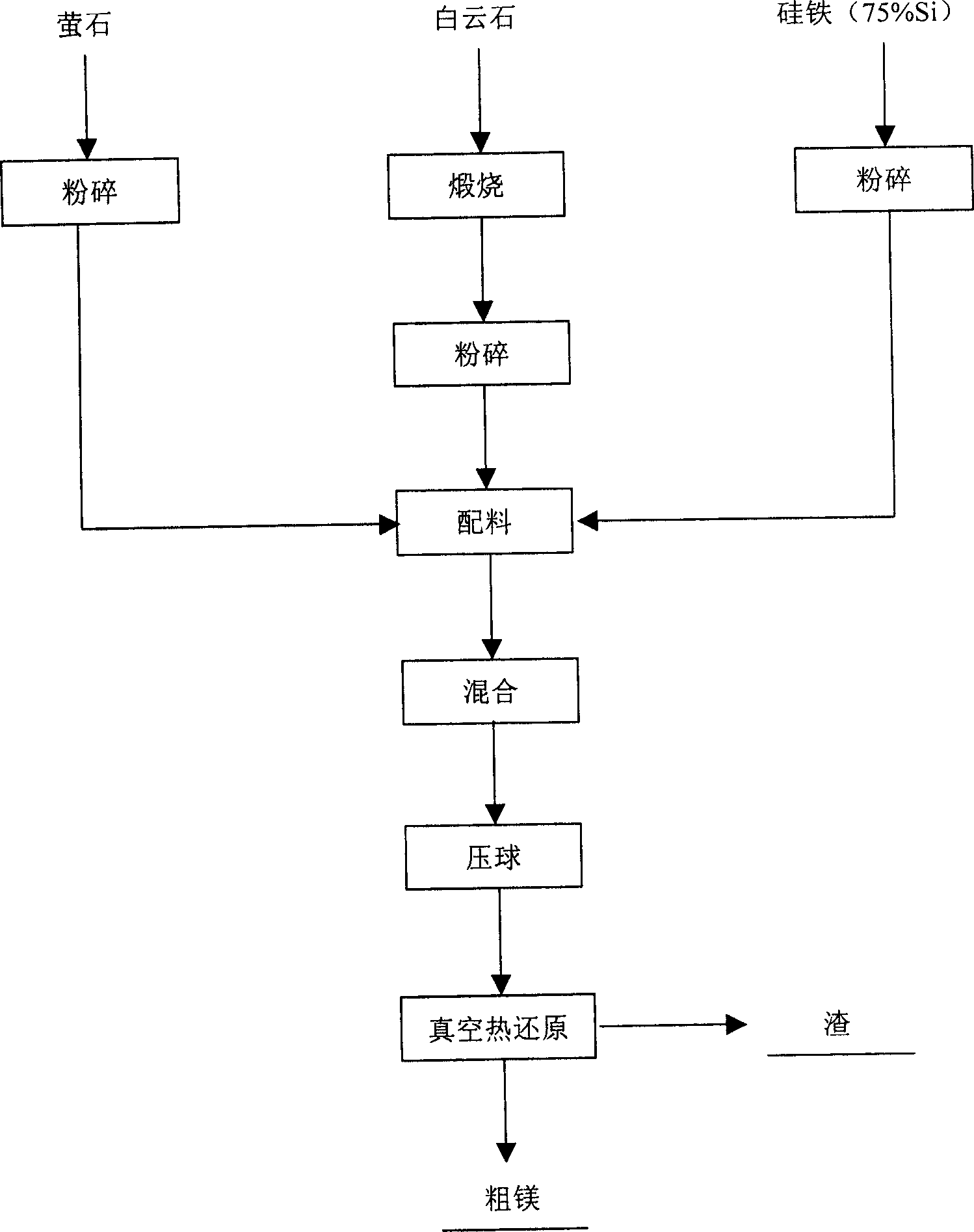
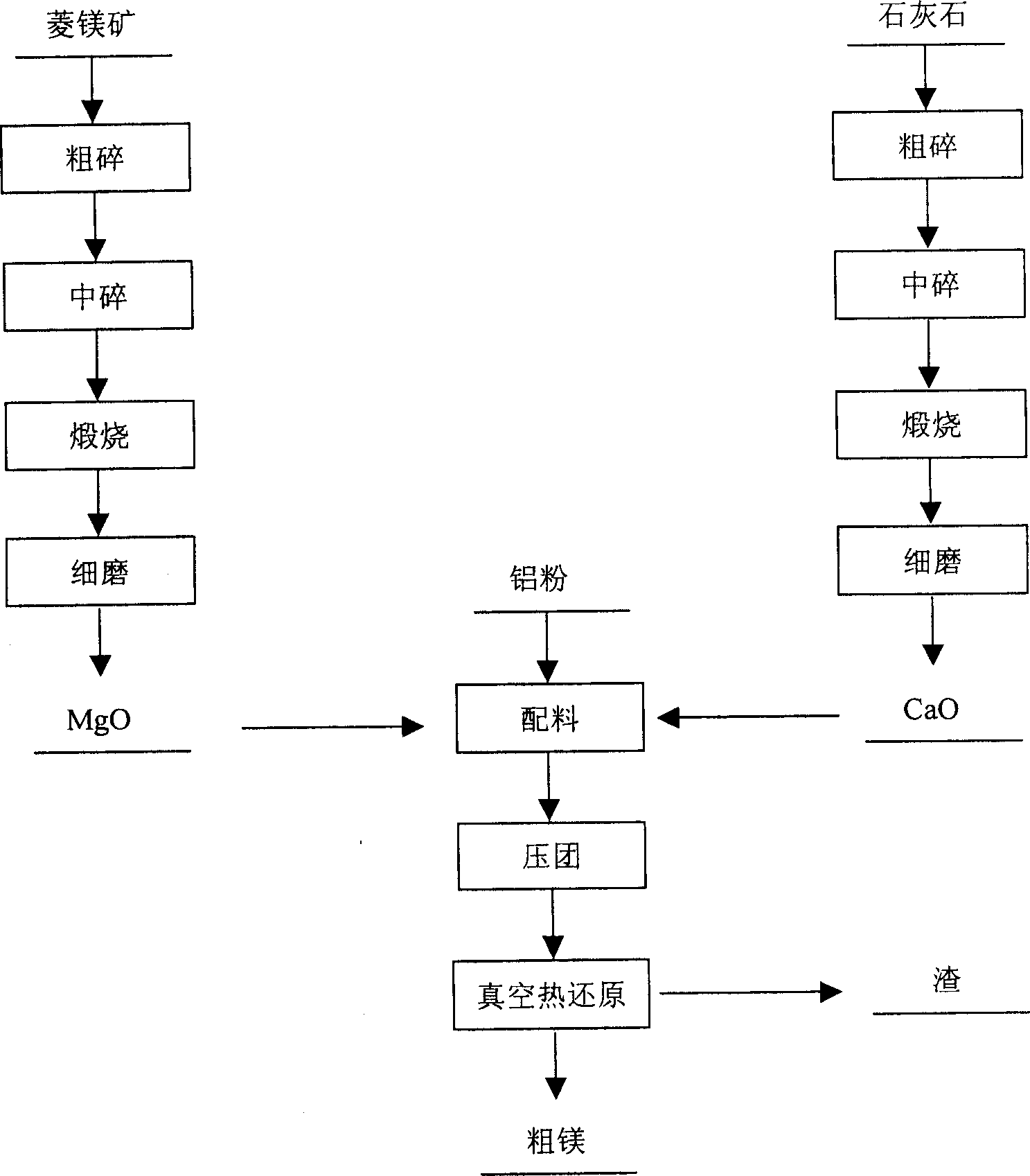
Aluminothermic reduction method and technology of giobertite calcination to produce magnesium
Disclosed is an aluminothermic reduction method and technology of giobertite calcination to produce magnesium which comprises using magnesite powder as raw material, aluminum powder as reducing agent, the invention is characterized in that, (1) charging 5-15 wt% calcined limestone powder (CaO) as adjuvant, (2) calcining magnesite powder at 700-1000 deg C for 1 hour to prepare active MgO, (3) mixing magnesite powder, limestone powder and aluminum powder by the weight ratio of 35-80:5-15:15-54, making into blocks under 40-450MPa, (4) loading the block into retort, evacuating and heating in reducing furnace, reducing 4-8 hours at 1050-1170 deg. C to obtain crude magnesium. The invention also discloses the optimum parameter for the process.
Owner:路忠胜
Reduction kiln equipment and method for directly reducing iron
InactiveCN102643942AImprove thermal conductivityFacilitate conductionFluidised-bed furnacesCombustion chamberEngineering
Owner:辽宁博联特冶金科技有限公司
Method for directly reducing laterite-nickel ore to produce ferronickel alloy
The invention discloses a method for directly reducing laterite-nickel ore to produce a ferronickel alloy, belonging to the technical field of metallurgy and chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing the raw laterite-nickel ore with a carbonaceous reducing agent and a compound additive, and grinding in a ball mill; (2) uniformly stirring the mixture obtained by the step (1), and pelletizing; (3) feeding the pellets obtained by the step (2) into a preheater for preheating to remove natural moisture, and directly feeding the preheated pellets into a silicon nitride bonded silicon carbide reducing tank for reduction; and (4) performing water quenching grinding on the reduced product obtained by the step (3), and performing slag-iron separation by use of a magnetic separator to obtain the ferronickel alloy. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the reducing time is shortened, the production cost is reduced, the production efficiency is improved, and a new high-quality raw material is provided for smelting high-class nickel alloy particles; meanwhile, the production cost is only 1 / 3 of that of a traditional technology; and the technology has the advantages of large-scale continuous production, high automation degree and short technological flow.
Owner:王晓彬
Method for recovering refined stannum for tinning from electroplate tin mud
ActiveCN104131177AReduce wear and tearLow pricePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodTinning
The invention discloses a method for recovering refined stannum for tinning from electroplate tin mud, and the method belongs to the technical field of tin recovery methods and is used to recover refined stannum for tinning from electroplate tin mud. The technical scheme employs the following recovery process: performing dewatering drying on electroplate tin mud subjected to acid leaching; performing oxidation roasting, and mixing with proper amount of a reducer for preparing a material; performing protective-atmosphere reduction at a relatively low reducing temperature for relatively short reducing time; and performing electrorefining and remelting on obtained crude tin to obtain refined tin for tinning. The method removes Bi, As, Sb and other harmful elements through acid leaching and roasting manners; the reducer is cheap in price and easily available; the reducing conditions are easily controlled, and the reducing time is substantially shortened compared with that of conventional reduction smelting; and the obtained refined tin is extremely less in impurities and completely accords with electroplating requirement. The recovering method helps to obtain refined tin for electrotinning and alleviate the problem that a large amount of tin is loss during electroplating, also solves the problems that tin mud is difficult is process and easily causes environment pollution, and has economic benefit and environmental benefit.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Reducing roasting method for powdered iron ores in tunnel kiln
The invention discloses a reducing roasting method for powdered iron ores in a tunnel kiln, which is designed for solving the problems of low heat transfer efficiency, long reducing time, non-uniform material reduction quality, and the like when powdered iron ores are subjected to reducing roasting in a tunnel kiln. According to the invention, by reasonably selecting the particle size range and distribution of iron ores, iron ores with different particle sizes and reducing coal are mixed and distributed in layers, and then the obtained object is subjected to reducing roasting, so that the iron ores with different particle sizes achieve a same roasting effect, thereby increasing the metal recovery rate of roasted iron ores, improving the quality of roasting, shortening the roasting time, reducing the roasting temperature, and lowering the production cost.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
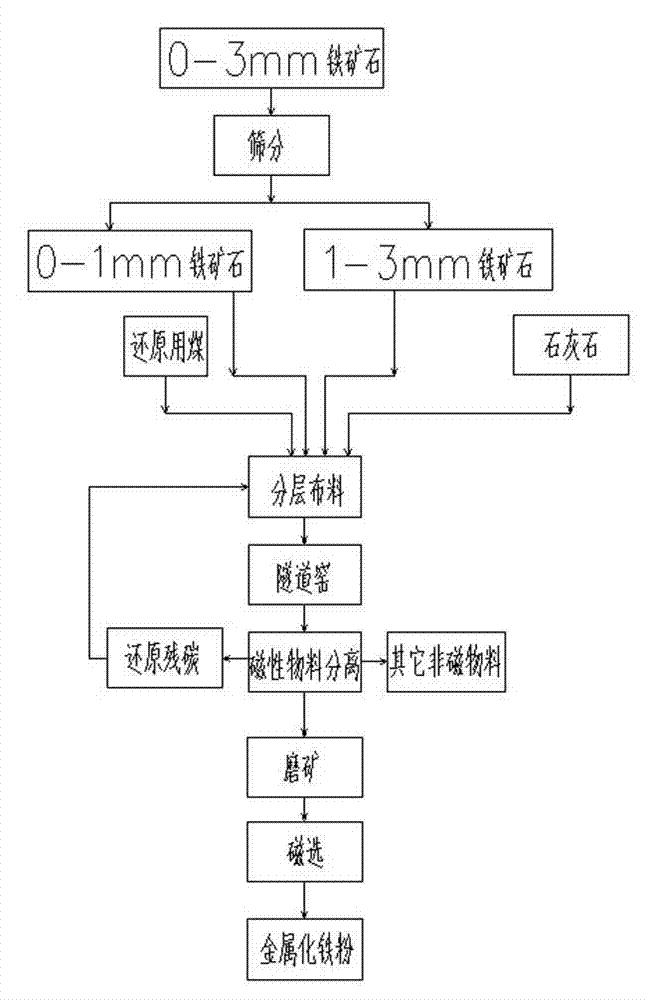
Combined direct reduction technology of blast furnace gas ash and refractory low-grade iron ore in tunnel kiln
ActiveCN104004874AEfficient use ofImprove carbon use efficiencyRecycling and recovery technologiesTunnel kilnIron powder
The invention provides a combined direct reduction technology of blast furnace gas ash and refractory low-grade iron ore in a tunnel kiln. The combined direct reduction technology mainly comprises the following processing steps: (1) burdening and mixing the iron ore with grain sizes of 0-3mm and the blast furnace gas ash so as to obtain fine-graded materials; grading the iron ore with grain sizes of above 1mm according to different grain size ranges, burdening and mixing the iron ore and reduced coal in the same grain size range so as to obtain coarse-graded materials; (2) sequentially laying the fine-graded materials and the coarse-graded materials on a fire-resistant thermal conducting plate of a kiln car of a tunnel kiln from top to bottom; and (3) placing the materials in the tunnel kiln along with the kiln car so as to carry out high temperature reduction. The combined direct reduction technology has the advantages that the blast furnace gas ash is effectively utilized, and the utilization efficiency of carbon in the blast furnace gas ash is greatly improved; by adopting a layering distribution step-by-step oxygenation reduction method, the metallization ratio of iron ore direct reduction is increased, and the reduction time is shortened; and the iron grade of metallizing iron powder produced by the technology reaches above 84%, and the metallization ratio reaches above 88%.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Stainless steel dust treatment process
InactiveCN107937711AEfficient use ofAchieve recyclingMagnetic separationProcess efficiency improvementReduction treatmentCoal
The invention relates to a stainless steel dust rotary kiln direct reduction treatment process. The stainless steel dust rotary kiln direct reduction treatment process comprises the steps that (1), stainless steel dust and reducing coal are dosed and mixed according to a ratio of 100:(10-20), and granular materials with a water content of 10-12% and a particle size of 3-5mm are prepared; (2), thegranular materials are dried and preheated in a preheating zone of a rotary kiln and are entered a high-temperature reduction zone and are reduced at a temperature of 1100-1200 DEG C for 90-120 minutes, high-volatile pea coal and high-grade grain ore are injected into the rotary kiln for carbon and hydrogen combined reduction and carbon cycle oxygenation reduction in a middle-late stage of dust reduction, so that the stainless steel dust can be sufficiently reduced in the rotary kiln; and (3), high-temperature calcined materials from the rotary kiln are subjected to cooling and magnetic separation, and granular metallized products used in a power supply furnace or a converter can be obtained. According to the stainless steel dust rotary kiln direct reduction treatment process, while processing stainless steel dust from iron and steel enterprises, the iron, nickel and chromium resources in the dust mud are effectively utilized to produce high-quality metallized materials containing nickel and chromium.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
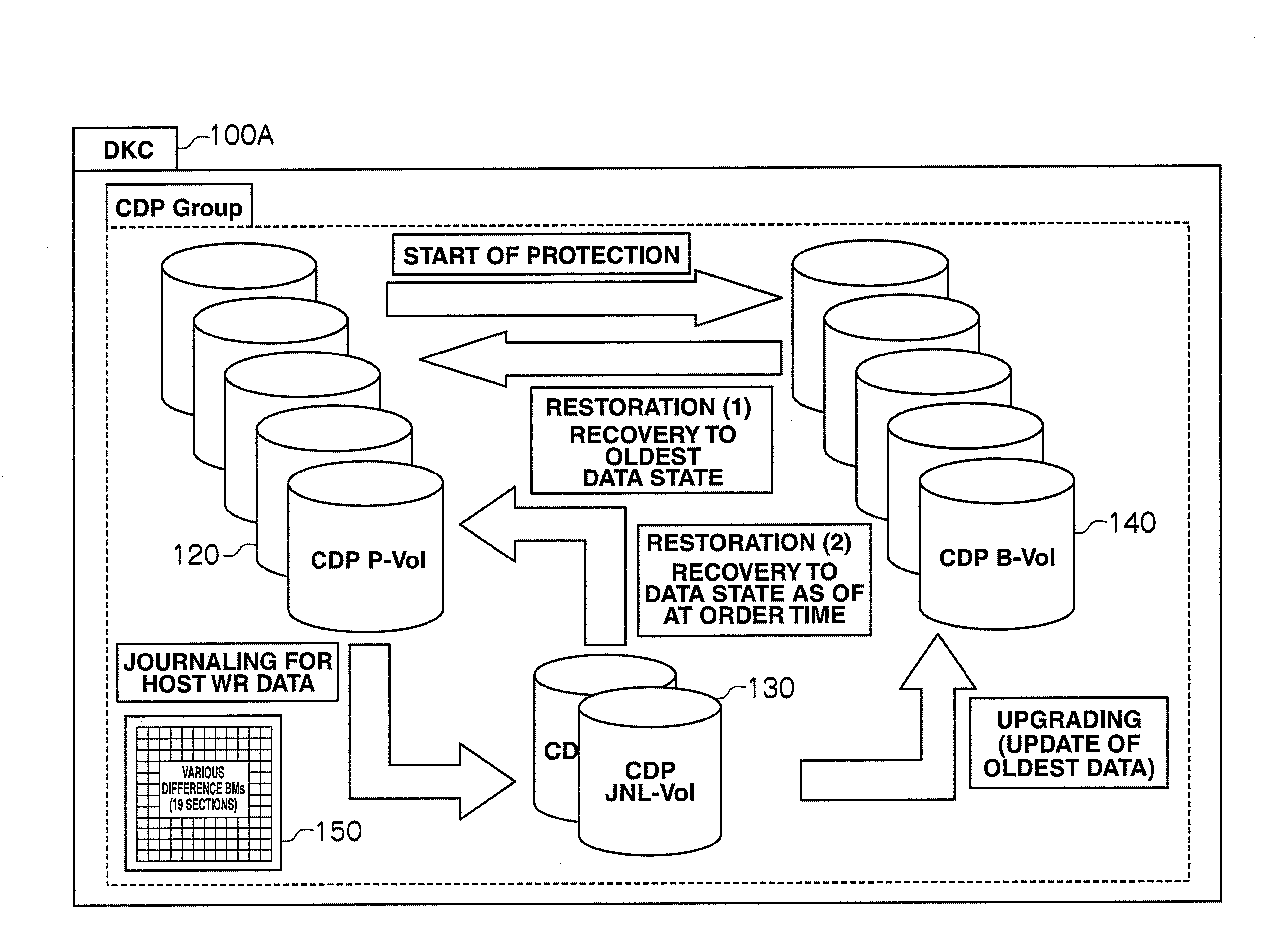
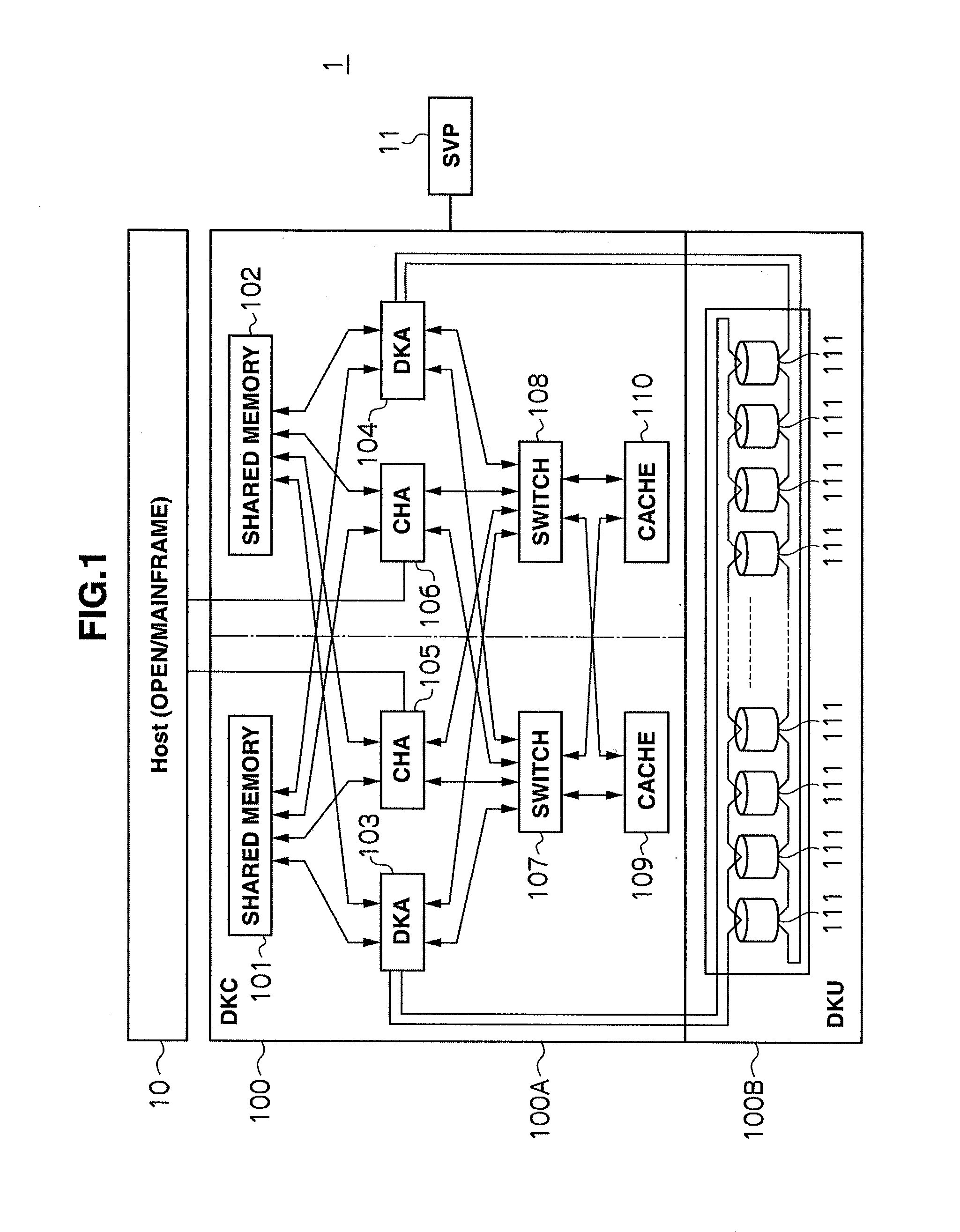
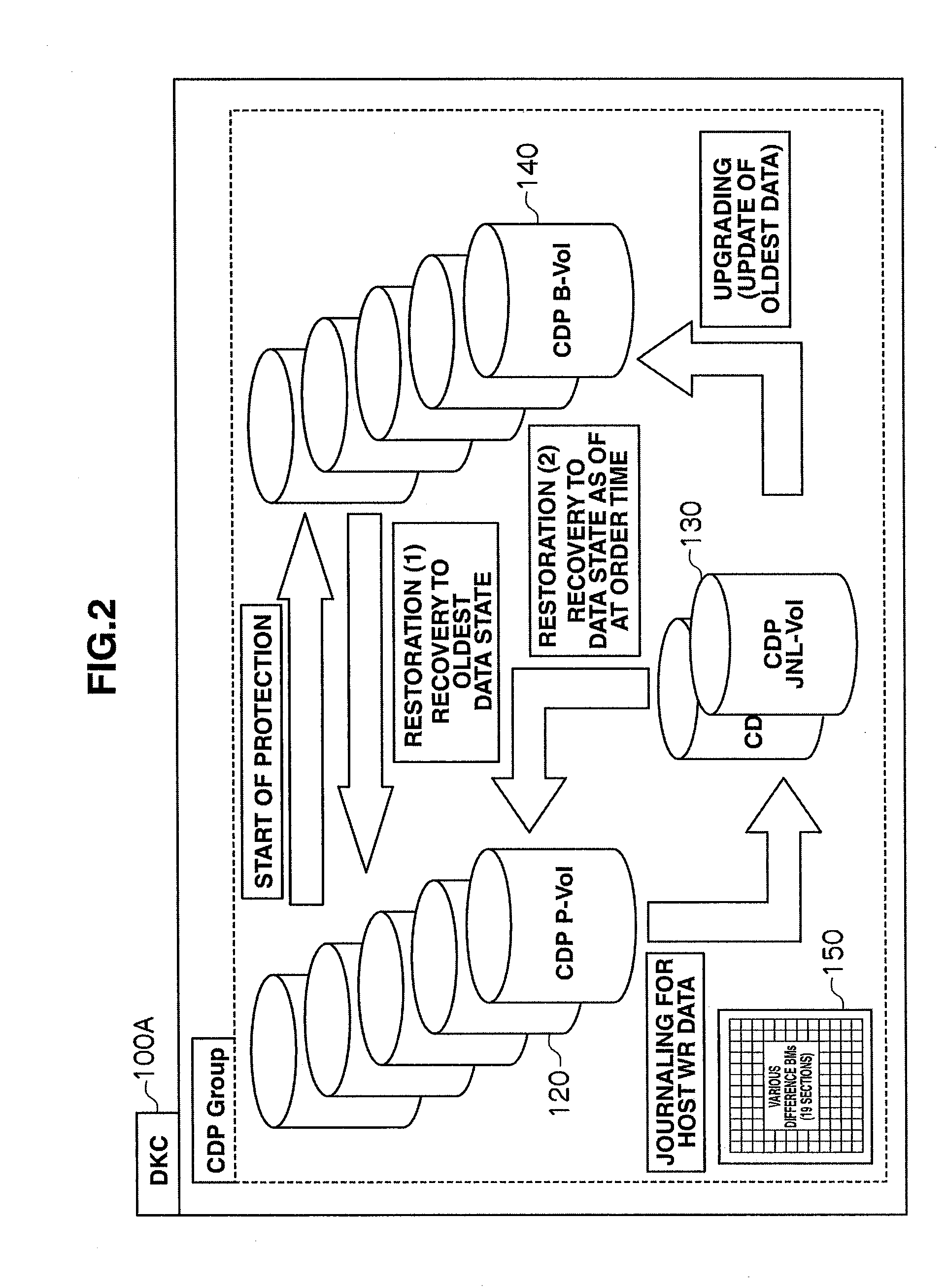
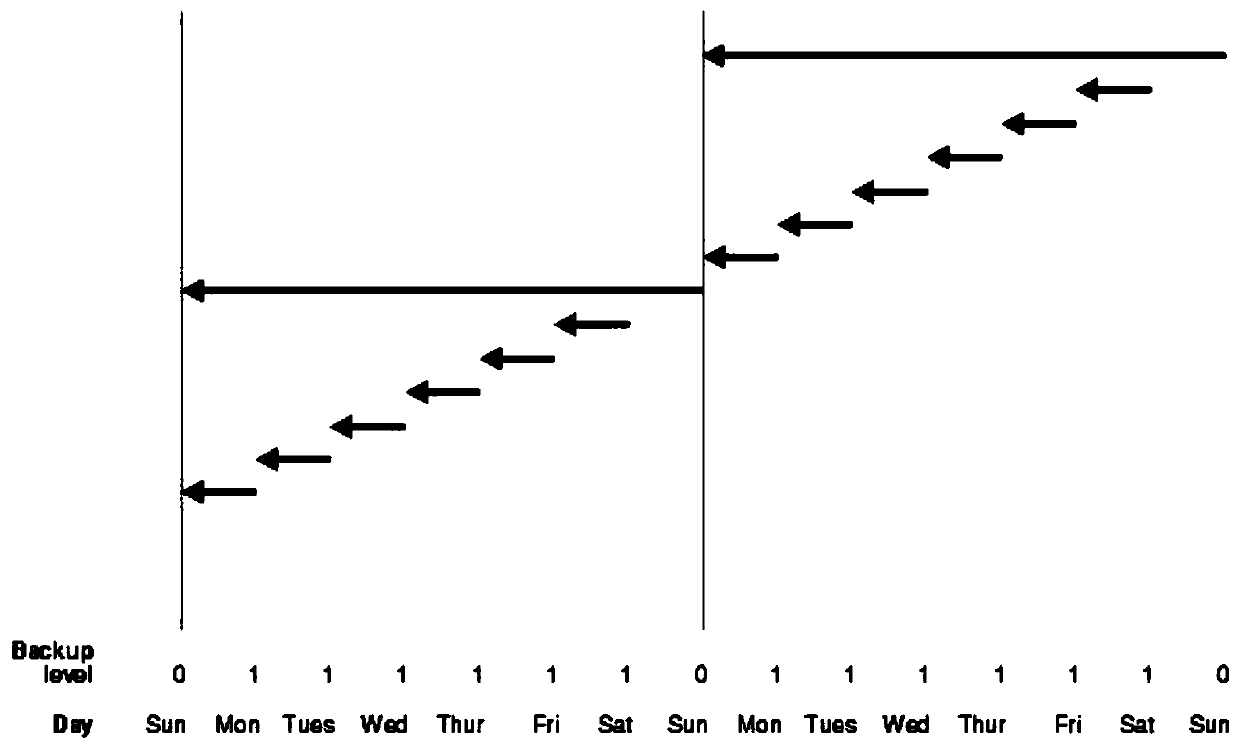
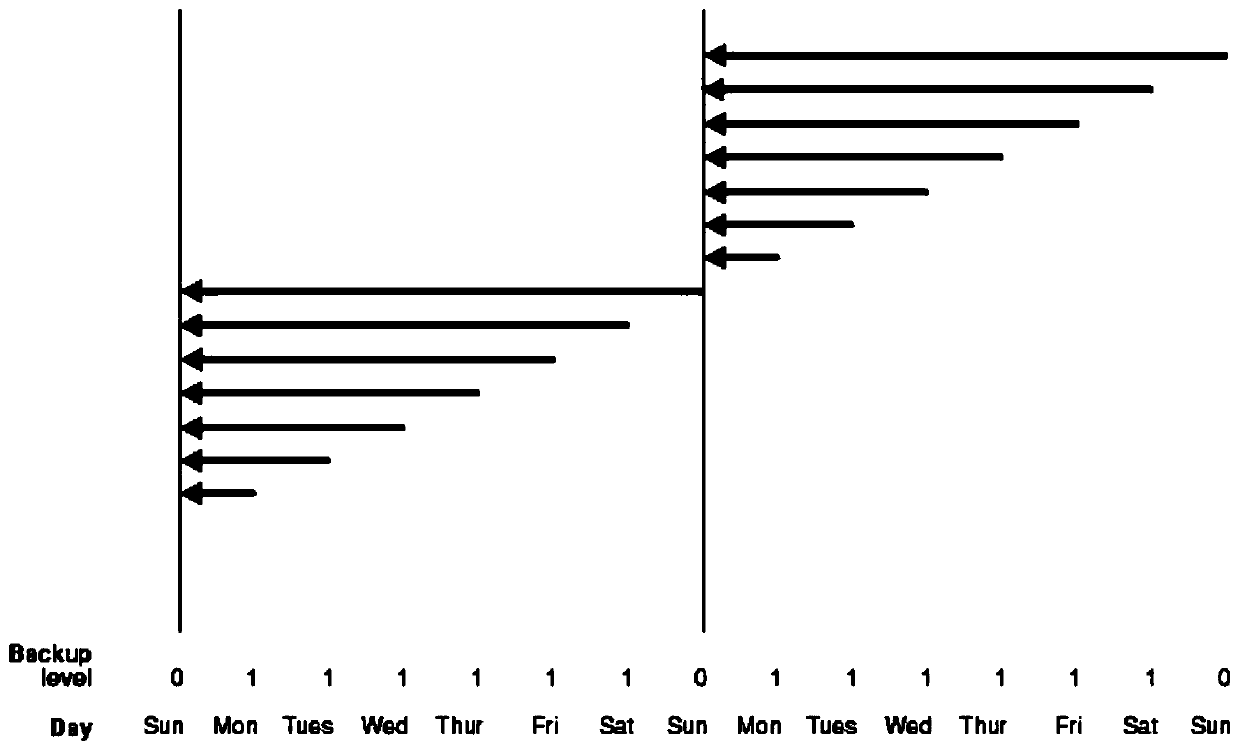
Storage apparatus and volume restoration method
InactiveUS20090254721A1Reduce amount of dataReduce restore timeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRestoration methodOperating system
A storage apparatus conducts, in a protection period, data protection processing for protecting, in a third logical volume, data stored in a first logical volume by using backup data stored in a second logical volume, and suspends the data protection processing in a no-protection period, during which backup relative to the second logical volume is suspended, in the protection period. Then, upon receiving an external order for restoring the first logical volume to its state as of at a time not in the no-protection period within the protection period, the storage apparatus restores the first logical volume to its state as of at a time of the order by using the data backed up in the second logical volume and the data protected in the third logical volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
QDF (quiescent direct furnace) direct reduction technology
InactiveCN104630404AAchieve the desired effectReduced strength requirementsFluidised-bed furnacesCombustion chamberProduct gas
The invention relates to a QDF (quiescent direct furnace) direct reduction technology which comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a metal-containing raw material and reducing agent powder, and putting into each reducing chamber, wherein in a reducing process, the reducing chambers and the reduced material are all kept in a stationary state; uniformly heating the materials in the reducing chambers by use of the heat generated by the combustion of the fuel in a combustion chamber and a combustion-supporting gas so as to perform a reduction reaction between the metal-containing raw material and the reducing agent, wherein each reducing chamber is a narrow long one-section reactor. According to the technology provided by the invention, the reducing chambers and the reduced material are all in a stationary state, the requirement on the strength of the granular raw material is reduced, and the production efficiency of a granulation process is improved; and the reducing time can be prolonged, and the metallization ratio of the reduction product is improved. The reducing chamber is not provided with a preheating area or a cooling area, the temperature is uniform, the atmosphere is uniform and consistent, and the overall quality of the reduction product is improved. The direct reduction technology has remarkable advantages of wide application range of raw materials, uniform temperature field, easy control on reduction process, high product metallization ratio, high yield and the like.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Method for preparing high-quality reduced graphene through high-energy-pulse microwave rapid recovery
The invention provides a method for preparing high-quality reduced graphene through high-energy-pulse microwave rapid recovery. The method comprises the main steps that crystalline flake graphite is added into fuming nitric acid under ice-water bath, hydrogen peroxide is added for a reaction for a certain time, washing and drying are conducted, and expanded graphite is obtained through microwave puffing; the expanded graphite and potassium permanganate are sequentially added in a mixed-acid system of 0-DEG C concentrated sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid, the strong oxidizing performance of the potassium permanganate is used, and the graphene is oxidized into graphene oxide under the low temperature of 0 DEG C; the graphene oxide is placed in a tube furnace to be subjected to insulation treatment, and pre-reduced graphene oxide powder is obtained; and finally, the pre-reduced graphene oxide powder is placed in a high-energy-pulse microwave cavity, microwave is opened, and a high-quality reduced graphene product is obtained. According to the high-quality reduced graphene prepared through the method, the lamellar structure is complete, the reduced graphene finally obtained through high-energy-pulse microwave rapid recovery is high in quality, and a good foundation is provided for preparation of graphene oxide, and graphene-based nanocomposite materials.
Owner:徐州宇帆机电科技有限公司 +1
Two-component complexing system indirect electrochemical reduction method and system for indigo dye and preparation method of system
InactiveCN106868533AReduce consumptionPlay a synergistic roleElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionPower flowShielding gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of indigo dye reduction dying and particularly relates to a two-component complexing system indirect electrochemical reduction method and system for an indigo dye and a preparation method of the system. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, under the alkaline condition, Fe(II / III) salt is fully mixed with triethanolamine, so that a complexing system is obtained; and 2, gluconate is added to the complexing system obtained in step 1, so that a two-component complexing system is obtained. The indirect electrochemical reduction method comprises the step that under protection of protective gas, the two-component complexing system serves as a medium, indirect electrochemical reduction is conducted on the indigo dye in an electrolytic cell at the temperature of 25-75 DEG C and under the alkaline condition. According to the two-component complexing system indirect electrochemical reduction method and system for the indigo dye and the preparation method of the system, the mixed medium of a certain condition is jointly formed by gluconic acid and iron-triethanolamine, and the synergistically-reinforcing effect can be achieved; the current required in the energized reduction process is reduced, reduction time is shortened, and thus current efficiency is improved; and energy consumption is remarkably lowered, and cost is saved.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Freeze drying preparation method for ultra-fine tungsten-doped yttrium oxide composite powder
The invention provides a freeze drying preparation method for ultra-fine tungsten-doped yttrium oxide composite powder. According to the freeze drying preparation method, a surface-active agent polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) or polyoxyethylene lauryl ether are added on the basis of freeze drying for in-situ preparing of about 10 nm of ultra-fine nanometer W-Y2O3 composite powder. The freeze drying preparation method comprises the steps that ammonium meta-tungstate, yttrium nitrate hexahydrate and a surface-active agent are dissolved into water and are fully dispersed anddissolved through ultrasonic treatment; then a mixture is placed in a refrigerator to be pre-frozen for a period of time; after being pre-frozen, the mixture is put into a freeze dryer to be subjected to freeze drying; a freeze-dried loose structure is ground and calcined in air so as to remove the surface-active agent, and thus WO3-Y2O3 composite powder is obtained; and finally, two-step reduction is conducted through hydrogen, and thus the ultra-fine tungsten-doped yttrium oxide composite powder is obtained. The powder, with the surface-active agent being added, prepared through the freezedrying method is small in particle aggregation, the average grain size reaches about 10 nm, granularity distribution of grains is extremely narrow, and second-phase Y2O3 is distributed quite evenly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Black ceramic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104046879ALow reduction temperatureReduce energy consumptionFluidised-bed furnacesMetallic materialsSolar absorptivity
The invention relates to a black ceramic material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the inorganic nonmetallic material field. The black ceramic material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1.82-3.7 parts of Gr2O3, 10.9-18.18 parts of TiO2, 1.94-4.13 parts of V2O5, 6.06-11.91 parts of MnO, 8-14 parts of Fe2O3, 0.001-0.01 part of Ni and 12-24.3 parts of SiO2. The black ceramic material is sintered by use of mill tailings and vanadium extraction tailings as the raw materials, and the solar absorptivity of the obtained black ceramic material is 0.85-0.90.
Owner:PANZHIHUA UNIV
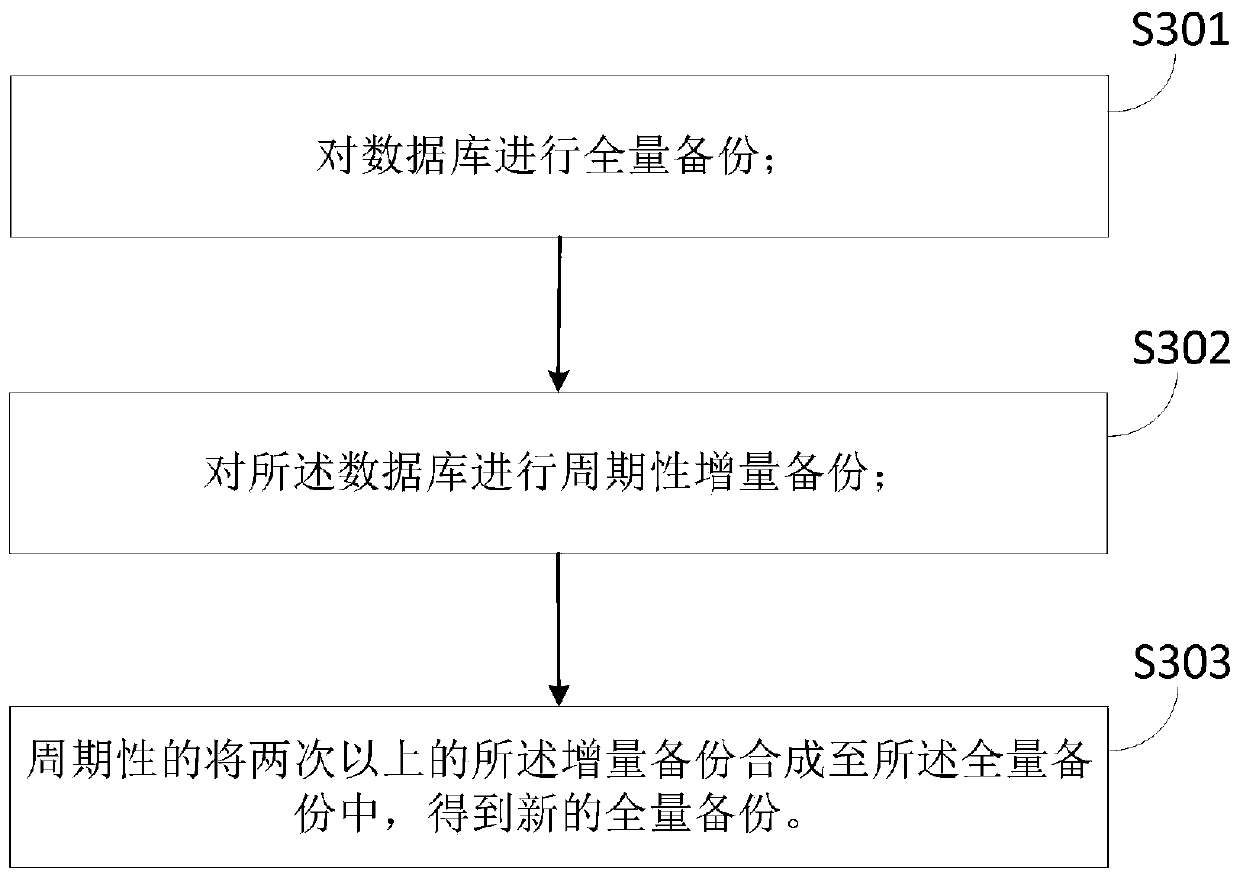
Database backup method, database restoration method and storage medium
PendingCN110083490AImprove backup efficiencyReduce data volumeRedundant operation error correctionDatabase backupAccess time
The invention relates to the technical field of databases, and provides a database backup method, a database restoration method and a storage medium. The database backup method comprises the followingsteps: carrying out full backup on a database; performing periodic incremental backup on the database; and periodically synthesizing more than two times of incremental backups into a full backup to obtain a new full backup. The database restoration method comprises the following steps: directly mounting a memory of the back-end platform on a database access terminal; constructing a database operation environment on the database access terminal; and enabling the database access terminal to directly access the database from the memory of the back-end platform. According to the method, the backup data volume of the database can be greatly reduced, the database restoration time is shortened, and the access time of database failure or restoration is prolonged.
Owner:浙江豪联信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com