Combined direct reduction technology of blast furnace gas ash and refractory low-grade iron ore in tunnel kiln
A blast furnace gas ash and iron ore technology, applied in the field of combined direct reduction process of blast furnace gas ash and refractory low-grade iron ore tunnel kiln, can solve the problem of long reduction time, poor separation efficiency, and carbon utilization efficiency of blast furnace gas ash It can achieve the effect of increasing the reduction speed, increasing the contact area and shortening the reduction time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1 technique comprises the steps:
[0056] (1) Mix 0-3mm iron ore and blast furnace gas ash at a ratio of 100:185 to obtain fine-grained materials; mix 1-5mm iron ore and 1-5mm reduced coal by The ratio of 100:38 is mixed to obtain coarse-grained materials;
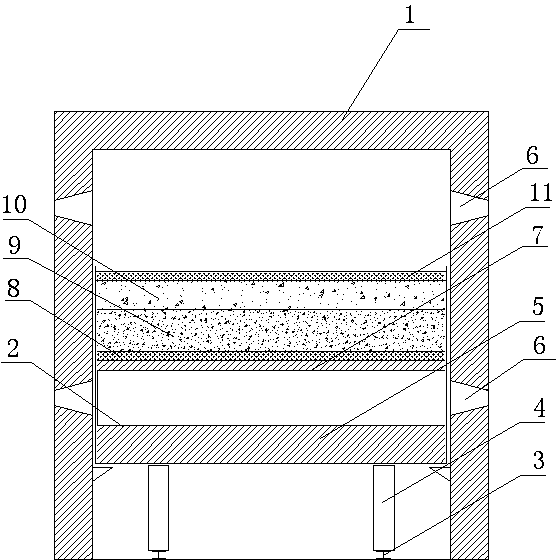
[0057] (2) Lay reduced coal with a thickness of 5mm, fine-grained materials with a thickness of 90mm, coarse-grained materials with 50mm and reduced coal with a thickness of 10mm (such as figure 1 shown);
[0058] (3) Put the material into the tunnel kiln with the kiln car for high-temperature reduction. The reduction temperature is 1100°C and the reduction time is 90 minutes.
[0059] It was determined that the iron grade of the metallized iron powder obtained in Example 1 was 86.1%, and the metallization rate was 90.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2 technology comprises the steps:
[0062] (1) Mix 0-3mm iron ore and blast furnace gas ash at a ratio of 100:210 to obtain fine-grained materials; mix 1-5mm iron ore and 1-5mm reduced coal by The proportion of 100:35 is mixed to obtain coarse-grained materials;
[0063] (2) Lay reduced coal with a thickness of 10mm, fine-grained materials with a thickness of 80mm, coarse-grained materials with 20mm and reduced coal with a thickness of 5mm on the refractory heat-conducting plate of the tunnel kiln car from bottom to top (such as figure 1 shown);
[0064] (3) Put the material into the tunnel kiln with the kiln car for high-temperature reduction. The reduction temperature is 1050°C and the reduction time is 120 minutes.
[0065] It was determined that the iron grade of the metallized iron powder obtained in Example 2 was 85.1%, and the metallization rate was 88.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3 technology comprises the steps:
[0068] (1) Mix 0-3mm iron ore and blast furnace gas ash at a ratio of 100: 235 to obtain fine-grained materials; mix 1-5mm iron ore and 1-5mm reduced coal by The ratio of 100: 40 is mixed to obtain coarse-grained materials;
[0069] (2) Lay reduced coal with a thickness of 8mm, fine-grained materials with a thickness of 100mm, coarse-grained materials with 35mm and reduced coal with a thickness of 8mm (such as figure 1 shown);
[0070] (3) Put the material into the tunnel kiln with the kiln car for high-temperature reduction. The reduction temperature is 1150°C and the reduction time is 60 minutes.
[0071] It was determined that the iron grade of the metallized iron powder obtained in Example 3 was 84.1%, and the metallization rate was 92.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com